Frontiers in Materials Research—— Focusing on the latest advancements in materials science research. Over one million faculty members in the materials field subscribe to our WeChat account. Click the blue text under the title “Frontiers in Materials Research” to follow us, and we will provide you with valuable and cutting-edge materials research information.

In the field of energy, the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) has always been a research hotspot. Professor Cao Rui’s team at Shaanxi Normal University has made significant progress in cobalt-based electrocatalysts for selective two-electron (2e⁻) and four-electron (4e⁻) oxygen reduction reactions, providing important references for related research.
ORR can proceed via two pathways: 4e⁻ and 2e⁻. The product of 4e⁻ ORR is solely water, which is the core reaction for fuel cells and metal-air batteries; 2e⁻ ORR can be used for electrocatalytic synthesis of hydrogen peroxide. Precise control of ORR pathway selectivity is crucial, and understanding the structural effects on ORR selectivity is the theoretical basis for achieving this control. Cobalt-based electrocatalysts are of great interest in the ORR field due to their high activity, low cost, and ease of synthesis. By rationally designing their structures, it is possible to achieve high selectivity for either the 2e⁻ or 4e⁻ ORR pathway, making them ideal model systems for studying the intrinsic structure-activity relationships of ORR.
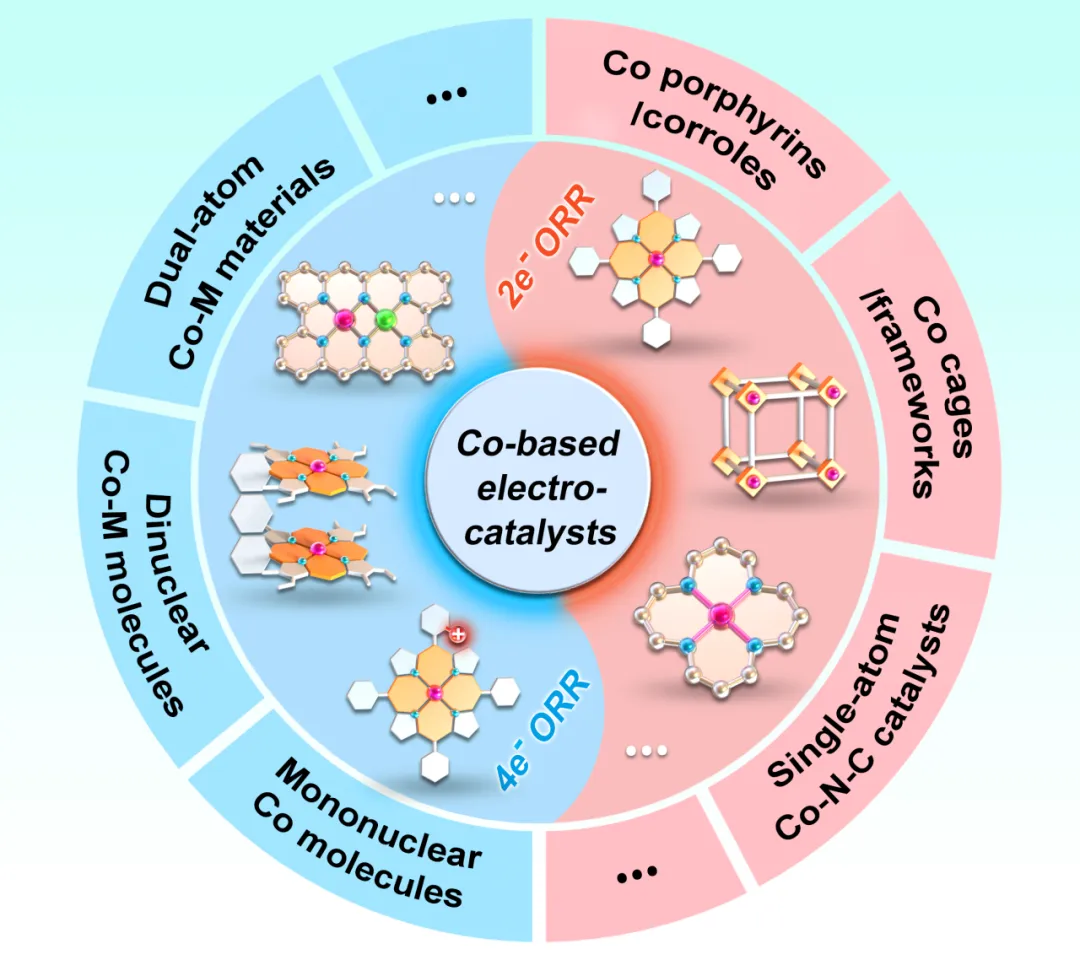
Professor Cao Rui’s team’s review article elaborates on the reaction mechanisms of ORR and the methods for evaluating selectivity, systematically summarizing the research progress of cobalt-based electrocatalysts with 2e⁻ and 4e⁻ selectivity (especially cobalt porphyrin catalysts), and identifying several key structural factors that regulate ORR selectivity. For example, the structure of the catalyst can affect its adsorption and activation capabilities for reaction intermediates, thereby influencing ORR selectivity. The unique structure of cobalt-based catalysts makes them more favorable for guiding reactions towards the 2e⁻ or 4e⁻ pathway under specific conditions. Through comparative analysis of different types of cobalt-based catalysts, the team further clarified the relationship between structural factors and ORR performance, providing insights for the optimization design of future catalysts.
This review offers targeted suggestions for the future development of cobalt-based electrocatalysts, providing a scientific basis for the rational design of highly selective 4e⁻/2e⁻ ORR molecular catalysts and material catalysts. At the same time, the structural regulation strategies of cobalt-based electrocatalysts also point the way for the design and development of other metal-based ORR electrocatalysts, which is expected to promote deeper research in the entire field of oxygen reduction catalysts and contribute to the advancement of new energy technologies.




Note:
🔹 This article is intended for academic exchange among researchers.
🔹 If there are any copyright issues with this article, please contact us for timely resolution.
🔹 Readers are welcome to share and promote this article.
🔹 “Frontiers in Materials Research” will continuously improve its standards to share higher quality interpretations of materials research results with readers. We welcome you to follow us.
We welcome researchers to submit their latest research results.
Feel free to share and give a “like”~