1. Serial Communication Principles
Serial communication refers to a method of transmitting data bit by bit between peripherals and computers through data signal lines, ground lines, etc. Serial ports are a type of interface standard that specifies the electrical standards of the interface, but does not specify the interface plug cable and the protocol used.Serial ports are classified according to electrical standards and protocols, includingRS-232-C, RS-422, RS485, etc.
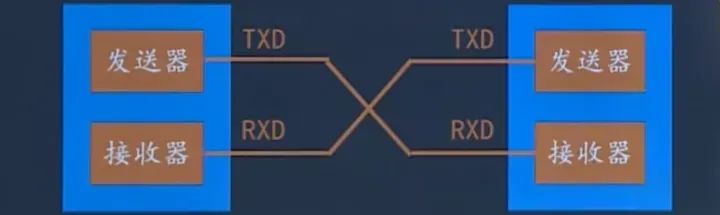
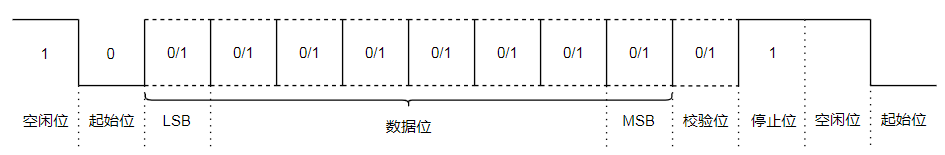
Data is transmitted one character at a time, with each character transmitted bit by bit, and the transmission of a character always starts with a “start bit” and ends with a “stop bit”; there is no fixed time interval requirement between characters. Each character has a start bit (low level) in front of it, the character itself consists of 7 data bits, followed by a parity bit (the parity bit can be odd parity, even parity, or no parity bit), and finally one, one and a half, or two stop bits, followed by an indefinite length of idle bits, with the stop bits and idle bits both defined as high level.During actual transmission, the signal width of each bit is related to the baud rate; the higher the baud rate, the smaller the width. Before transmission, both parties must use the same baud rate settings.
2. Raspberry Pi Serial Communication Interface
The serial port of the Raspberry Pi isUART, which stands for Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, or UART (serial) controller. Using the UART controller for data transmission is called serial communication, which is a general-purpose full-duplex serial, asynchronous communication method. It is commonly used for communication between the host and auxiliary devices in embedded systems. Asynchronous means that the clocks of the transmitter and receiver are not synchronized. UART communication has three lines: transmit line TX, receive line RX, and ground reference line GND.
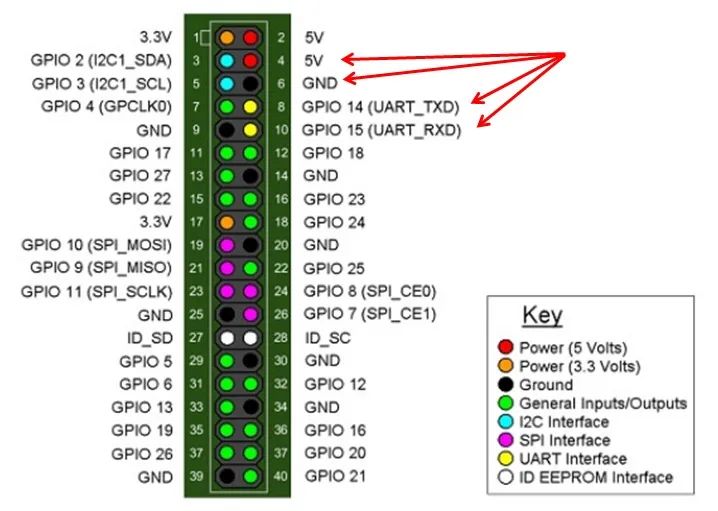
The wiring method is as follows:
-
VDD connects to the Raspberry Pi’s 5V power supply
-
GND connects to the Raspberry Pi’s ground
-
TXD connects to the Raspberry Pi’s RXD
-
RXD connects to the Raspberry Pi’s TXD
3. Steps for Serial Communication
Hardware Connection: Use a suitable serial cable to connect the serial device to the Raspberry Pi’s GPIO pins, specifically connecting the serial TX (transmit) pin to the Raspberry Pi’s RXD pin and the serial RX (receive) pin to the Raspberry Pi’s TXD pin. Please ensure correct connections.
Disable Serial Terminal: In Raspbian Stretch, by default, the Raspberry Pi’s serial port is used as a terminal, not as a general serial port. Therefore, it is necessary to disable the serial terminal by modifying the boot configuration file.
Open the terminal and enter the following command to edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /boot/cmdline.txt
In the editor, find a line similar to the following text:
Remove this line or comment it out (add # at the beginning of the line), then save and exit the editor.
Enable Serial Hardware: Open the terminal and enter the following command to edit another configuration file:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt
Add the following two lines at the end of the file:
enable_uart=1
dtoverlay=pi3-miniuart-bt



