
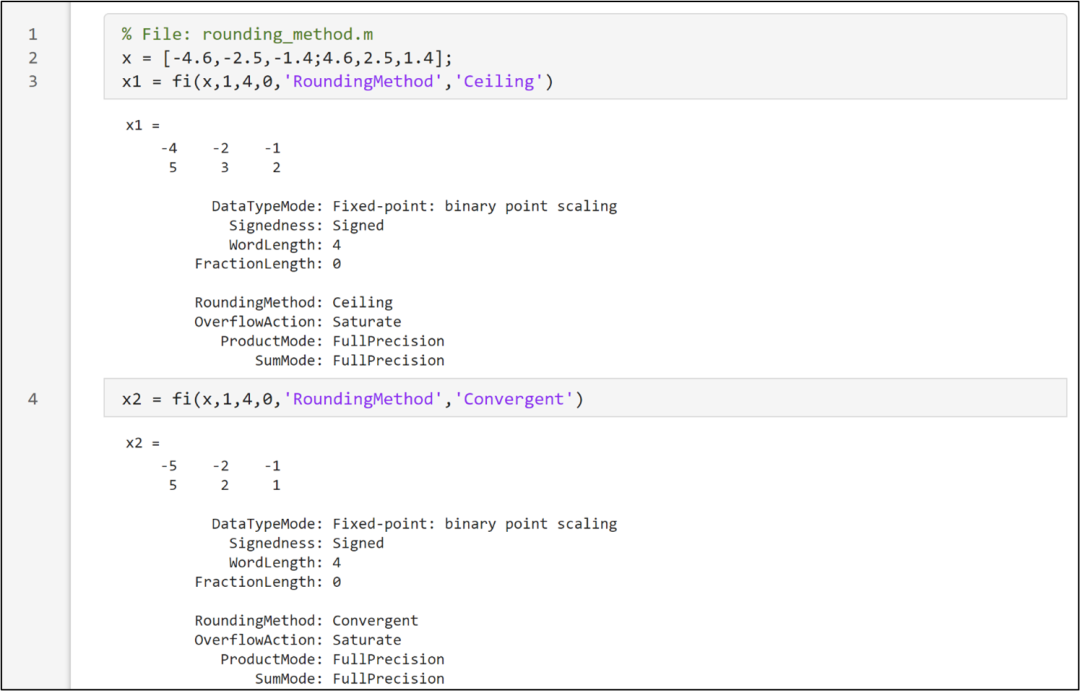
The fi function supports six rounding modes, which can be observed through the code snippets shown in the following three images. The input data x is a double-precision floating-point number, and it is to be converted into a fixed-point number with a sign bit of 1, a word length of 4, and a fractional length of 0, which is essentially a 4-bit signed integer.The Ceiling mode rounds towards positive infinity to the nearest representable value, so the conversion result of -4.6 is -4.The Convergent mode rounds to the nearest representable value, rounding to the nearest even number when the rounding opportunities are equal, so the conversion result of -4.6 is -5, and the conversion result of -2.5 is -2.
 The floor mode rounds towards negative infinity to the nearest representable value, equivalent to 2 ‘s two’s complement truncation, so the conversion result of -4.6 is -5 (the binary two’s complement form of -4.6 is 1011.011010, the integer part is 1011, which is -5).The Zero mode rounds towards zero to the nearest representable value, so the conversion result of -2.5 is -2, and the conversion result of 2.5 is 2, as shown in the code snippet below.
The floor mode rounds towards negative infinity to the nearest representable value, equivalent to 2 ‘s two’s complement truncation, so the conversion result of -4.6 is -5 (the binary two’s complement form of -4.6 is 1011.011010, the integer part is 1011, which is -5).The Zero mode rounds towards zero to the nearest representable value, so the conversion result of -2.5 is -2, and the conversion result of 2.5 is 2, as shown in the code snippet below.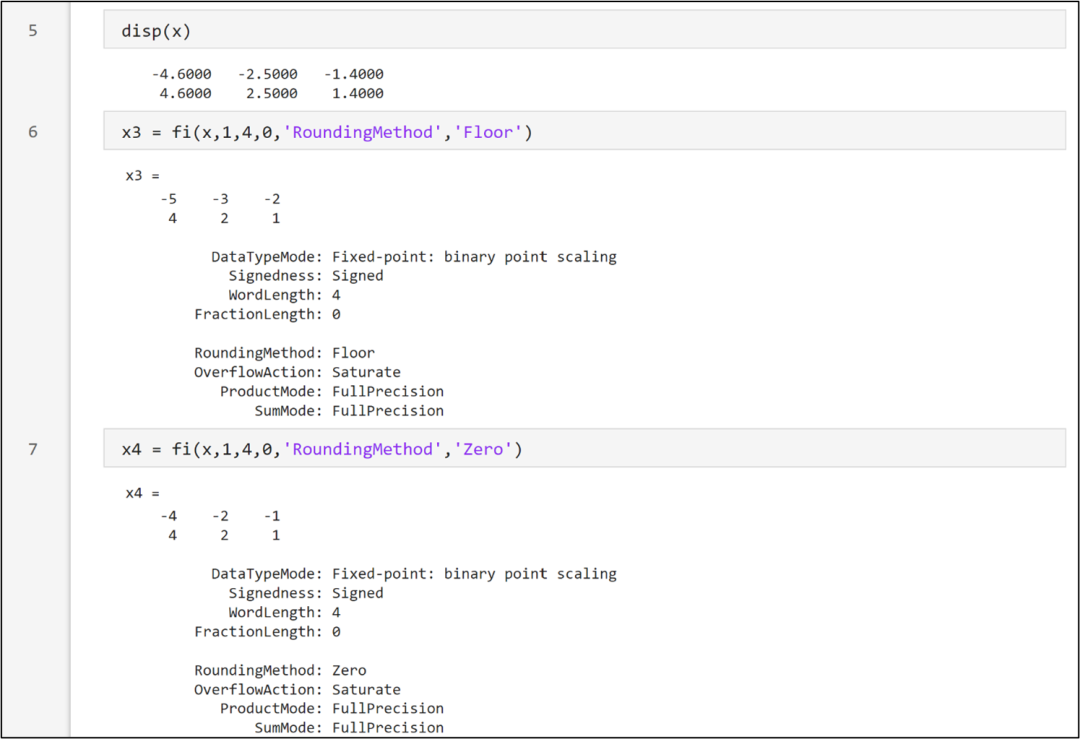
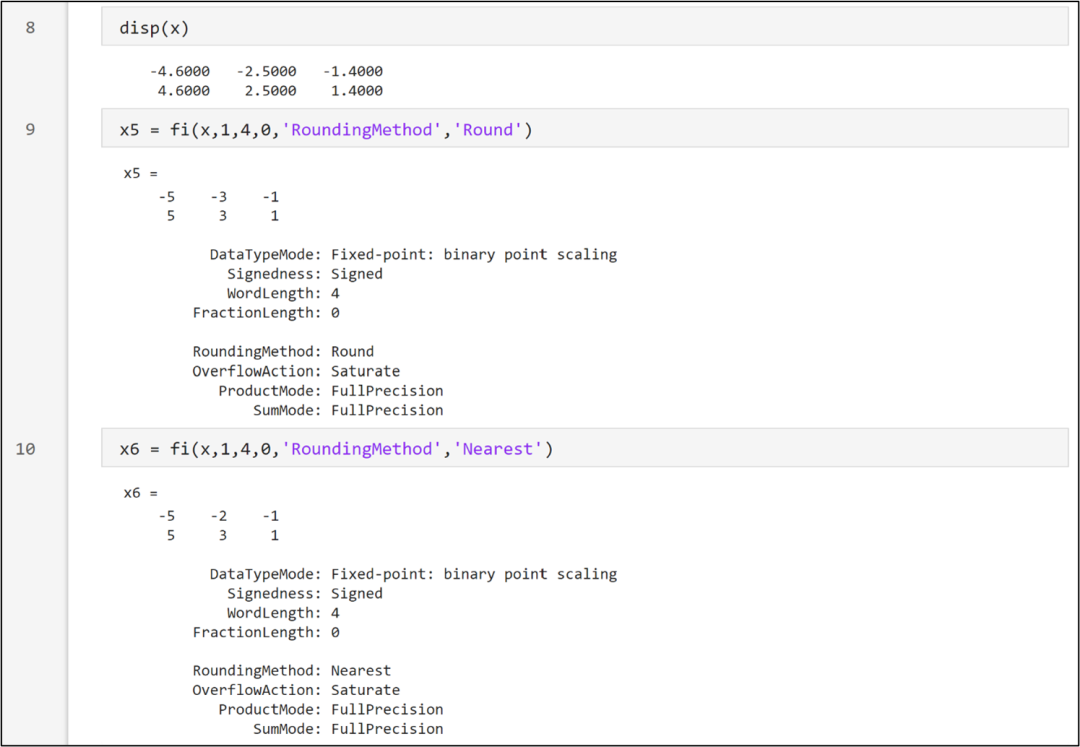
The Round rounding mechanism is slightly more complex, rounding to the nearest representable value, where positive numbers are rounded towards positive infinity and negative numbers are rounded towards negative infinity when the rounding opportunities are equal. Therefore, the conversion result of 2.5 is 3, and the conversion result of -2.5 is -3.The Nearest mode rounds to the nearest representable value, rounding towards positive infinity when the rounding opportunities are equal. This rounding method is the default for creating fi objects and performing fi arithmetic. Therefore, the conversion result of -2.5 is -2, and the conversion result of 2.5 is 3.
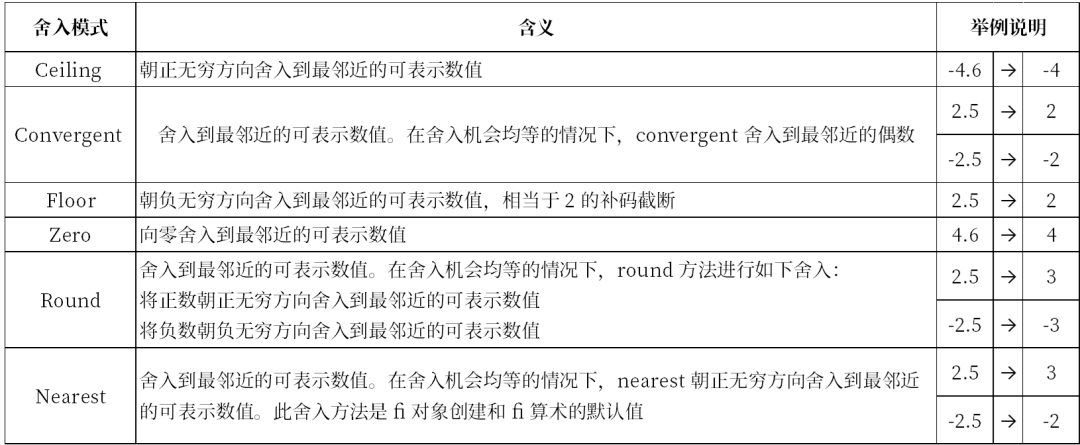
The comparison of the six rounding modes is shown in the table below, from which the differences between them can be further appreciated.
The fi function supports two overflow modes: Saturate and Wrap. When set to Saturate, overflow is limited to the maximum or minimum value within that range by saturation, which is the default mode. When set to Wrap, any overflow will wrap around; for unsigned values, modulo operation is used for wrapping, while for signed values, two’s complement wrapping is applied.
<img src=”https://mmbiz.qpic.cn/mmbiz_png/amLPbwsBTyvwMu4ORA6LVLUZ7sibmFkwl263KnXxIWkHpIKNTww0iapwQBhXn27jCIianhLY3NicDBicT9uoXXkHUNg/640?wx_fmt=png&from=appmsg”