Waste printed circuit boards (PCBs) contain high-grade precious metals and are an important part of the electronic waste value chain. However, our country lacks key technologies for environmentally friendly extraction of precious metals. For a long time, outdated processes such as open-air incineration and acid leaching have been used to extract metals, resulting in serious environmental pollution. Many domestic enterprises have built a number of PCB precious metal extraction production lines through foreign technology introduction and independent research and development, but only physical methods have achieved industrial application, while pyrolysis, fire treatment, and hydrometallurgical technologies have not been industrially applied.
The technology for recovering precious metals from circuit boards is divided into two main categories: physical methods and chemical methods. The chemical methods are further divided into hydrometallurgical and fire treatment methods. Fire treatment technology has advantages such as large processing capacity, relatively simple processes, high recovery efficiency, and no pollution issues from non-metallic residues in waste circuit boards, making it a widely used method in large-scale processing plants at this stage.
The differences in fire treatment processes mainly lie in the types of furnaces used. Table 1 compares different fire treatment processes.
Table 1 Comparison of Different Fire Treatment Processes
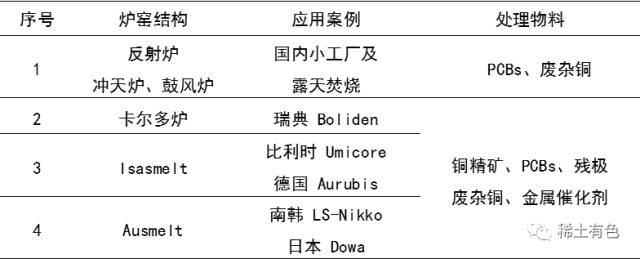
There are relatively few practical applications of fire treatment processes for circuit boards in the country. The fire treatment needs to be combined with non-contaminated copper recovery and copper smelting to reflect economic value. Fire treatment of circuit boards is an inevitable path for the future processing of circuit boards in our country.