All multimeters are equipped with a dial on the front, which not only has several scales corresponding to various measurement items but also includes various symbols, scale lines, and values, as shown in the figure. Correctly reading and understanding these symbols is fundamental to effectively using a multimeter.
Letter Symbols and Their Meanings on Multimeters
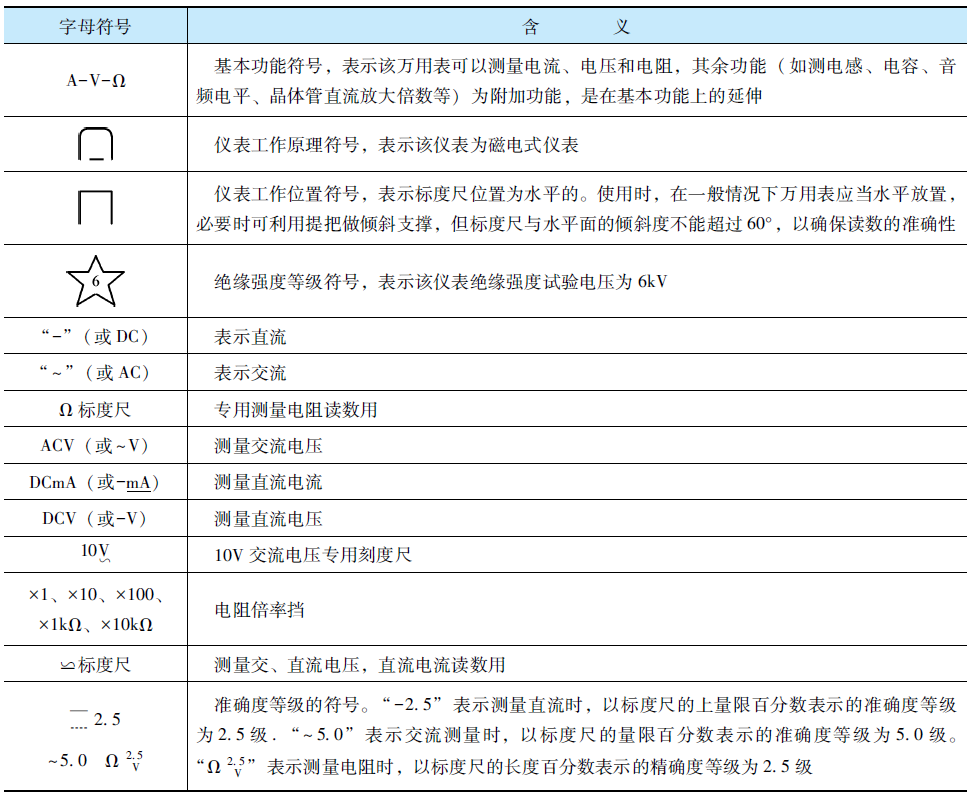
Meanings of Several Symbols on the MF47 Multimeter Dial
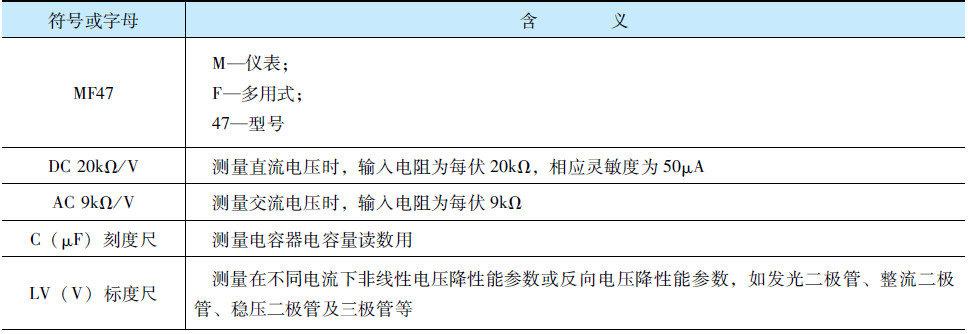
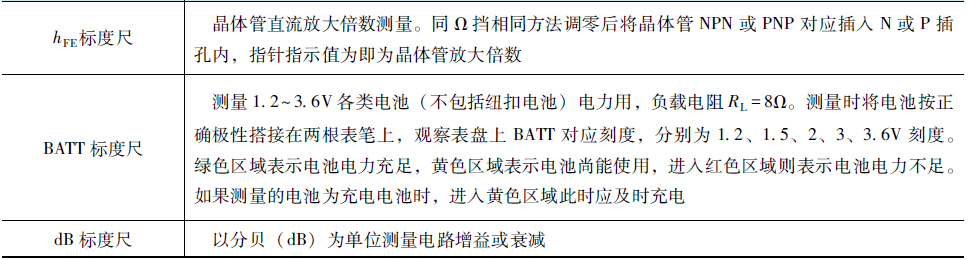
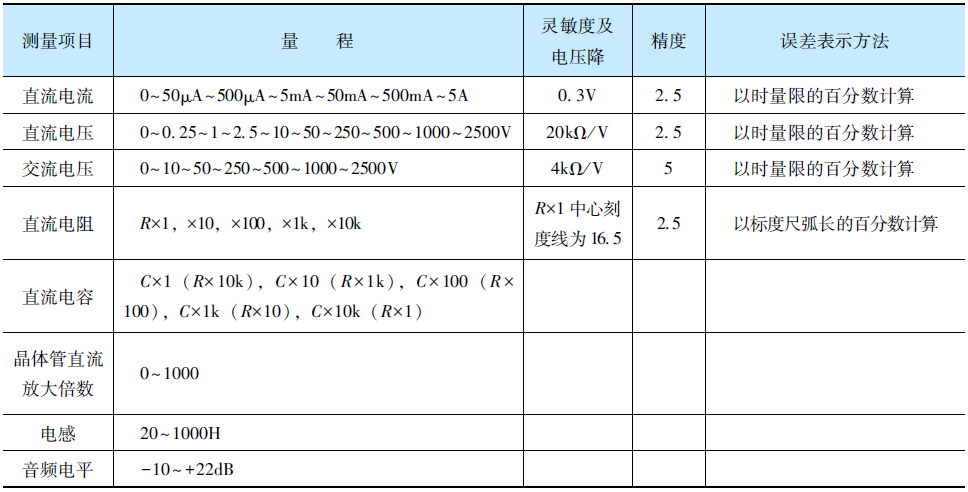
Measurement Ranges and Parameters of the MF47 Multimeter
Safety Precautions When Using a Multimeter
(1) It is strictly prohibited to use the resistance, current, or capacitance settings to measure voltage.
(2) It is strictly prohibited to use the resistance setting to test the resistance of live circuits. It is also prohibited to use the resistance setting to test power supply filter capacitors or power compensation capacitors that have just been powered off and have not yet discharged. Do not short-circuit the “+” and “-” terminals of electrolytic capacitors directly with wires. If discharge is necessary, a discharge resistor should be added; otherwise, the capacitor may be easily damaged. When discharging a capacitor, wear insulated gloves rated for a voltage higher than the capacitor’s voltage level to prevent burns from arcing during discharge.
(3) It is strictly prohibited to switch the range or function switch of the multimeter while it is powered on during testing.
(4) When measuring voltages below 50V, avoid direct contact with the metal parts of the test leads with both hands. If the measured voltage exceeds 50V, one-handed operation is required, meaning that the reference point’s test lead should be secured first, and then the insulated handle of the probe should be used to measure the voltage. It is prohibited to use a multimeter with a voltage range lower than the measured voltage level to measure high-voltage power supplies, transmission signals, or active transformers. When measuring voltages exceeding 500V, appropriate voltage-rated insulated gloves must be worn. If conditions are not suitable, appropriate safety measures should be taken. In addition to selecting measuring instruments with corresponding voltage ratings for high voltage testing, the tester should also ensure personal safety protection, and there should be a designated person monitoring or other personnel present to provide safety protection for the tester.
(5) It is strictly prohibited to connect the ammeter to a circuit with unknown parameters, high voltage, or high current for risky testing while powered on. If testing is necessary, a clamp meter can be used for a rough measurement of the AC current in larger circuits, and then the appropriate range of the multimeter can be selected based on the rough measurement results for accurate measurement.
(6) High voltage testing should not be conducted outdoors during thunderstorms to prevent lightning strikes to the testing personnel.
(7) Test leads with poor insulation or cracks should not be used. If the multimeter panel has multiple sockets available for testing, do not insert the leads incorrectly; otherwise, serious consequences may occur.
(8) Each time the test probe is picked up for measurement, double-check the measurement item and the position of the range switch to ensure they are correct, to avoid accidental damage to the multimeter due to carelessness.