Ophthalmic medical devices include ophthalmic equipment and related instruments, auxiliary devices, and implants used for diagnosing and treating ophthalmic diseases. They can be divided into ophthalmic diagnostic devices, ophthalmic treatment devices, and ophthalmic consumables. Ophthalmic diagnostic devices help diagnose the occurrence of ophthalmic diseases through detection imaging and data analysis, obtaining accurate diagnostic results.
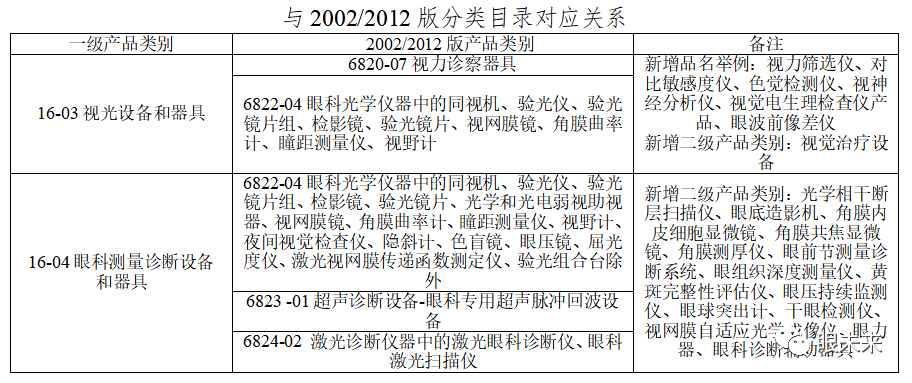
In the Chinese medical device classification directory, Part 16 covers ophthalmic devices, including various ophthalmic instruments and related auxiliary devices used in ophthalmic examination, surgery, treatment, and protection, excluding ophthalmic rehabilitation training devices (which fall under subdirectory 19). Ophthalmic diagnostic devices mainly correspond to optometry equipment and ophthalmic measurement diagnostics, as shown below.
01
Introduction to Ophthalmic Diagnostic Equipment
Ophthalmic diagnosis includes general eye examinations that check patients’ vision, visual fields, and other preliminary screenings, as well as fundus examinations conducted using ophthalmic medical diagnostic instruments. Ophthalmic diagnostic instruments can help doctors obtain clear fundus images and structural features, leading to accurate diagnoses.
The main ophthalmic diagnostic instruments currently on the market include slit lamp microscopes, fundus cameras, retinoscopes, ophthalmic OCT, and corneal topography devices.
With the increasing awareness of related eye health and technological advancements, the variety of ophthalmic diagnostic devices has further enriched, opening up the ophthalmic diagnostic device market. The table below introduces the main ophthalmic diagnostic devices.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
02
Market Size of Ophthalmic Diagnostic Equipment
According to the “2022 International Myopia Surgery White Paper” report, there are approximately 2.5 billion myopia cases globally, with 600 million in China. The incidence of myopia in Asia is higher than in Europe and the United States, and China has the highest myopia incidence in Asia, reaching 48.5%. According to the seventh national population census, China’s total population has reached 1.41 billion, with 260 million people aged 60 and above, and the cataract incidence rate among people over 60 in China is about 80%.
According to the forecast in the “Global Prevalence of Myopia and High Myopia and Temporal Trends from 2000 through 2050,” the number of myopia cases worldwide will exceed 4.758 billion by 2050 (with a myopia rate of about 50%), indicating a stable increase in the myopic population and a concerning global myopia situation. There are differences in myopia rates across different regions worldwide, with China’s myopic population ratio ranking among the highest in the world.

(▲Source: Frost & Sullivan)
Ophthalmic diagnostic medical equipment can be categorized by energy source into laser diagnostic devices, non-laser optical diagnostic devices, ultrasound devices, and electrophysiological devices. Optical diagnostic instruments have the advantages of intuitive and clear examinations, and they remain the mainstream products in ophthalmic medical diagnostics. In 2021, the market size for ophthalmic laser diagnostic instruments in China was approximately 1.2 billion RMB, accounting for 48% of the entire ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment market, while the non-laser optical diagnostic instrument market size was around 1.1 billion RMB, accounting for 44% of the total ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment market.
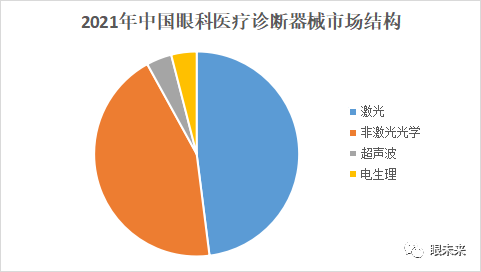
(▲Source: Qianzhan Industry Research Institute)
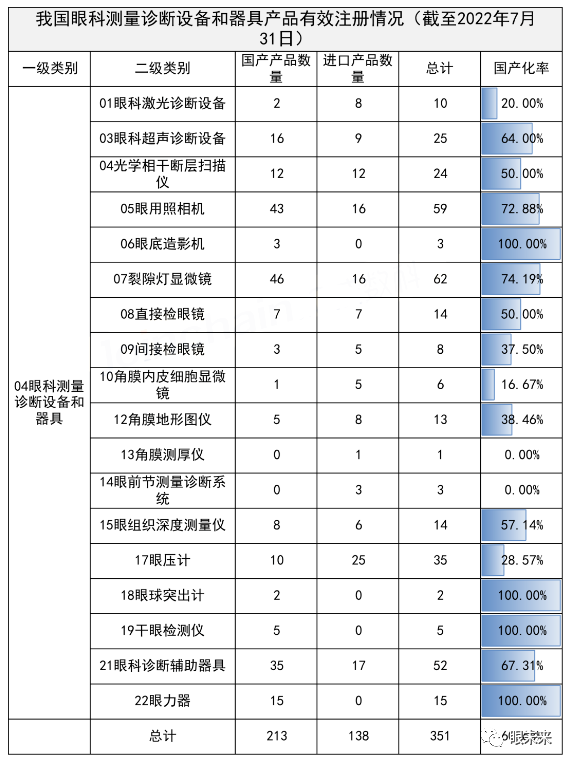
According to medical device data cloud statistics, as of the end of July 2022, the effective registration number of ophthalmic diagnostic devices in China (according to the “Medical Device Classification Directory” 16 ophthalmic devices – 04 ophthalmic measurement diagnostic devices and instruments) was 351, including 213 domestic products and 138 imported products.
03
Development of the Ophthalmic Diagnostic Equipment Industry
(1) Upstream of the Industry Chain
Leading enterprises in the ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment industry have begun to extend the industry chain, gradually entering the raw material production field to avoid high costs of imported raw materials and capture upstream gross profits. In addition, with the acceleration of the restructuring process of upstream raw material production enterprises and the improvement of the technical level of market participants in China, the upstream raw material supply for the ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment industry is expected to continue developing towards specialization and scale.
(2) Midstream of the Industry Chain
Midstream enterprises in the ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment industry rely mostly on imported raw materials. The main reason is that downstream consumer terminals require high stability in product quality to safeguard research results. Therefore, midstream research and preparation manufacturers prefer to choose advanced instruments and stable supply chain import raw material suppliers. The product prices of enterprises are mainly influenced by market supply and demand relationships. Since the gross profit of ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment enterprises is relatively high, fluctuations in raw material prices will not significantly impact their profitability.
(3) Downstream of the Industry Chain
Downstream enterprises in the ophthalmic medical diagnostic equipment industry have broad market space, wide sales range, dispersed users, small batch quantities, and high sales prices. With the deepening of research in the biopharmaceutical industry globally and the increasing degree of industrialization, the variety of industry products in China has further enriched, and the application fields continue to increase. Personalized and high-end products will gradually gain broader application space.
04
Main Players in the Ophthalmic Diagnostic Equipment Industry

(▲Source: Alcon Company Official Website)
Alcon Laboratories, established in 1947, is a global leader in ophthalmic pharmaceuticals and medical devices, with subsidiaries in 75 countries and regions, 5 research and development centers, and 14 production factories, with products sold in over 180 countries and regions. Alcon develops, produces, and markets ophthalmic pharmaceuticals, surgical devices, contact lens-related care products, and other consumer products for treating diseases and alleviating discomfort in eye care.
(2) Johnson & Johnson Vision

(▲Source: Johnson & Johnson Company Official Website)
Johnson & Johnson Vision is the eye health business under Johnson & Johnson, including the “Acuvue” business, which encompasses ophthalmic implants, surgical medical devices, and consumables, as well as the “Vision Care” business, which includes contact lenses, contact lens care solutions, and eye drops. In 2016, Johnson & Johnson acquired Abbott Medical Optics (AMO), a wholly-owned subsidiary of Abbott, for $4.3 billion, gaining ophthalmic products related to cataract surgery, laser refractive surgery, and consumer eye health, forming the current Acuvue business.
(3) Zeiss

(▲Source: Zeiss Group Official Website)
Zeiss Group is a German company that manufactures optical and optoelectronic equipment, founded in 1846 and headquartered in Oberkochen, Baden-Württemberg. The company’s name comes from one of its founders, Mr. Carl Zeiss. Zeiss operates in about 50 countries worldwide, with more than 30 production bases, over 60 sales and service companies, and more than 30 research and development bases. In the health sector, Zeiss provides patients with comprehensive eye health management solutions throughout their life cycle, offers digital solutions for myopia prevention in adolescents, and provides innovative solutions for refractive correction in adults, presbyopia treatment, and the prevention and treatment of chronic eye diseases.

(▲Source: Bausch + Lomb Company Official Website)
Bausch + Lomb was founded in 1853 in Rochester, New York, and its core business can be divided into vision care, ophthalmic surgery, and ophthalmic medications, including contact lenses, care solutions, ophthalmic drugs, refractive, cataract, and vitreoretinal products.
In October 2007, Warburg Pincus acquired Bausch + Lomb, which was previously listed on the New York Stock Exchange. In 2013, Bausch Health, the parent company of Bausch + Lomb, formerly Valeant, purchased Bausch + Lomb for $8.7 billion. In August 2020, Bausch Health announced plans to spin off Bausch + Lomb as an independent publicly traded company. In May 2022, Bausch + Lomb successfully went public on both the New York Stock Exchange and the Toronto Stock Exchange.
(▲Source: Essilor Official Website)
Essilor Luxottica Group is a vertically integrated multinational company based in Italy and France, formed in 2018 by the merger of Italy’s Luxottica and France’s Essilor. The group designs, produces, and sells ophthalmic lenses, optical equipment, prescription glasses, and sunglasses.
Essilor, based in Charenton-le-Pont, France, was founded in 1972 by the merger of Essel and Silor, and is now one of the world’s leading lens manufacturers. Luxottica is a leading sunglasses company founded in Italy in 1961, covering production, wholesale, and retail, with brands including Ray-Ban, Oakley, and some luxury brand sunglasses.
(6) Hoya

(▲Source: Hoya Group Official Website)
Hoya Group was founded in 1941 in Tokyo, Japan, and has established headquarters in Japan, Asia Pacific, Europe, and North America across 38 countries and regions, with 7 production bases and over 90 branches, providing services worldwide. Initially, Hoya was a factory producing special optical glass, but it has now expanded its business scope to include health care, medical imaging, electronics, IT system construction, and software development, evolving into a diversified group enterprise with three main departments: electronic optics, vision protection, and crystal manufacturing.
(7) Nidek

(▲Source: Nidek Official Website)
Nidek Co., Ltd. was established in 1971 and is headquartered in Aichi Prefecture, Japan. It has factories in Goshi, Hama-cho, Tsuhara, Higashihara, and Oozawa and overseas branches in Beijing and Dubai. The company’s ophthalmic and optometry business includes the design, development, manufacturing, and sales of ophthalmic surgical instruments, examination and diagnostic instruments, electronic medical records/medical documentation systems, intraocular lenses, and dermatological surgical lasers, as well as the sales and import/export of optometry instruments, lenses, optical components, and filter coatings.
05
Conclusion
In recent years, as the trend of population aging becomes increasingly evident, there has been a gradual increase in eye diseases such as glaucoma and diabetic retinopathy, leading to a growing demand for ophthalmic diagnostic medical devices. The state supports social forces to deepen their involvement in specialized service fields such as ophthalmic medical care, and the development of optometry service institutions is flourishing. The ophthalmic medical health industry is in a rapid development stage, and with the continuous improvement of China’s economic level, the public’s emphasis on medical health is also increasing, indicating that domestic ophthalmic diagnostic equipment development will usher in a period of prosperity.
Editor-in-chief: Zhao Qing Review: Yi He Typesetting: Miya
