Core Logic:
Electronic skin is a flexible tactile sensor that mimics the sensory capabilities of human skin, serving as a fundamental component for robots to perceive their environment and perform tasks.Currently, the application of electronic skin in humanoid robots mainly focuses on dexterous fingertips. In the future, as the trend of “humanization” evolves, it is expected to further extend to areas such as palms, shoulders, and thighs, with the value proportion likely to continue increasing. It is estimated that if the future production scale of humanoid robots reaches1 million units, it could drive the market scale of flexible tactile sensors to12.8 billion, which is almost equivalent to the current global overall market scale, indicating significant growth potential.
Related Companies:
Hanwei Technology, Fule New Materials, Keli Sensor, Shenhao Technology, Riying Electronics, Xiangyuan New Materials, etc.

01 Tactile Sensors and the Basic Concept of Electronic Skin
Tactile sensorsare sensors used tomimic tactile functions, capable of sensing various information when an object makes contact, including contact force, pressure, and sliding, thus helping robots interact more naturally with the external environment..
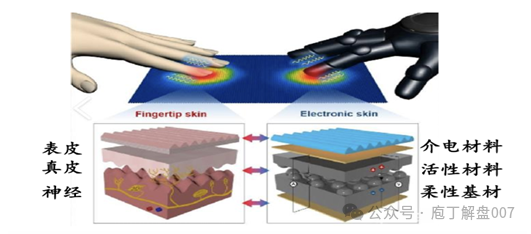
Electronic skinis a type offlexible tactile sensor that mimics the sensory capabilities of human skin, belonging to a major category of tactile sensors. It integrates pressure, temperature, humidity, and other sensors, and can be applied to robot fingers, arms, etc., enabling robots to perceive external touch sensations. Its core consists of flexible materials, sensor arrays, and signal processing modules, making it a hot research direction at the intersection of flexible electronics and artificial intelligence.
Figure 1 Comparison of Electronic Skin and Biological Skin
02 Several Technical Solutions and Features of Flexible Tactile Sensors
Generally, flexible tactile sensors can be classified into four types based on their sensing mechanisms: resistive, capacitive, piezoelectric, and triboelectric. Below is an overview of the mechanisms and characteristics of these four types of commonly used flexible pressure tactile sensors:
——Resistive Tactile Sensors:Resistive tactile sensors are made using the property that the resistivity of elastomeric materials changes with the amount of pressure applied. They have a simple structure, low cost, and convenient signal acquisition methods, but they also have issues with low sensitivity and poor linearity, making them one of the most commonly used tactile sensors.
——Capacitive Tactile Sensors:These sensors operate by changing the relative position between two plates under external force, resulting in a change in capacitance between the plates. Tactile detection is achieved by detecting the change in capacitance, with advantages including a simple structure, ease of lightweight and miniaturization, and insensitivity to temperature. However, the signal detection circuit is relatively complex.
——Piezoelectric Tactile Sensors:These sensors are based on the piezoelectric effect, where piezoelectric materials generate an electrical signal proportional to the external force applied, thus achieving tactile detection. They have advantages such as small size, light weight, high operating frequency, sensitivity, and stable performance, but they also have drawbacks like high noise levels and susceptibility to external electromagnetic interference.
——Triboelectric Tactile Sensors:These sensors operate similarly to piezoelectric sensors, but differ in that triboelectric tactile sensors can self-power and respond to dynamic pressure, featuring fast response times.
Figure 2 Four Types Based on Sensing Mechanism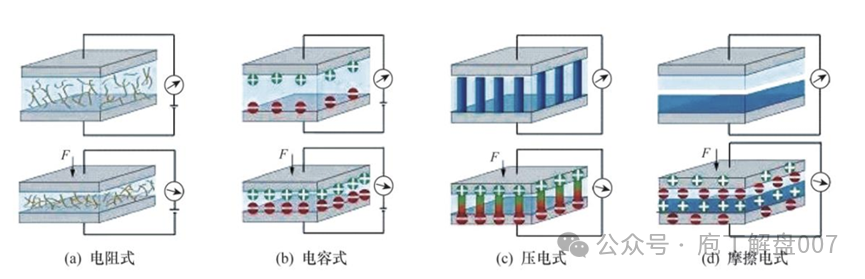
03 Application Fields of Flexible Tactile Sensors
Electronic skin belongs to the broader category of flexible tactile sensors, with core application directions including humanoid robots and smart prosthetics. Other important application fields for current flexible tactile sensors include consumer electronics, automotive, and medical devices.
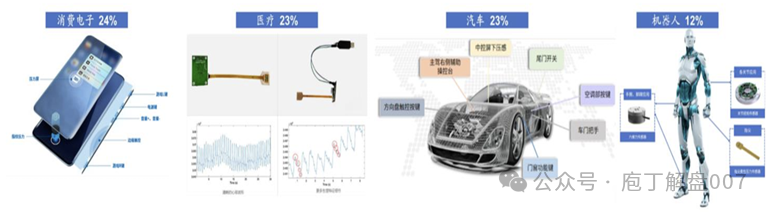
Globally, the consumer electronics sector, including smartphones, wireless earbuds, VR/XR, and smartwatches, accounts for approximately24% of the market share, ranking first; medical devices and automotive sectors each hold23% of the market share, primarily applied in areas such as heart rate monitoring and intelligent automotive cockpits; the robotics sector currently accounts for12%, but is expected to grow rapidly in the future, becoming a major demand direction.
Figure 3 Current Application Field Shares of Flexible Tactile Sensors
04 Market Size of Flexible Tactile Sensors and Demand Elasticity Estimation for Humanoid Robots
According toQY Research,in 2022 the global market size for flexible tactile sensors was1.53 billion USD (equivalent to 10.9 billion RMB), and it is expected to grow to2 billion USD (equivalent to 14 billion RMB) by2024, with a compound annual growth rate of15%. According to Zhiyan Consulting,in 2023 the market size for flexible sensors in China is2.356 billion RMB, with a compound annual growth rate of17.2% since 2015.
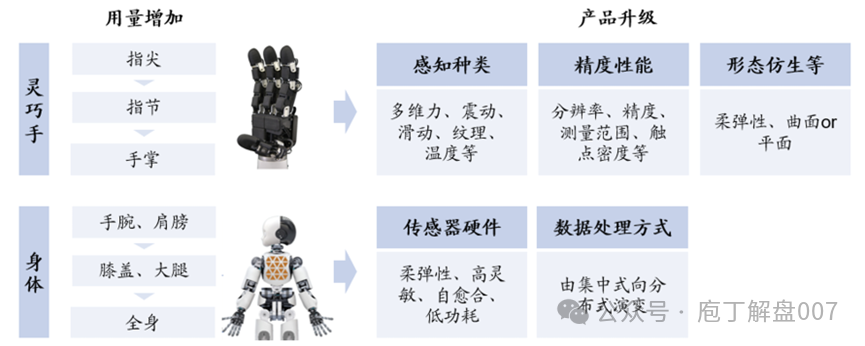
Based on previously disclosed information, the precise force control achieved by Tesla’s humanoid robot, which can delicately pinch an egg, is significantly attributed to the array of tactile sensors in its dexterous fingertips. In the future, humanoid robots will become the most important demand driver for electronic skin.Referring to human tactile needs, electronic skin will first penetrate the fingertips, knuckles, and palms of dexterous hands to enhance the ability to handle complex tasks; subsequently, it will extend to wrists, shoulders, knees, and thighs to improve interaction capabilities; finally, it will gradually cover the entire body, moving towards generalization and intelligence.
Referring to the price of TekScan A201 film pressure sensors, the current price of flexible sensors covering each square centimeter is approximately267 RMB. Assuming that the electronic skin of humanoid robots expands from the fingertips to the palms, the coverage area increases from10cm2 to160cm2, and if the price decreases by70% to80 RMB/cm2, the value of a single robot could reach12,800 RMB. This suggests that if the future production of humanoid robots reaches1 million units, it could drive the electronic skin market size to12.8 billion RMB, exceeding the current global market size of 10 billion.
Figure 4 The Future Use of Electronic Skin in Robotics is Expected to Increase Continuously
05 Competitive Landscape of Flexible Tactile Sensors
From a global supply perspective, the technology threshold for flexible tactile sensors is high, and the R&D cycle is long, with high-end production capacity almost monopolized by foreign companies, leading to a high market concentration.The current top five manufacturers globally areNovasentis (USA),Tekscan (USA),Japan Display Inc (Japan JDI),Baumer (Switzerland), andFraba (Germany), collectively holding57.1% of the market share. Domestic companies such as Hanwei Technology, Fule New Materials, Keli Sensor, Shenhao Technology, Pasini, Nudi Rui, Taishen Technology, and Puhui Technology have made good progress, with some companies entering the sample delivery stage.In the future, domestic flexible tactile sensors are expected to gradually narrow the gap with overseas counterparts, thereby promoting the process of localization.
Figure 5 Global Competitive Landscape of Flexible Sensors Market
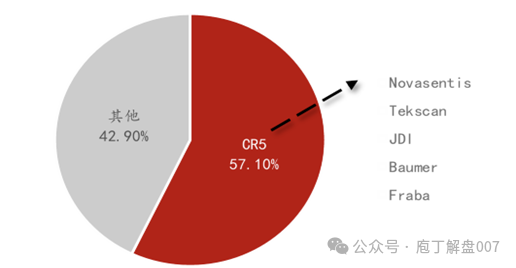
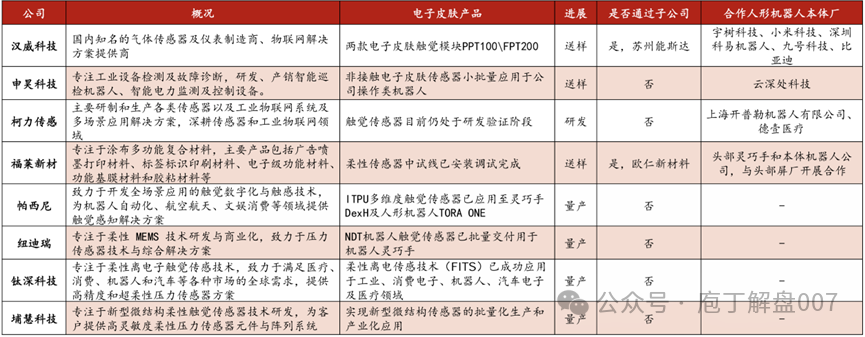
Figure 6 Progress of Domestic Flexible Tactile Sensor Companies
06 Main Companies Involved in Electronic Skin
——Hanwei Technology:One of the earliest companies in China to layout flexible tactile sensors, with several production lines capable of producing tens of millions of flexible sensors annually. The company’s flexible sensor products have already collaborated with multiple humanoid robot manufacturers and have begun small batch deliveries to some robot manufacturers.
——Fule New Materials:As a leading supplier of coated multifunctional composite materials in China, the company has extended its product line into the flexible sensor field based on its core coating technology. Its wholly-owned subsidiary, Zhejiang Ouren New Materials, has been researching flexible sensor-related products since2017. The company is actively connecting with relevant dexterous hand and mainframe manufacturers and is building a pilot line for flexible sensors, with hopes of obtaining small batch orders.
——Keli Sensor:The company is a leading enterprise in the sensor industry, advancing tactile sensor products through collaboration with enterprises and academic institutions as well as self-research models. Currently, it is in the R&D verification stage; flexible tactile sensors are being developed through investment and mergers, and the company has signed a deep cooperation agreement with Shanghai Kepler Robotics.
——Shenhao Technology:The company has independently developed a non-contact electronic skin sensor, which is currently being applied in small batches to its own intelligent robot products, such as switch room operation robots, achieving obstacle avoidance functions to ensure safety. In March 2025, it formally reached a strategic cooperation agreement with Yundong Technology.2025 March3 with Yundong Technology.
——Riying Electronics:In the new field of humanoid robots, the company is using the opportunity of developing new products for flexible tactile sensor electronic skin to accelerate the layout of flexible harnesses and other humanoid robot products, continuously enriching its product matrix, and leveraging the localization advantages of Riying in North America to actively expand overseas customers and markets.
——Xiangyuan New Materials:The company has a clear layout in the field of electronic skin materials for humanoid robots, with related products already entering the sample delivery stage for a few customers. The intelligent skin module jointly developed with Riying Electronics has passedISO13448 medical device certification and has achieved commercial application in the field of rehabilitation robots.
Disclaimer:This article is for personal learning purposes only and does not constitute any investment advice. Many of the information quoted in the text are based on publicly available reports or information, and all judgments are based on personal subjective assumptions, which may inevitably contain many errors and omissions. Any actions taken based on this information are at your own risk. The stock market has risks, and investment should be cautious!
