Author: Zhao Xiaofei
IoT Think Tank Original
Reprint with source and origin indicated
Introduction
Recently, the IoT market research organization IoT Analytics released the latest “Global Cellular IoT Module Tracking Report”. This article analyzes the market landscape and future trends over the past year based on this report.

Recently, the IoT market research organization IoT Analytics released the latest “Global Cellular IoT Module Tracking Report”. Last month, the market research organization Counterpoint released data on global cellular IoT module shipments for Q4 2020 (see “Overview of Global Cellular IoT Module Data“). The data from both organizations is generally consistent. However, there are differences in focus between the two in segmented fields. This article will analyze the market landscape and future trends based on the IoT Analytics report.
Global Market Decline, China Maintains Growth
Based on a survey of 33 mainstream IoT module companies worldwide, IoT Analytics has formed the latest tracking data for cellular IoT modules. The data shows that the global cellular IoT module market size was $3.1 billion in 2020, a year-on-year decline of 8%. The decline in revenue is mainly due to the global outbreak of COVID-19, which severely impacted the IoT market, forcing many overseas IoT deployment and application plans to be canceled.
In contrast, the situation in China was different. In 2020, while the shipment volume of cellular IoT modules in other regions of the world declined, China’s cellular IoT module shipments increased by 14% year-on-year. This is largely due to China’s effective epidemic control measures, allowing companies to quickly resume work and production. Additionally, I believe that under the influence of the COVID-19 pandemic, many domestic industries have gained a new understanding of intelligent and unmanned production operations, leading to an increased demand for digital deployment, which directly boosted the demand for IoT solutions.
IoT Analytics predicts that by 2025, the number of cellular IoT connections will exceed 4.5 billion. Most types of cellular IoT connected devices will use cellular IoT modules, while some will embed cellular IoT chips into the device’s circuit board. Cellular IoT modules can significantly shorten the time to market for customers’ smart devices, making them popular among terminal manufacturers. In recent years, cellular IoT modules have also been continuously innovating, such as chip-based modules, which lower the threshold for terminal customers to use modules.
According to the latest data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology, as of the end of April 2021, the three operators had developed 1.236 billion cellular IoT connections, achieving a net increase of 100 million in just the first four months. In fact, the net increase for the entire year of 2020 was only 10.8 million. After experiencing a slowdown in 2020, the number of domestic cellular IoT connections has returned to a rapid growth trend in 2021. Accordingly, it can be expected that the shipment volume of cellular IoT modules in 2021 will also exceed that of 2020 significantly.
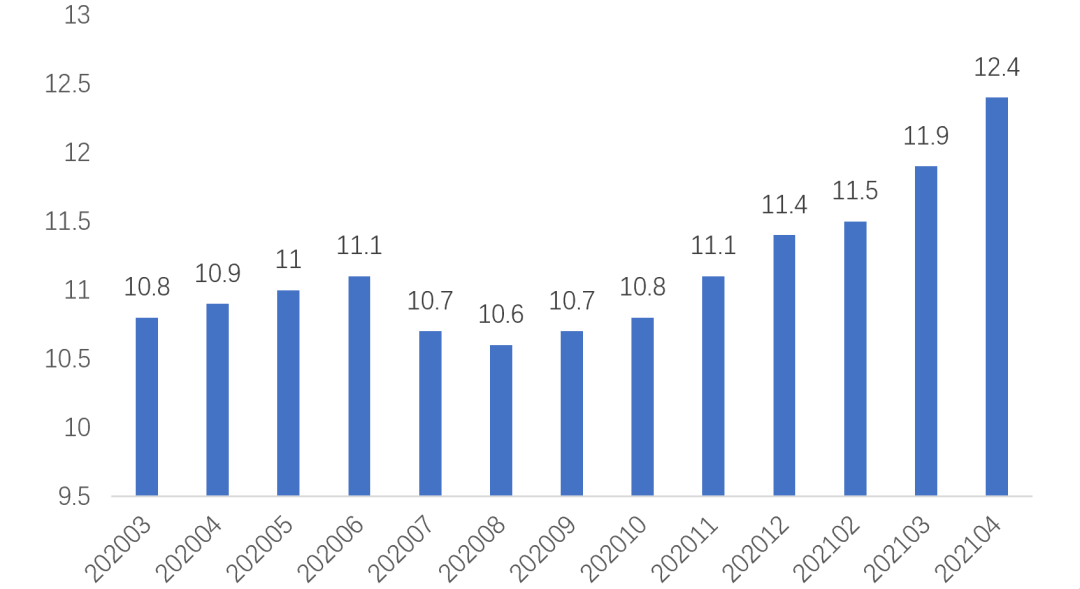
Cellular IoT connections from 2020 to the end of April 2021 (unit: 100 million, source: Ministry of Industry and Information Technology)
However, the global chip shortage casts a shadow over the IoT module market. According to IoT Analytics’ survey, most cellular module manufacturers have a large backlog of orders, and the chip shortage has led to increased price volatility. Therefore, IoT Analytics predicts that by mid-2021, the overall global shipment volume of cellular IoT modules will decline, and the profit margins of module manufacturers will decrease.
NB-IoT Occupies Half of the New Market, Cat 1 Rapidly Rises
Due to the differences in cellular network deployment and IoT demand among countries, the shipment structure of cellular IoT modules varied significantly in 2020. The market structure in China stands in stark contrast to that of other countries. IoT Analytics’ monitoring data reveals several distinct characteristics.
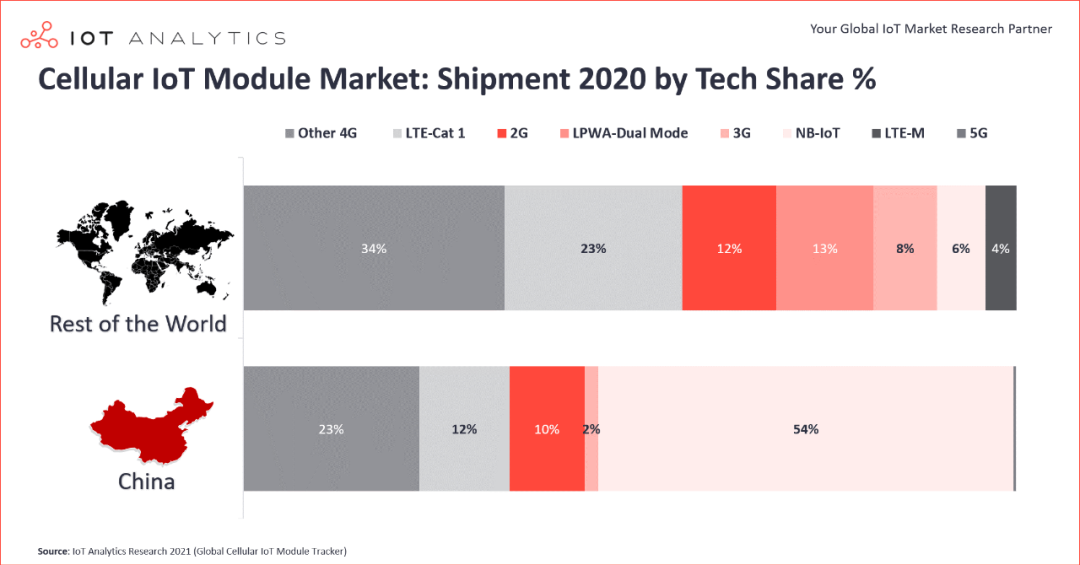
Comparison of cellular IoT shipment structures between China and other countries/regions (source: IoT Analytics)
(1) NB-IoT occupies half of the new shipments in China’s cellular IoT market
From the comparative data, it can be seen that in 2020, NB-IoT modules accounted for 54% of the shipment volume of cellular IoT modules in China, while LTE-M, another low-power wide-area network based on the 3GPP standard, has not been commercially deployed in the domestic market. In contrast, the market share of NB-IoT modules in overseas markets is only 6%, while LTE-M accounts for 4%.
This result stems from the differences in infrastructure and market strategies for NB-IoT domestically and internationally. Currently, China has approximately 1 million NB-IoT base stations in operation, establishing the world’s largest NB-IoT network, with the most diverse application scenarios globally. For example, China Telecom announced on May 17 that its number of NB-IoT connections has surpassed 100 million, making it the world’s largest NB-IoT operator and the first operator globally to exceed 100 million NB-IoT users. Currently, China Telecom has deployed over 400,000 NB-IoT base stations, and the industry application scenarios continue to expand, with NB-IoT smart gas and smart water services reaching nearly 30 million each. According to IoT Analytics’ monitoring, 90% of the global NB-IoT module shipments in 2020 came from China. Data from the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology shows that as of April 2021, the number of smart public utility connections in China increased by 18.9% year-on-year, indicating that smart water and smart gas services will remain the main battlefield for NB-IoT in the future.
Although dozens of operators overseas have built NB-IoT networks, the scale and application of these networks are very limited, resulting in low demand for NB-IoT modules. However, many operators in North America have launched LTE-M networks, leading to a certain demand for LTE-M modules. Additionally, the difference in shipments of LPWA multi-mode modules between domestic and overseas markets reflects the disparity in IoT demand. There are virtually no LPWA multi-mode module shipments domestically, while overseas they account for 13% of the market. Due to the fragmented deployment of NB-IoT and LTE-M networks in many countries and regions overseas, LPWA multi-mode modules are significant for addressing network fragmentation. Previously, Qualcomm launched chips such as MDM9206 and 9205 that support NB-IoT/LTE-M/2G multi-mode networks, facilitating module deployment overseas. However, domestically, as the deployment of NB-IoT networks has gradually improved, operators have abandoned LTE-M, and due to cost factors, multi-mode modules have not found a place.
(2) The Rapid Rise of Cat 1 in the Domestic Market
Another notable feature of cellular IoT modules is the rapid rise of Cat 1. In the overseas market, Cat 1 modules accounted for 23% of the shipments, while in the domestic market, Cat 1 modules held a 12% share. It seems that the overseas market is developing faster, but in reality, the domestic market reached this share in a very short time, indicating that Cat 1 is rising rapidly in China.
Cat 1 emerged in North America several years ago, with the largest operators Verizon and AT&T providing a timeline for phasing out 2G in 2016, and 3G phasing out is also on the agenda. Cat 1 was proposed as the best alternative for 2G/3G IoT applications in 3GPP R8. The large-scale migration from 2G/3G to Cat 1 in overseas markets began in 2018. According to IoT Analytics statistics, in the past three years, IoT module manufacturers such as Telit, Thales, and Sierra Wireless have shipped over 40 million Cat 1 modules outside of China, supporting the 23% market share of Cat 1 overseas.
In the domestic market, although Cat 1 modules only account for 12% of the market share, they only began to gain traction at the end of 2019, and in just over a year, they surged from nearly zero to a 12% share, indicating an astonishing growth rate.
(3) A Reasonable IoT Connection Structure is Forming
For the connection structure of different cellular IoT standards, there is a consensus in the industry of “60%-30%-10%”. Currently, the shipment volume of cellular IoT modules is evolving towards this structure, promoting the rationalization of IoT connection structures. In May 2020, the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology issued the “Notice on Deepening the Comprehensive Development of Mobile IoT” (Document No. 25), which clearly proposed the establishment of a comprehensive ecological system for mobile IoT that coordinates the development of NB-IoT, 4G (including Cat 1), and 5G, and promotes the migration of 2G/3G IoT services to new networks. The development of the IoT industry over the past year has been moving in these directions.
According to IoT Analytics data, NB-IoT, as a representative of low-rate IoT, has already captured 54% of the new shipment volume, making the 60% target easily achievable. The shipment volume of 2G modules should not be underestimated, accounting for 10% of the market share, along with 2% for 3G modules. In 2020, the combined shipment volume of 2G and 3G modules was almost on par with that of Cat 1. However, 2G and 3G are on a downward trend, and under the backdrop of network phasing out, their new shipment volume will rapidly decline, migrating towards NB-IoT and Cat 1. Especially with the maturity of single-antenna Cat 1 bis, which further optimizes cost and size, it will significantly increase the market share of Cat 1. Additionally, in Cat 4 LTE scenarios, due to cost and availability advantages, Cat 1 will form a downward attack, replacing many markets originally held by Cat 4. Cat 4 and higher LTE modules and 5G will focus on a few high-end scenarios requiring high bandwidth and low latency.
China’s Supplier Position Further Consolidated
In terms of the landscape of cellular IoT module suppliers, the monitoring data from IoT Analytics is largely consistent with that of Counterpoint. A typical example is that both research institutions show that three Chinese manufacturers account for more than half of the global market share.
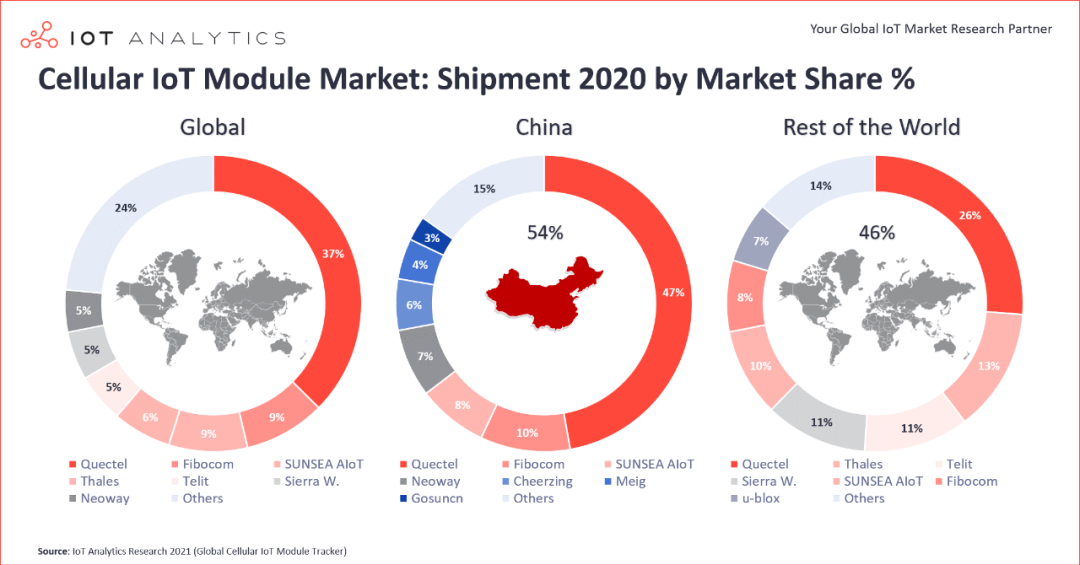
Comparison of market shares among manufacturers (source: IoT Analytics)
According to IoT Analytics monitoring data, from a global market perspective, Quectel, Fibocom, and Ruijie are the top three Chinese manufacturers in terms of shipment volume, with the three accounting for 55% of the global total, solidifying the global position of Chinese manufacturers; followed by Telit, Thales, and Sierra Wireless, whose total shipment volume accounts for only 16% of the global total, showing a significant gap compared to Chinese manufacturers. In the domestic market, Quectel alone accounts for nearly 50% of the domestic market share, followed by Fibocom, Ruijie, Youfang, Qijun, Meige, and Gaoxin, with the top seven accounting for 75% of the national share. Even from an overseas market perspective, Quectel remains the highest market share manufacturer, while Ruijie and Fibocom rank behind the top three overseas manufacturers.
According to public data, Quectel’s revenue from cellular IoT modules increased by 44% year-on-year in 2020 due to the increase in shipments of 4G series (including Cat 1) and NB-IoT modules. Fibocom also achieved rapid revenue growth in 2020 due to the increase in shipments of Cat 1 bis and NB-IoT modules. In contrast, overseas module manufacturers experienced declines, with the impact of COVID-19 being particularly evident. Affected by COVID-19, Telit saw a significant decline in the automotive sector, while Thales attributed part of the decline to the downturn in utility metering in the Asia-Pacific region. Additionally, Sierra Wireless’s automotive module assets were acquired by a consortium involving Fibocom, and the upstream chip shortage is also a significant factor.
According to IoT Analytics monitoring, the current demand for Cat 1 bis in the European market is beginning to grow. On one hand, the Chinese market has achieved certain results with Cat 1 bis; on the other hand, the fragmented deployment of LTE-M networks in the European market, along with the continuity of 4G network deployment in Europe, provides an opportunity for Cat 1 bis to replace existing solutions.
As the upstream field of IoT terminals, cellular IoT modules have a certain cycle from shipment to the final formation of IoT applications. Therefore, the development of the module industry is a leading indicator that can reflect the eventual application landing of cellular IoT to some extent. It is hoped that the data analysis of cellular IoT modules can provide some insights for the industry.
The author’s new book “The New Infrastructure Era: Focusing on 5G and IoT” is now available
Long press the QR code to purchase



Selected Past Articles
Nearly 20 million IoT cards nearly flowed into the black market!
The state has launched the “Card Disconnection Action 2.0”

Missing the TWS headset market, the world’s number one
Headphone giant Sennheiser has fallen

“Glass King” Cao Dewang invests 10 billion to build
Fuyao Technology University, positioning……

Female car owner rights protection at the Shanghai Auto Show was forcibly removed by security,
Tesla’s Tao Lin: We will not meet her demands……

Rare! 16 ministries jointly issued a document, smart home
Welcomes significant policy dividends, by 2025……
Huawei’s autonomous driving real vehicle testing video
Exposed! Xu Zhijun: Much better than Tesla