Follow the “Bofei Industrial Design” brand for Chinese industrial design
Follow the “Bofei Industrial Design” brand for Chinese industrial design

Fei Jie Says:Handheld medical devices have gained widespread popularity, but they have not developed along the expected path. Many handheld medical devices have started to focus on gimmicks and aesthetics, resulting in a continuous decline in practical value. While their surface functions appear robust, they do not significantly assist patients or medical personnel. Therefore, in future design work, designers must grasp the key design points of handheld medical devices, starting from practical needs and steadily enhancing their value.
The source text is from [Medtec Medical Device Design and Manufacturing]. Images are sourced from [Device Home]
Compared to general medical devices, handheld medical devices serve a broader purpose, such as meeting diverse patient needs, occupying less space, being easy to maintain, and being portable. Due to their widespread application and the significant assistance they provide to medical personnel and patients, many handheld medical devices are beginning to expand into new fields, giving rise to a series of products.
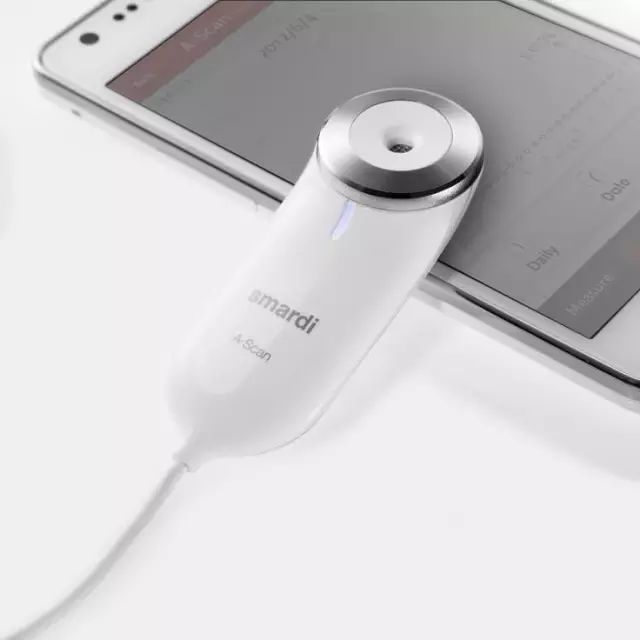

In practical applications, these products have not consistently received positive reviews, but have instead sparked discussions in society and debates in academia. The key issue lies in the design points of handheld medical devices being flawed, which affects their overall usage and subsequent development. This study primarily analyzes the design points of handheld medical devices, and presents the following overview.
Characteristics of Handheld Medical Devices
1.1 Safety
The widespread daily application of handheld medical devices is largely due to their high safety standards. The application fields of medical devices are extensive, and they hold significant positive implications for healthcare personnel, disabled patients, and research in the medical field. They can objectively change the status quo of medical work and improve patients’ lifestyles, reaching new heights. As a key part of the medical device sector, the safety of handheld medical devices is subject to strict regulations.
First, when a handheld medical device malfunctions, it must ensure the safety of the user, rather than cause accidents.
Second, if a handheld medical device is damaged during daily use, it should prominently indicate the issue to inform the patient, preventing further use.
Third, the areas of frequent contact on handheld medical devices are the hands of the users, so protective measures must be enhanced to avoid wear and tear or cuts.

1.2 Complexity
Modern medical devices integrate results from multiple disciplines, leading to complex functions and diverse modules. Additionally, the users of medical devices are also diverse; not all users of handheld medical devices are professional healthcare personnel. The user environment surrounding handheld medical devices is not limited to healthcare workers. For instance, in home settings, users may often be non-medical professionals or even the patients themselves. They may lack basic medical knowledge and operational skills for medical devices.
The complexity of handheld medical devices is a core characteristic that influences other features and significantly affects their practical application. This study believes that the complexity of handheld medical devices is not easily grasped. In future work, efforts should be made to reduce complexity while enhancing other characteristics to enable handheld medical devices to acquire more functions; at the same time, the impacts of complexity should be managed to avoid affecting design and development.

Design Points of Handheld Medical Devices
2.1 Safety
The market for handheld medical devices is very broad. To further meet the needs of a large number of patients, handheld medical devices must satisfy fixed requirements during the design process, commonly referred to as design points, while also achieving greater breakthroughs in these design points; otherwise, it will be difficult to meet practical work demands. Long-term exploration has revealed that one of the key design points for handheld medical devices is safety.
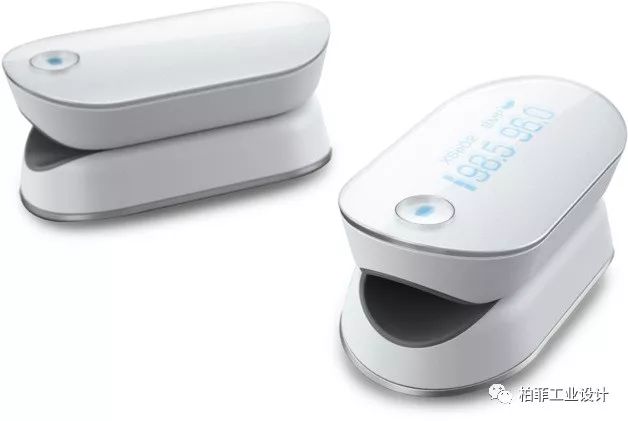

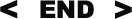
Finger pulse oximeters can measure pulse rates and blood oxygen saturation. This device is lightweight and elegantly designed; placing a finger in the middle position allows for measurement results in just a few seconds. This product is suitable for individuals and sports enthusiasts, and can also be used for home care and medical applications. It can connect via Bluetooth to smartphones, synchronizing measurement results.
2.2 Shape Design
A key distinction of handheld medical devices from other medical devices is their small size; they are primarily operated by hand, and the details of operation often determine the final outcome. Therefore, the shape design of handheld medical devices is crucial.
First, the shape of handheld medical devices must be compact, allowing operators to quickly discern their function. In terms of overall design, it should stand out, making it easy to locate among various medical devices.
Second, the colors of handheld medical devices should be distinct, as different colors convey different meanings, and practical applications must be considered. If the lighting is dim, the design should use bright colors to stand out; if the lighting is bright, softer colors should be applied. Ultimately, it is important to consider various situations, especially for individuals with color blindness, as the meaning conveyed by colors can vary significantly.
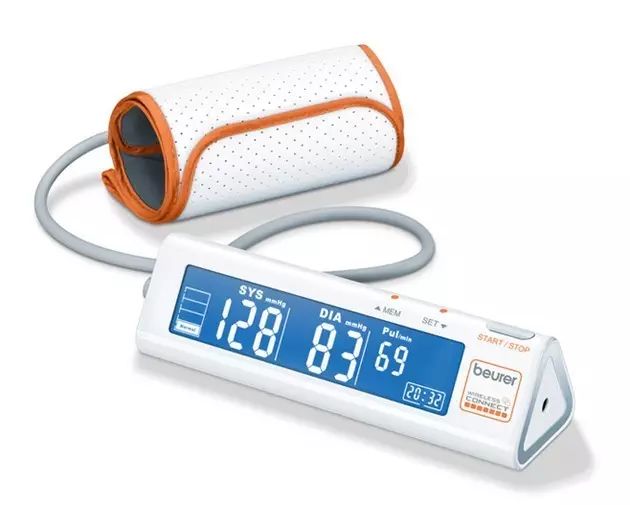

Third, the shape design of handheld medical devices must facilitate practical operation. Since these medical products are mainly used in delicate surgeries and applications for patients with disabilities, operational performance must meet a high standard, while also being resistant to pollution and corrosion, ensuring no harm comes to patients or healthcare personnel.
2.3 Tactile Design
In addition to the two aforementioned design points, the tactile design of handheld medical devices is also a very important aspect. Tactile design primarily allows operators to clearly feel their operation of the medical device, while avoiding excessive or insufficient force that could lead to adverse effects.
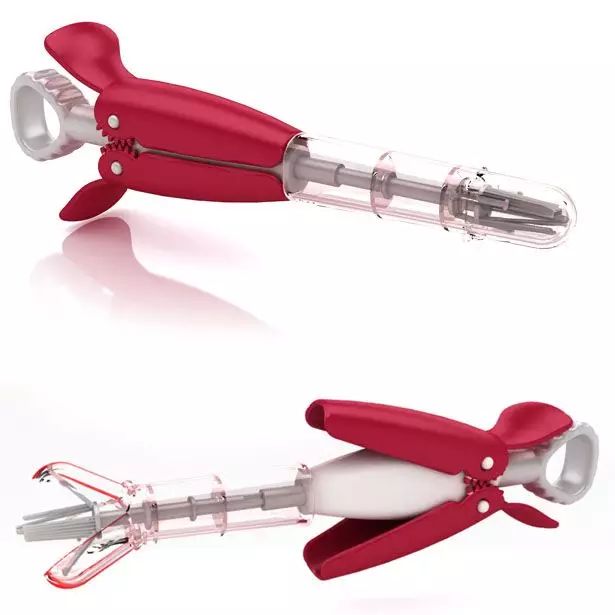

Tactile design has always been an important aspect of handheld medical device design, often serving as a bottleneck for breakthroughs. For example, membrane buttons have become a primary type of lightweight tactile controller. The functions on the membrane button of a pulse oximeter not only include on/off control in power supply but also other switching functions: it can also feature step control functionality. Taking the pulse oximeter plus as an example, the design of the membrane button must comply with the single-handed operation procedures, ensuring that the control keys can be operated with a single finger, and that the arrangement of control keys minimizes the risk of misoperation. From the above description, it can be seen that tactile design will directly affect the daily use, repair, and optimization of handheld medical devices, significantly impacting the users.
In future work, tactile design must become more user-friendly, enhancing sensitivity while also increasing features to prevent erroneous operations. Even in the event of incorrect operations, the tactile design should be able to promptly address any potential issues. Conclusion: This study analyzes the design points of handheld medical devices. To a large extent, existing handheld medical devices have met the needs of healthcare personnel and patients. However, with the increasing number of patients and the emergence of special cases, some handheld medical devices exhibit deficiencies in performance, indicating a need for further design in the future.

In summary, there are numerous design points for handheld medical devices. In design work, not only must all design point specifications be met, but the value of handheld medical devices must also be enhanced to provide more assistance to healthcare personnel and patients.