Follow+Star Public Account Number, don’t miss out on exciting content

Source | IoT Town
Today, I will describe the process of downloading the OTA upgrade package in IoT devices through images and text.
1Overview of OTA
Hello everyone, I am asoftware upgrade package.In the next few days, I will embark on a magical journey across the network, traveling from the developer’scomputer to the terminalembedded device.This journey is commonly referred to as OTA, which stands for online upgrade.So what is OTA?The full name is:Over the Air Technology, which means downloading a new software package from the server over the network and updating it to the device.
First, there is a question: why is it called asoftware upgrade package instead of afirmware upgrade package?
In essence, firmware is also a type of software, as both are written in code!
Although these two terms are very similar, some people still make a slight distinction between them in anarrow sense.
Since that’s the case, let’s briefly differentiate between the two:
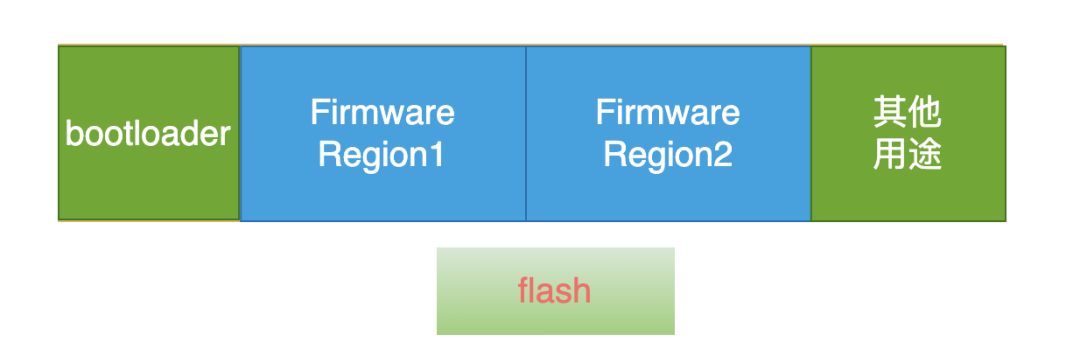
Firmware: Refers to embedded devices without a file system, where Flash is divided into different functional partitions. Executable programs need to be placed at a fixed starting position to be booted by the bootloader.
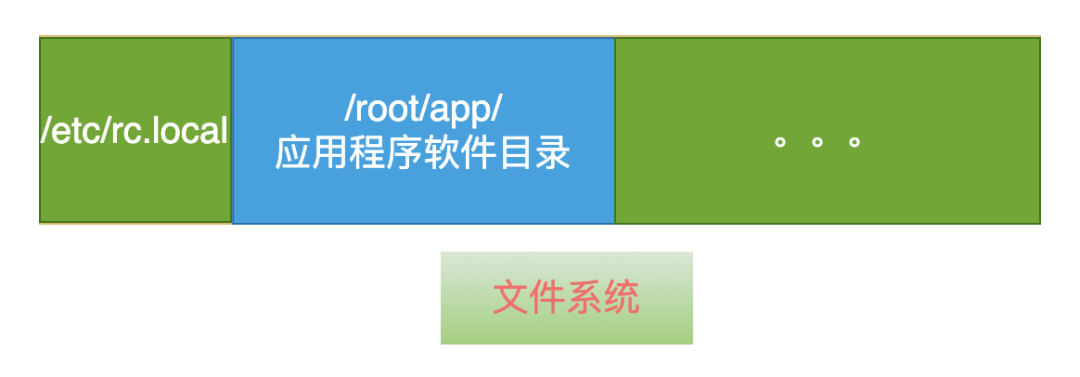
Software: Refers to embedded devices with a file system, where executable programs are placed directly in the file system. When the device starts, the operating system will launch the executable program from the file system.
Embedded devices without a file system:
Devices with a file system:
I know that the above distinction isnot very rigorous, but who can clearly define what a rigorous definition is?
For now, let’s differentiate this way, as long as it doesn’t affect the understanding of the article!
When an embedded device performs a software upgrade, from amacro perspective, it can be divided into2 stages:
Download the upgrade package;
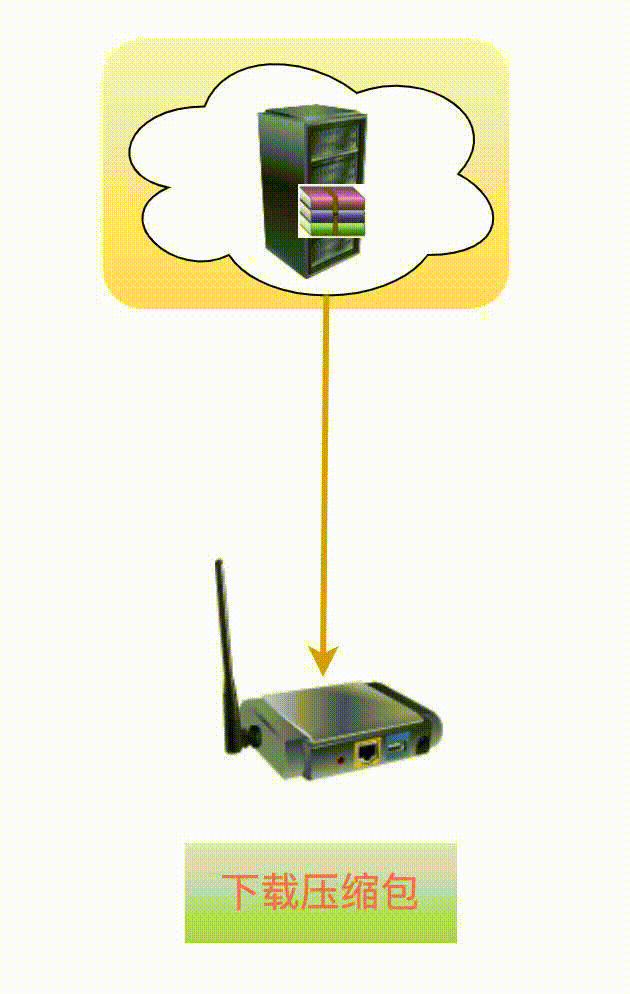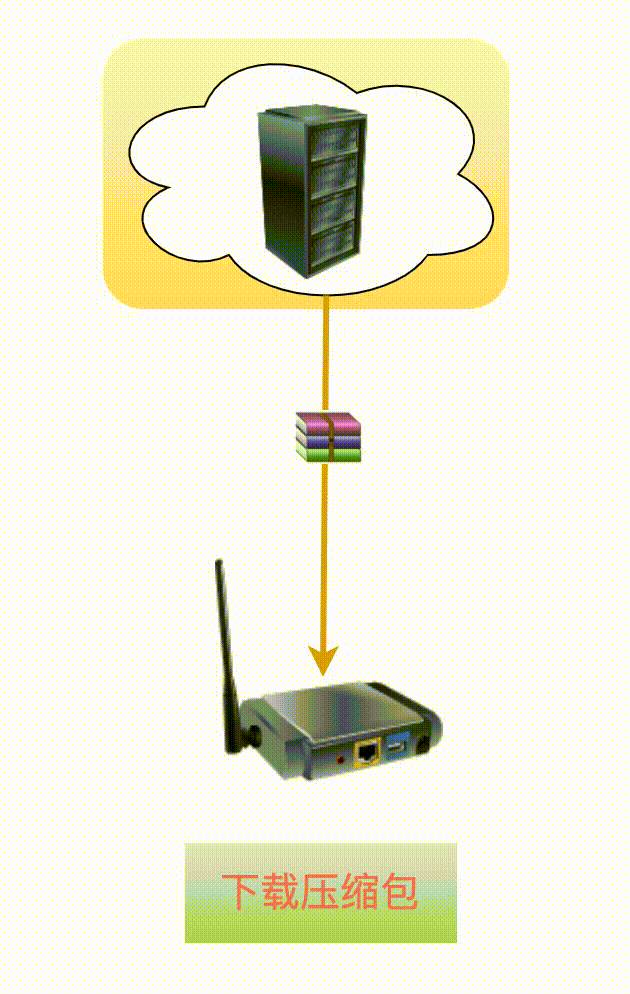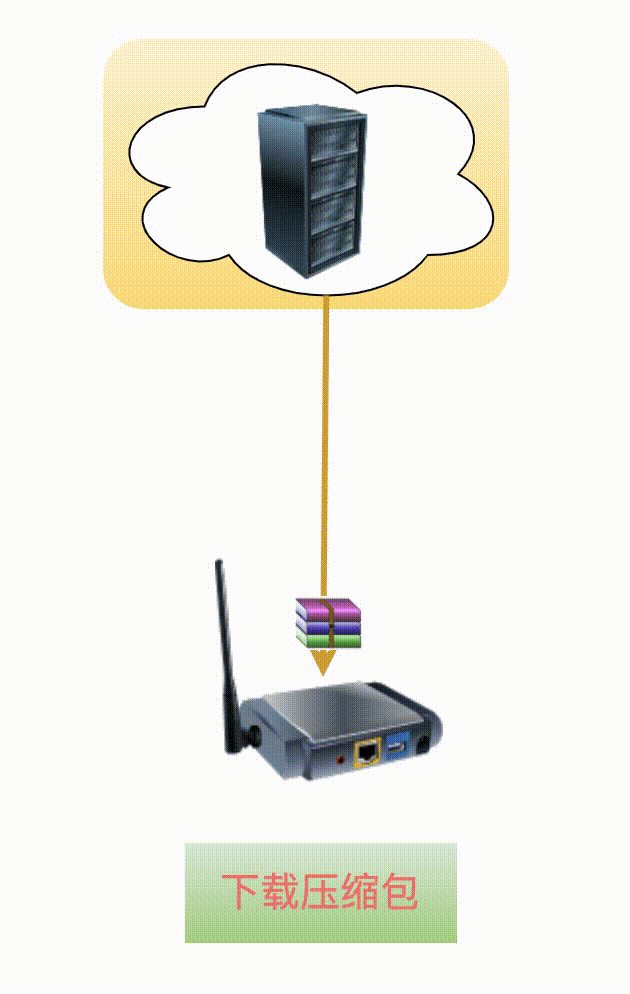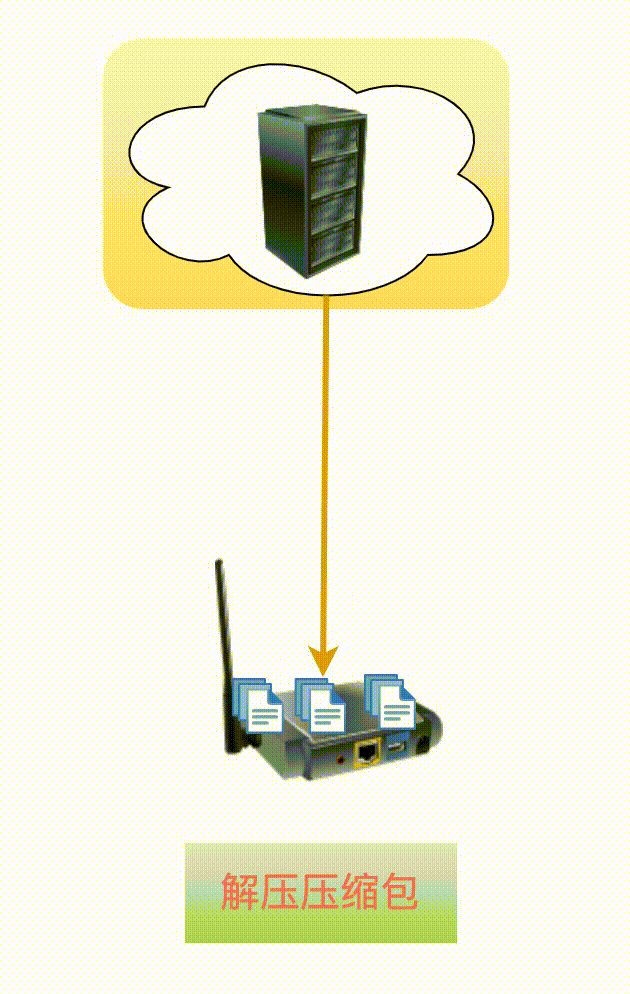
Unzip the upgrade package and write it to flash or the file system;
Today, we will focus on the first 1 stage, showing you how I am downloaded step by step from the developer’s computer to the embedded device.
Here is a complete process for you toget a sneak peek!
2Upload Upgrade Package
To facilitate the description, let’s assume a scenario:There are a total of 3 files running on the device:
Main file: executable program;
config.ini: configuration file;
mylib.so: a dynamic library file containing an algorithm called by the main file;
Currently, the version running on the device is V1.0, and the developers have optimized the algorithm in the mylib.so library, upgrading it to V2.0. Now, this new version needs to be uploaded to the embedded device.
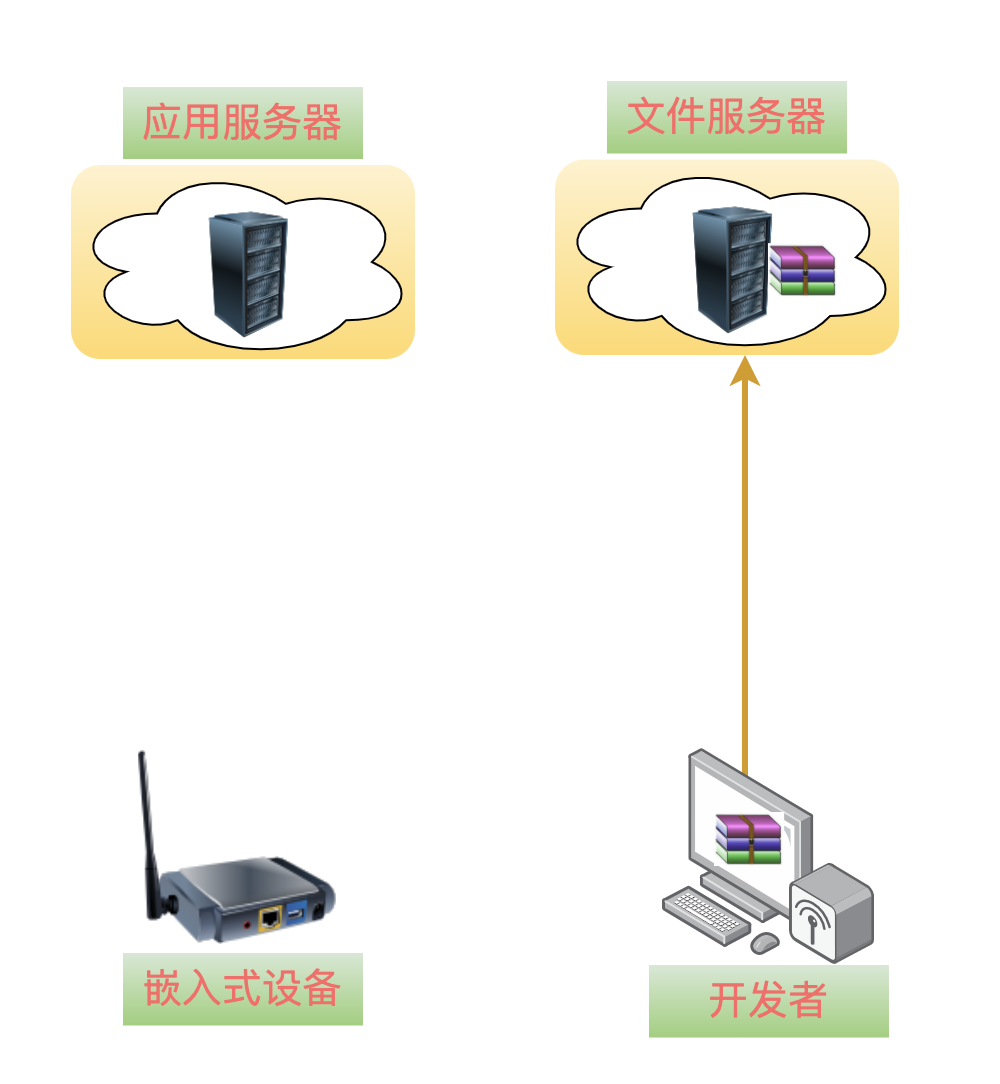
The first step is something we can all think of, which is to upload the V2.0 version of the software to thefile server.
One point to note: many cloud platforms distinguish betweenapplication servers andfile servers. Of course, if it’s just for testing, they can coexist on the samephysical server.
For example, Amazon’s AWS platform uploads the upgrade package to the S3 server.
Now we need to package the V2.0 version of the program. In addition to the main, config.ini, and mylib.so files, we also include another script file upgrade.sh in the package.
The purpose of this file will be revealed later.
Bingo – the upgrade package for V2.0 has been created: app_v2_0.tgz. After uploading to the file server, the address is: http://fileserve/app_v2_0.tgz.
3Upload Upgrade Package Description File
Now,V2.0 version of the upgrade package has been uploaded to the file server. Can we now command the embedded device to download and upgrade?
We know that in an IoT system, there are generallymany terminal devices.
These devices may be in arunning state or in apower-off state, and we cannot assume that all devices will upgrade atthe same time.
Moreover, once a device is upgraded, it becomes the latest V2.0 version, and it should be able to know that the latest version on the server is V2.0, so it does not need to upgrade.
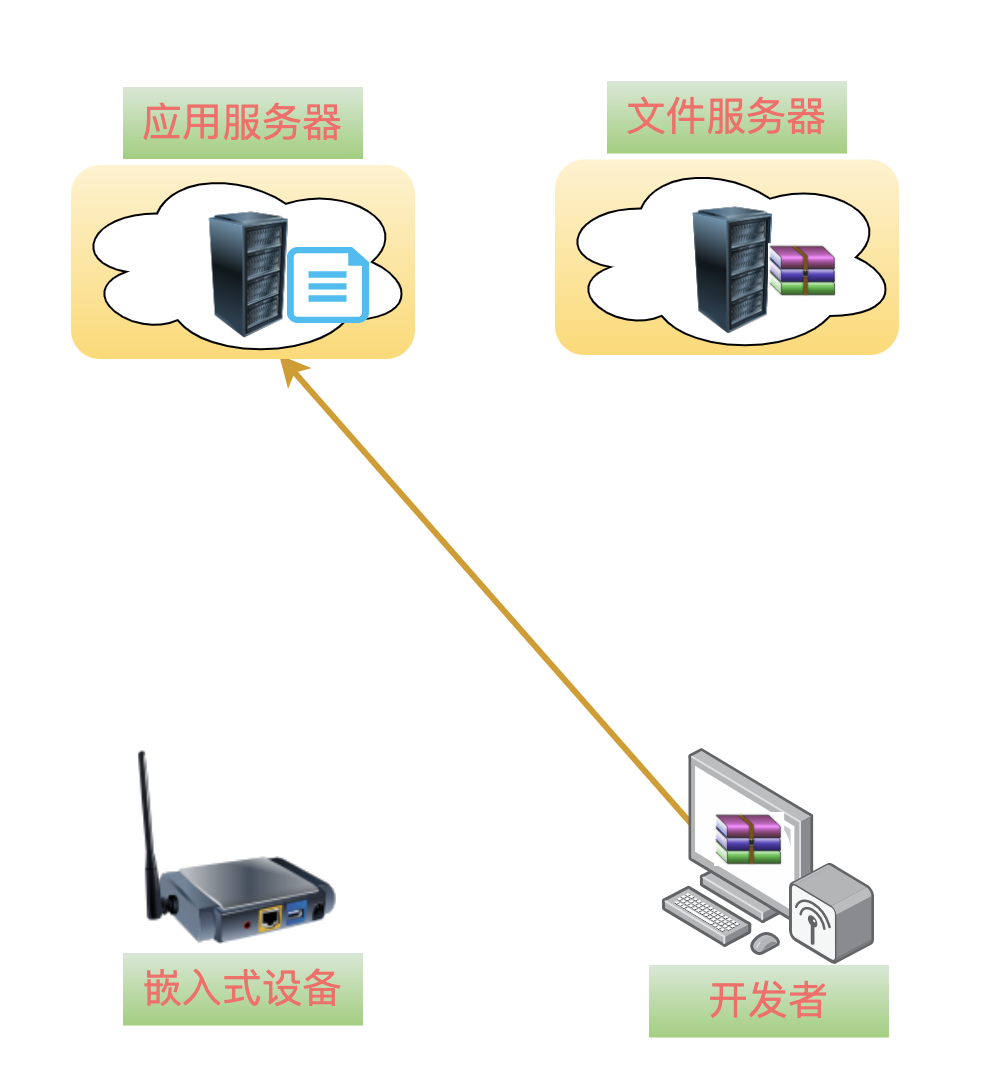
Therefore, a new file is needed to describe the V2.0 version of the upgrade package on the file server, which we will call: upgrade package description file app_desc.json, and its content is a json formatted string:
The version field describes theversion of the upgrade package on the file server, allowing the device to know the latest version on the server.
The url field describes thedownload address of the upgrade package. If the device finds that its version islower than the version in the version field, it can download the new upgrade package from this address.
The md5 field describes thefingerprint information of the latest upgrade package on the server. When the device downloads the upgrade package from the server, it needs to calculate the MD5 value of the upgrade package and compare it with the value in the md5 field. If they arethe same, it indicates that the downloaded upgrade package is fine and has not been tampered with.
After understanding the role of the upgrade package description file app_desc.json, this file is uploaded to theapplication server.

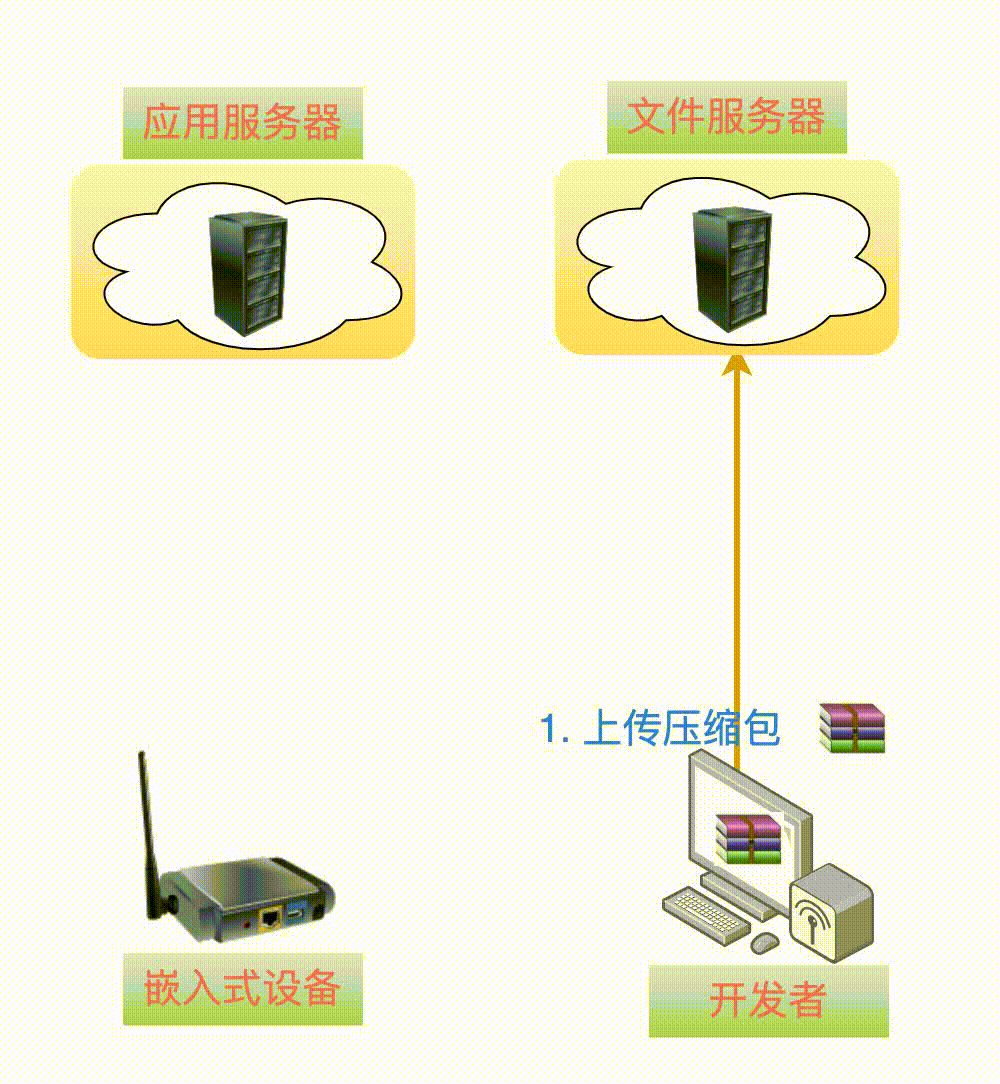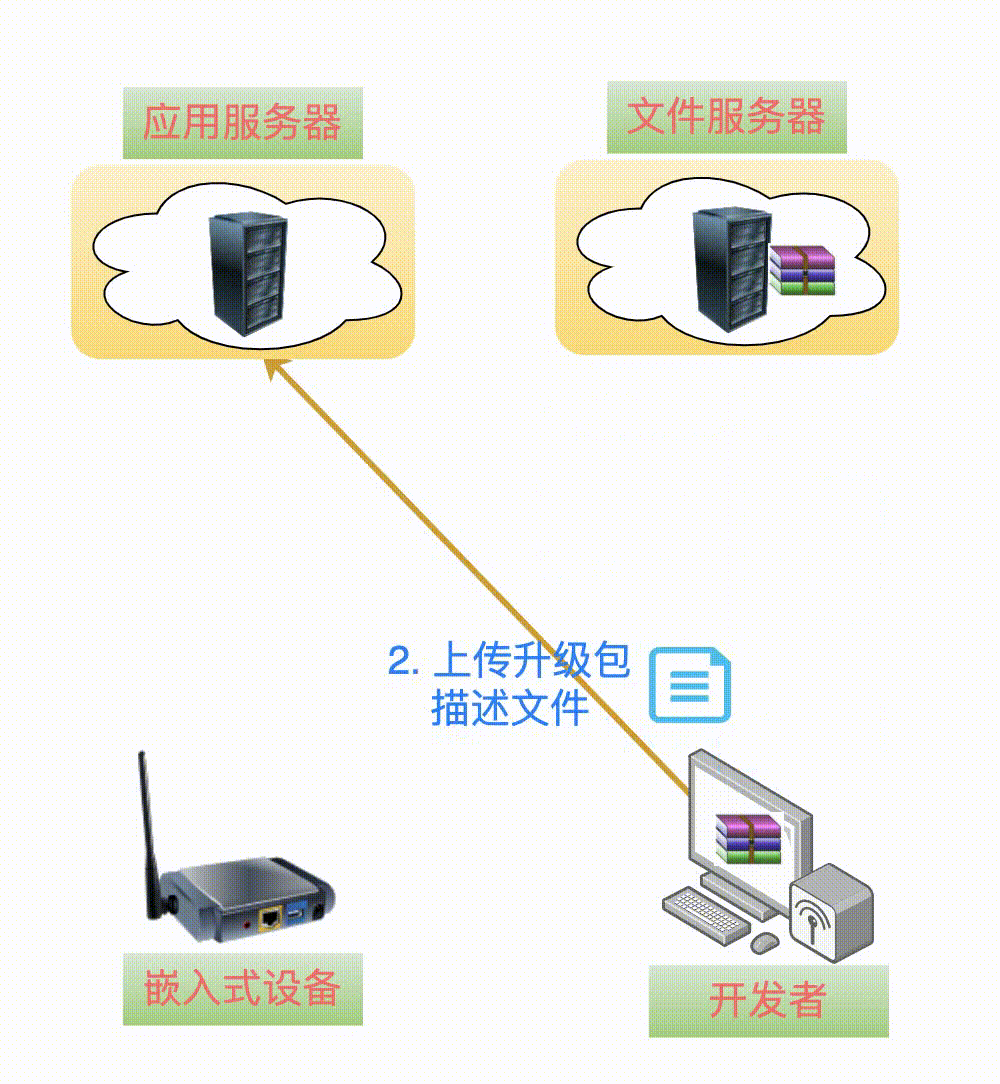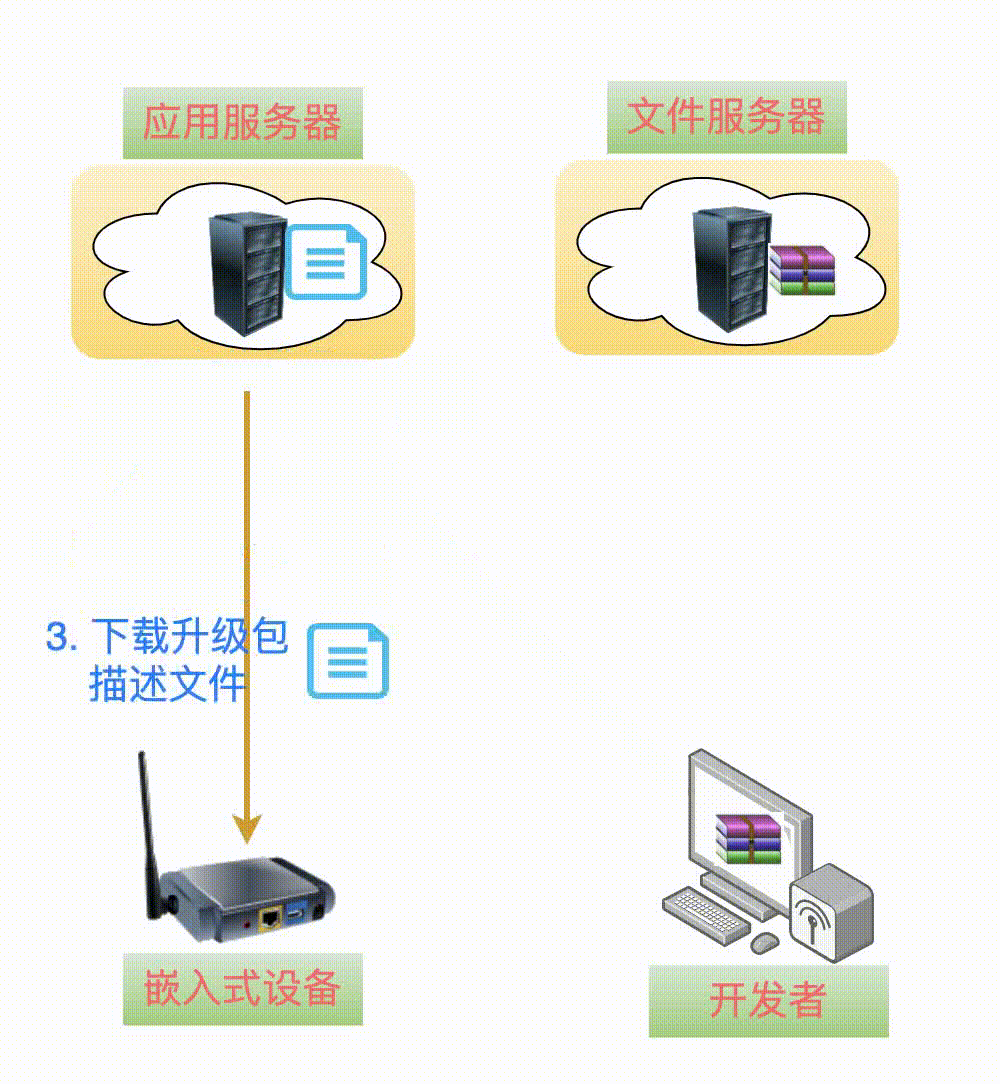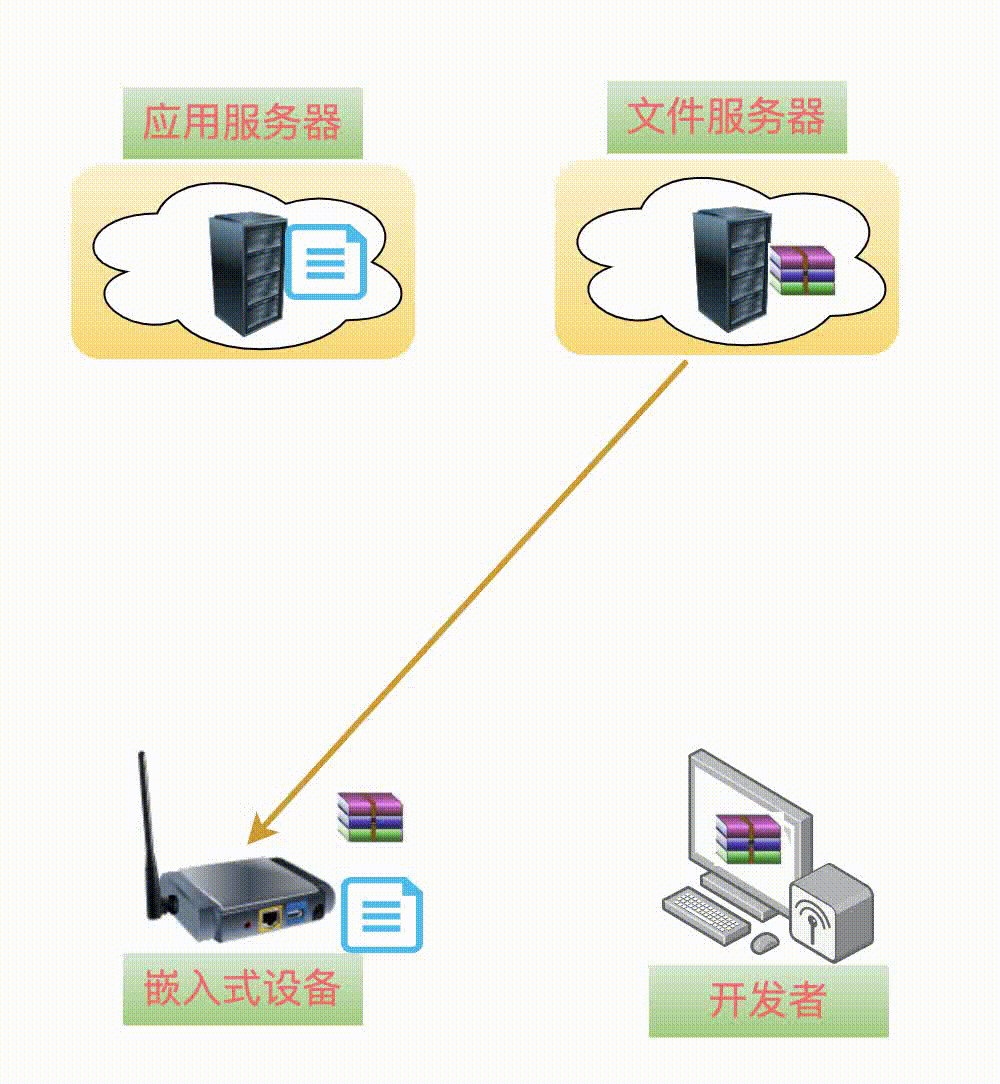
4Download Upgrade Package Description File
At this point, as theupgrade package, I am quietly lying on the file server, and my brotherupgrade package description fileapp_desc.json is also ready on the application server, just waiting for the embedded device to start the upgrade.
Everything is ready, just waiting for the right moment! It should be said that we are just waiting for atrigger action to prompt the embedded device to upgrade!
So, when shouldwho tell the device: your running software is too old, and there is a new version on the server, please upgrade!
The answer to this question is: various methods can be employed!
For example:
Amazon’s AWS platform notifies each device that needs to upgrade by deploying a job in the cloud platform;
It can also be done through a mobile app, actively sending a command to a specific embedded device: Hey, buddy, please upgrade your software;

When the terminal device receives the upgrade command, the first step is to download theupgrade package description information.
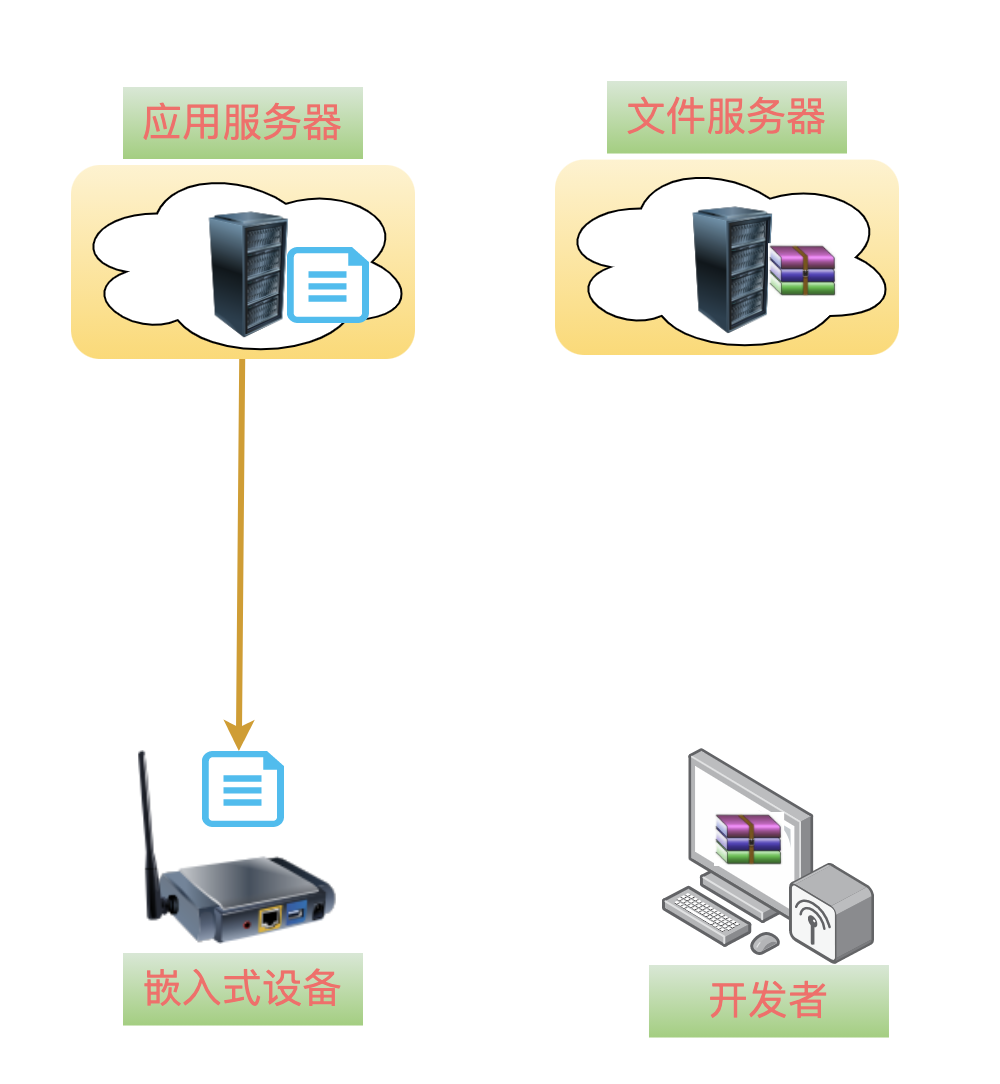
After downloading, parse this json formatted text content, extract the version information, and compare it with the currently running software version.
If the version on the server is newer, then continue to extract the download address from the url field and start downloading the new upgrade package from the file server.
If the current running version is already the latest, then the process ends here!
5Download Upgrade Package
When it comes to downloading the upgrade package, the process is simple. You can directly use wget or curl tools to download, or you can write your own download code using the curl library.
In short, you can have a thousand ways to download me to the device.
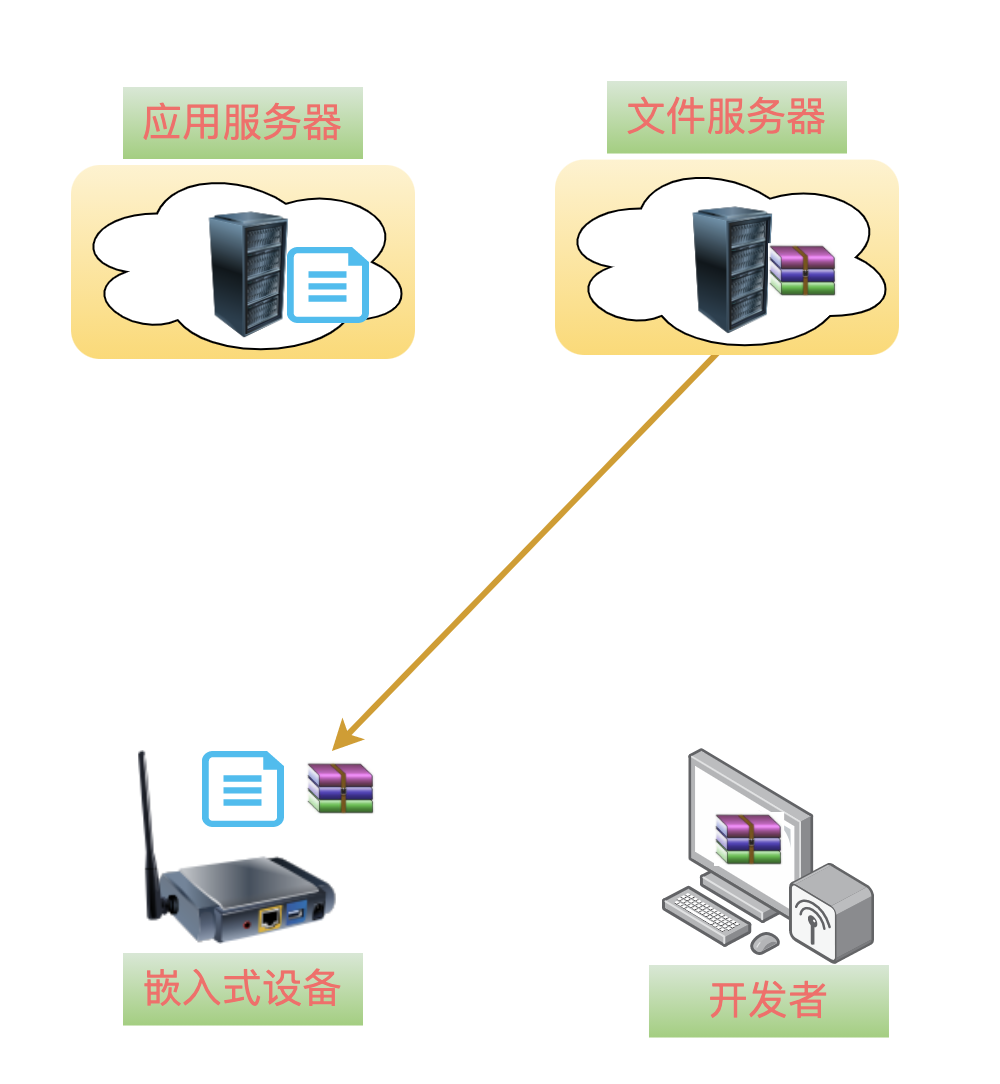
After the download is complete, onevery important thing must not be forgotten: check whether the downloaded upgrade package is correct!
Do you remember the md5 field in the upgrade package description file? That is myfingerprint information.
You need to first calculate the md5 value of the downloaded upgrade package and compare it with the value in the md5 field of the upgrade package description file. If they match exactly, then you can confidently start unzipping and upgrading!
———— END ————
Reply with『IoT』『IOT』 to read more related articles.
Welcome to follow my public account, reply “Join Group” to join the technical exchange group according to the rules, reply “1024” to see more content.Welcome to follow my video account:

Click “Read the original” to see more shares, and feel free to share, bookmark, like, and view.