Before the commercial application of autonomous vehicles, they need to undergo extensive road testing to meet commercial requirements. Using road tests to optimize autonomous driving algorithms is too time-consuming and costly, and open road testing is still subject to regulatory restrictions, with extreme traffic conditions and scenario reproduction being difficult, posing safety risks during testing. Currently, autonomous driving simulation testing has been widely accepted in the industry, with approximately 90% of autonomous driving algorithm testing completed through simulation platforms, 9% in test sites, and 1% through actual road tests.
Autonomous driving simulation testing platforms must possess several core capabilities: accurately reproducing test scenarios, efficiently utilizing road data to generate simulation scenarios, and cloud-based large-scale parallel acceleration, ensuring that simulation testing meets the closed-loop algorithms for autonomous driving perception, decision planning, and control. Currently, various entities, including technology companies, automotive manufacturers, autonomous driving solution providers, simulation software companies, universities, and research institutions, are actively engaged in the construction of virtual simulation platforms.
This article provides a detailed introduction to existing autonomous driving simulation software for readers’ understanding and reference; the software rankings are not in any particular order.
CarSim
CarSim, along with related TruckSim and BikeSim, is a powerful dynamics simulation software developed by Mechanical Simulation Corporation, widely used by OEMs and suppliers worldwide. CarSim targets four-wheeled vehicles and light trucks; TruckSim targets multi-axle and dual-tire trucks, while BikeSim targets two-wheeled motorcycles. CarSim is a complete vehicle dynamics simulation software that simulates from the overall vehicle perspective. It contains a considerable number of vehicle mathematical models, all with rich empirical parameters, allowing users to utilize them quickly, eliminating complex modeling and parameter tuning processes.
The CarSim model runs on computers at speeds up to 10 times faster than real-time, simulating vehicle responses to driver control, 3D surface, and aerodynamic inputs, with simulation results closely approximating real vehicles. It is primarily used to predict and simulate the handling stability, braking performance, ride comfort, power, and economy of the entire vehicle. CarSim comes with a standard Matlab/Simulink interface, facilitating co-simulation with Matlab/Simulink for control algorithm development, while generating a large amount of data results during simulation for subsequent analysis or visualization using Matlab or Excel. CarSim also provides an RT version that supports mainstream HIL testing systems, such as dSpace and NI systems, for convenient co-simulation of HIL.
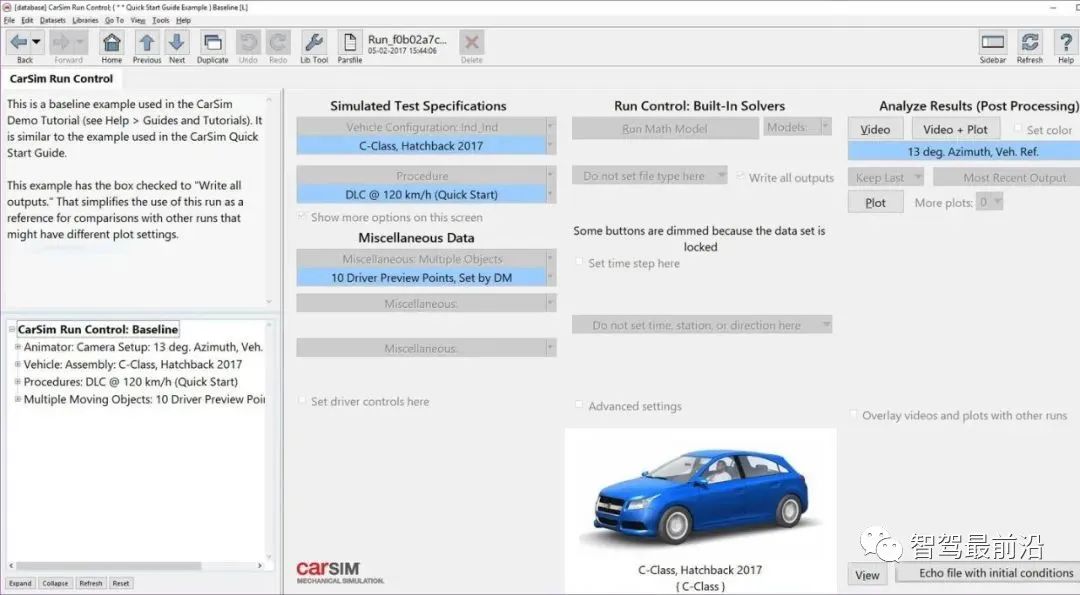
CarSim also supports ADAS-related functions, allowing the construction of parameterized road models and over 200 moving traffic objects, controlling their movement through scripts or external control via Simulink, while adding up to 99 sensors to detect moving and stationary objects. Recent versions of CarSim have strengthened capabilities in ADAS and autonomous driving development, adding more 3D resources like traffic signs, pedestrians, and high-precision map import processes. Additionally, CarSim provides an Unreal Engine plugin for co-simulation with Unreal Engine.
CarMaker
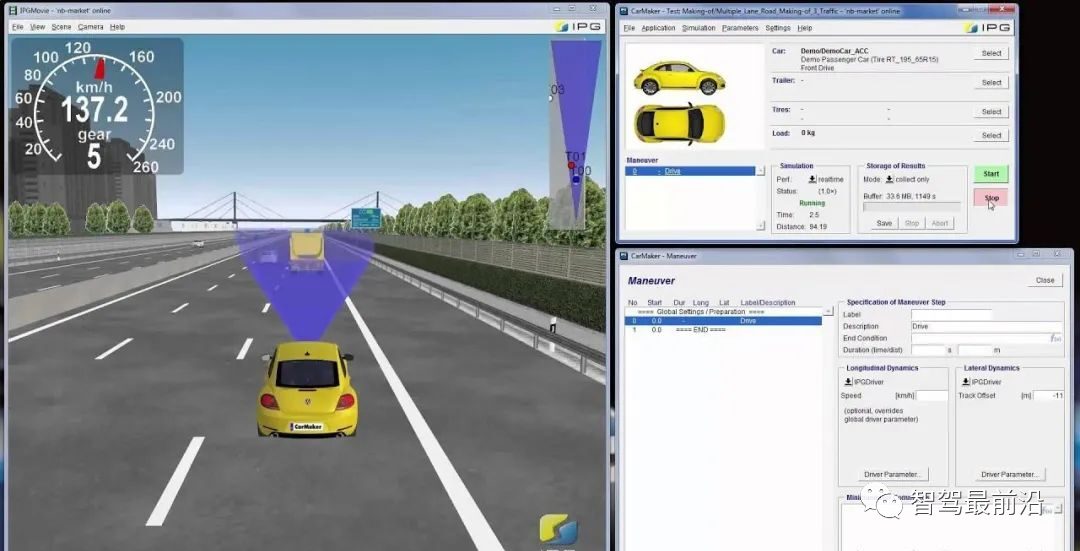
Carmaker, along with related TruckMaker and MotorcycleMaker, is a dynamics, ADAS, and autonomous driving simulation software launched by German IPG Company. Carmaker is primarily an excellent dynamics simulation software, providing precise vehicle body models (engine, chassis, suspension, transmission, steering, etc.). Furthermore, Carmaker has created a closed-loop simulation system that includes vehicles, drivers, roads, and traffic environments.
IPGRoad: can simulate various forms of roads, including multi-lane and intersections, and can generate conical, cylindrical, and other forms of obstacles through a configured GUI. It allows arbitrary definition of road geometries and surface conditions (roughness, roughness).
IPGTraffic: a traffic environment simulation tool, provides rich traffic object models (vehicles, pedestrians, road signs, traffic lights, road construction buildings, etc.). It can simulate real traffic environments. Test vehicles can recognize traffic objects and trigger actions accordingly (e.g., speed limit signs can trigger the vehicle to slow down).
IPGDriver: an advanced, self-learning driver model. It can control vehicles under various driving conditions, performing operations such as starting uphill, parking in a garage, and counter-steering. It can adapt to vehicle power characteristics (drive type, transmission type, etc.), road friction coefficients, wind speed, traffic conditions, and adjust driving strategies.
CarMaker, as a platform software, can integrate with many third-party software, such as ADAMS, AVL Cruise, rFpro, etc., leveraging the advantages of each software for co-simulation. At the same time, CarMaker’s accompanying hardware provides numerous board interfaces, facilitating HIL testing with ECUs or sensors.
PreScan
PreScan is an ADAS testing simulation software developed by TassInternational, acquired by Siemens in August 2017. PreScan is a simulation platform consisting of a GUI-based preprocessor for defining scenes and an execution environment for running scenes. Engineers use MATLAB and Simulink as the main interface to create and test algorithms. PreScan can be used for applications ranging from Model-in-the-Loop (MIL) controller design to real-time testing using Software-in-the-Loop (SIL) and Hardware-in-the-Loop (HIL) systems.
PreScan can operate in open-loop, closed-loop, offline, and online modes. It is an open software platform with a flexible interface that can connect to third-party vehicle dynamics models (e.g., CarSIM and dSPACE ASM) and third-party HIL simulators/hardware (e.g., ETAS, dSPACE, and Vector).
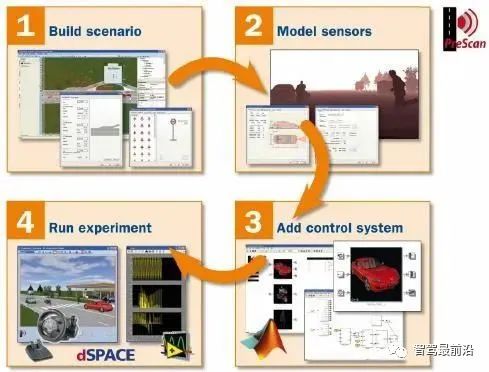
PreScan consists of several modules and is mainly divided into four steps: building scenes, adding sensors, adding control systems, and running simulations.
-
Scene building: PreScan provides a powerful graphical editor, allowing users to build rich simulation scenes using road segments, including traffic signs, trees, and a basic component library of buildings, including motor vehicles, bicycles, and pedestrian traffic participants. Users can modify weather conditions (e.g., rain, snow, and fog) and light sources (e.g., sunlight, headlights, and streetlights). The new version of PreScan also supports importing high-precision maps in OpenDrive format to create more realistic scenes.
-
Adding sensors: PreScan supports a wide variety of sensors, including ideal sensors, V2X sensors, LiDAR, millimeter-wave radar, ultrasonic radar, monocular and binocular cameras, and fisheye cameras. Users can add them according to their requirements.
-
Adding control systems: Control models can be established through MATLAB/Simulink, or closed-loop control can be performed with third-party dynamics simulation models (e.g., CarSim, VI-Grade, dSpace ASM vehicle dynamics models).
-
Running experiments: The 3D visualization viewer allows users to analyze experimental results while providing image and animation generation capabilities. Additionally, interfaces using ControlDesk and LabView can be used to automate the running of experimental batches and conduct hardware-in-the-loop simulations.
PTV Vissim
Vissim is a world-leading microscopic traffic flow simulation software provided by the German company PTV. Vissim can easily construct various complex traffic environments, including highways, large roundabouts, and parking lots, and can also simulate interactions between motor vehicles, trucks, rail traffic, and pedestrians in a simulation scene. It is an effective tool for planning and evaluating urban and suburban traffic facilities and can also simulate the impact of localized emergency situations and the evacuation of large numbers of pedestrians.
Vissim’s simulations can achieve high precision, including microscopic individual following behaviors and lane-changing behaviors, as well as group cooperation and conflicts. Vissim has built-in various analytical methods that can obtain multiple specific data results under different conditions and provide intuitive understanding from a high-quality 3D visualization engine. Autonomous driving algorithms can also be tested using simulated high-dynamic traffic environments by accessing Vissim.
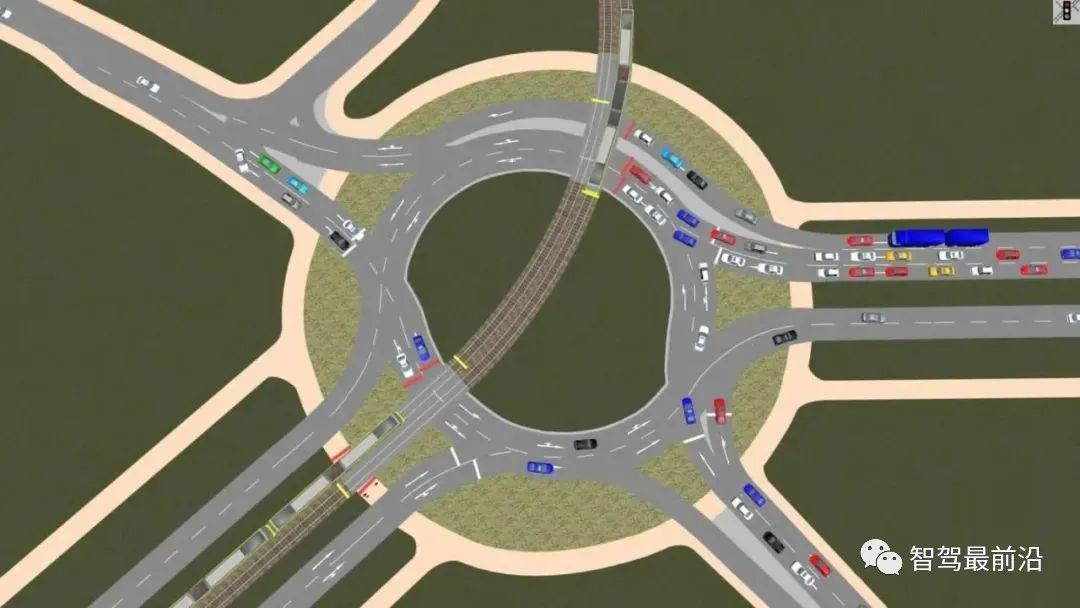

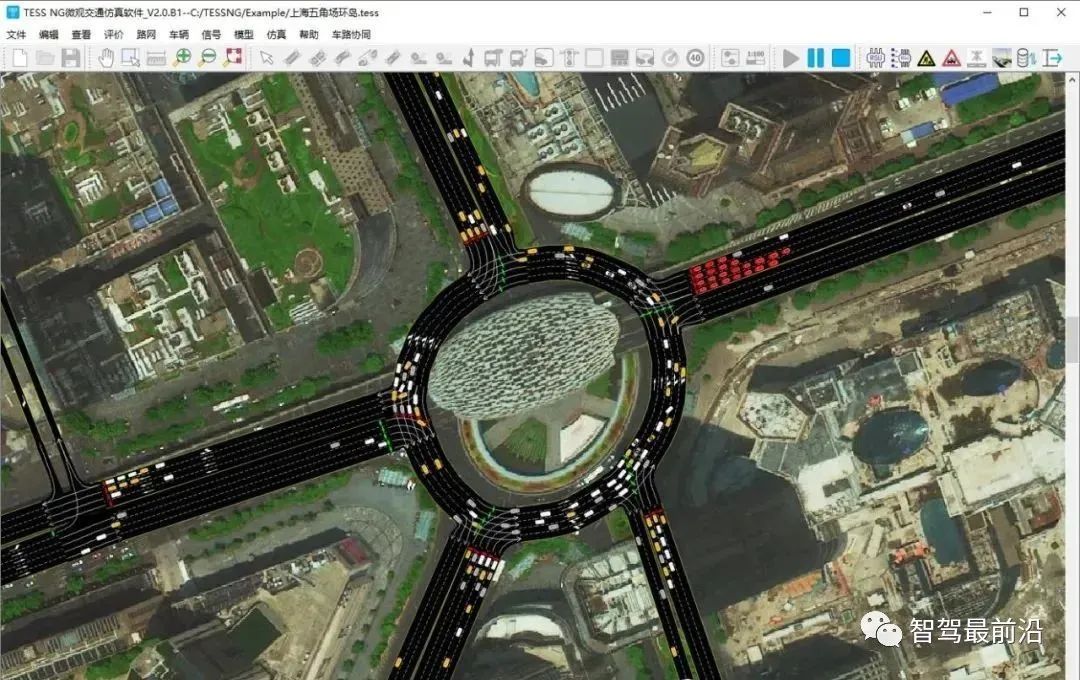
TESS NG
TESS simulation system is the first generation road traffic simulation system developed by Professor Sun Jian of Tongji University in 2006. Since then, over ten years, Professor Sun Jian’s research group has conducted more than 100 model innovations and simulation system application practices targeting the characteristics of mixed traffic flow operation in China. The main functions of the TESS NG microscopic traffic simulation system include: full traffic scene simulation, multi-mode traffic simulation, intelligent transportation system simulation, visual evaluation, secondary development interface, and support for 3D scene display. At the same time, TESS NG can be integrated with urban traffic brains, traffic control systems, computable road networks (such as OpenDrive, OpenStreetMap, etc.), and can also be integrated with driving simulators, BIM/CIM systems, and intelligent vehicle virtual testing tools to achieve cross-industry applications. Users can also achieve more cross-industry applications through customized services.
SUMO
SUMO is an open-source microscopic continuous traffic flow simulation software developed by the German Aerospace Center. It comes with a traffic simulation road network editor, allowing users to add roads, edit lane connections, handle intersection areas, and edit signal light timing through interactive editing. It can also convert road networks from Vissim, OpenStreetMap, and OpenDrive through a separate conversion program. Users can specify the route for each vehicle by editing route files or using parameters to generate routes randomly. During operation, it can handle continuous traffic simulation needs for several square kilometers and tens of thousands of vehicles simultaneously, while also providing a real-time display of traffic simulation results based on OpenGL visualization.
Additionally, SUMO provides convenient C++ and Matlab interfaces, allowing for flexible co-simulation with third-party simulation programs. SUMO is primarily used for traffic flow, timing, prediction, and other simulations in the traffic field, and has recently begun to be applied in autonomous driving simulations, providing a random complex dynamic environment for autonomous driving algorithms.
VIRES VTD
VTD (Virtual Test Drive) is a complete modular simulation toolchain developed by the German company VIRES for ADAS, active safety, and autonomous driving. VIRES was acquired by MSC Software Group in 2017. VTD currently runs on Linux platforms, covering functions such as road environment modeling, traffic scene modeling, weather and environmental simulation, simple and physically realistic sensor simulation, scene simulation management, and high-precision real-time rendering. It supports the entire development process from SIL to HIL and VIL, and its open modular framework allows for convenient co-simulation with third-party tools and plugins. VIRES is also a major contributor to the widely used autonomous driving simulation open formats OpenDrive, OpenCRG, and OpenScenario, with VTD’s functions and storage relying on these open formats. The simulation process of VTD mainly consists of three steps: road network construction, dynamic scene configuration, and simulation execution.
1) VTD provides a graphical interactive road network editor (RoadNetwork Editor, ROD), allowing users to build complex road simulation environments with multiple types of lanes while synchronously generating OpenDrive high-precision maps.
2) In dynamic scene establishment, VTD provides a graphical interactive scene editor (ScenarioEditor), allowing users to add traffic bodies with user-defined behavior controls based on OpenDrive or continuous traffic flows running in specific areas.
3) Whether SIL or HIL, real-time or non-real-time simulation, single-machine or high-performance computing environments, VTD provides corresponding solutions. VTD can simulate real-time high-quality lighting effects, road reflections, vehicle rendering, weather rendering for rain, snow, fog, and sensor imaging rendering, as well as visual effects from headlights.
rFpro
rFpro is a British company founded in 2008, initially as an internal track reconstruction and simulation project for an F1 team, which set high requirements for speed, real-time performance, and accuracy from the beginning. rFPro uses high-precision phase-shift laser radar scanning data to create road surfaces and shoulders, generating high-resolution digital models with a resolution of 1 cm, while using TOF laser radar to scan streets and scenes, providing virtual scenes that closely match real environments for dynamic simulation, ADAS, and autonomous driving testing. rFpro has created numerous high-precision virtual scenes for tracks and test sites, including F1, NASCAR, IndyCar, etc.
In dynamic scene simulation, rFpro can connect with SUMO or Vissim to generate continuous traffic flows to fill the entire scene, or co-simulate with Carmaker to provide more realistic sensor and road surface inputs for Carmaker’s test scenarios. rFpro also provides a physics-based lighting and weather system that can effectively simulate changes in daylight and weather conditions such as rain and fog.

Cognata
Cognata is an Israeli autonomous driving simulation startup founded in 2016, completing $18.5 million in Series B funding at the end of 2018. Cognata recreates cities on its 3D simulation platform using a combination of artificial intelligence, deep learning, and computer vision, providing customers with various simulated real-world test driving scenarios.
Cognata’s technology is mainly divided into three aspects: in static environments, Cognata’s TrueLife3DMesh engine uses computer vision and deep learning algorithms to automatically generate virtual simulation environments, including buildings, roads, lane markings, and traffic signs based on maps and satellite images. In dynamic simulation, Cognata builds accurate and scalable traffic simulation models and weather lighting models based on historical street traffic data, simulating various vehicles and pedestrians in real environments. The overall virtual simulation engine combines static and dynamic simulation models, simulating the interactions between sensors and various changes in the simulated environment, providing a complete feedback loop for the autonomous driving system to be tested.
Cognata’s simulation technology is supported by NVIDIA DGX Station, and in March 2019, Cognata announced a partnership with NVIDIA to utilize its powerful computing capabilities to simulate multiple virtual vehicles for large-scale testing in virtual environments.
RightHook
RightHook is a startup company based in California, USA, providing simulation solutions for the autonomous driving industry. RightHook offers a complete set of toolchains, including RightWorld, RightWorldHD, and RightWorldHIL. RightWorld provides a process to automatically reconstruct virtual scenes with rich details from high-precision maps, along with an easy-to-use test case creation process. After case creation, AI algorithms can organically expand the cases. RightWorld also includes deterministic intelligent traffic simulation models containing vehicles, pedestrians, and bicycles.
RightWorldHD simulates dynamics, weather, time changes, and sensors (including cameras, Lidar, Radar, IMU, and GPS), while supporting rich interfaces, including NVIDIA DriveWorks, LCM, and ROS. RightWorldHIL provides support for HIL testing that mixes software, algorithms, and hardware.

ParallelDomain
ParallelDomain is a startup company founded in California in 2017. At the end of 2018, ParallelDomain received investment from Toyota. ParallelDomain is dedicated to automatically generating high-quality virtual environments, and its developed software can automatically generate the required test urban blocks in a short time.
The ParallelDomain platform uses real-world map data, can accept various map formats, and uses additional elements in areas where the map does not provide sufficient data, relying on a procedural generation engine to automatically generate a virtual world. A significant feature is that all elements of the virtual world are adjustable and programmable, such as lane numbers, terrain types, mountain locations, and road curvature. ParallelDomain also provides dynamic traffic scenarios for automatically generated scenes.

51Sim-One
51Sim-One is an integrated autonomous driving simulation and testing platform independently developed by 51VR, combining multi-sensor simulation, traffic flow and agent simulation, perception and decision-making simulation, and autonomous driving behavior training. This simulation platform is based on physical characteristic mechanism modeling, featuring high precision and real-time simulation, used for the R&D, testing, and validation of autonomous driving products, allowing users to quickly accumulate autonomous driving experience, ensuring product performance safety and reliability, and improving product R&D speed while reducing development costs.
In scene construction, users can quickly create OpenDrive-based road networks from scratch using WorldEditor, or restore road network information using real data such as point cloud data and map images. It supports importing existing OpenDrive format files for secondary editing, ultimately allowing 51Sim-One to automatically generate the required static scenes. Users can freely configure global traffic flows, independent traffic agents, opponent vehicles, pedestrians, and other elements in the scene to construct dynamic scenes, combined with the simulation of lighting, weather, and other environments to present a rich and varied virtual world.
In sensor simulation, 51Sim-One supports multi-channel simulation of general or customized sensor types, meeting the testing and training needs for perception system algorithms, while also supporting various hardware-in-the-loop testing requirements. For camera simulation, 51Sim-One provides annotated image datasets such as semantic segmentation maps, depth maps, and 2D/3D bounding boxes, simulating monocular, wide-angle, and fisheye cameras. For radar simulation, it can provide raw data of LiDAR point clouds, annotated point cloud data, bounding box data for identified objects, and target-level millimeter-wave radar detection data.
Pilot-DGaiA
GaiA is an autonomous driving and ADAS development verification simulation tool developed by Peidai (Shanghai). It can reproduce complex roads by integrating road network databases and realistically recreate driving environments using an environmental building model library. GaiA provides rich C++ and Matlab interfaces, suitable for various vehicles and systems to be tested. GaiA can generate numerous traffic participants and manually or automatically set their traffic behavior planning, even changing the aggressiveness of driving behavior. GaiA also provides high-fidelity environmental perception sensors, including millimeter-wave radar, LiDAR, cameras, etc.

Metamoto
Metamoto was founded in 2016 and is a Silicon Valley startup. Metamoto provides “simulation as a service” for autonomous driving companies, attempting to help them achieve iterative development through an accelerated feedback loop. Its products mainly consist of three parts: designer, cloud platform, and analyzer. The designer can be used to add road networks, other environmental vehicles, pedestrians, and traffic lights to create a test scene, generating multiple test cases by controlling various parameter ranges.
The cloud platform is responsible for scheduling hardware resources based on the cases to be tested, running test cases in parallel, and generating a large amount of test data. After the run is complete, the analyzer can replay the simulated sensor data and various simulation information of the vehicles for debugging the autonomous driving system. Metamoto supports precise simulation of various sensors, including LiDAR, cameras, millimeter-wave radar, ultrasonic radar, GPS, IMU, etc., capable of reacting differently to different materials. A notable feature of Metamoto is the provision of a fast method to adjust and cover the parameters of the tests, allowing for a large number of tests to be run in a short time with the support of the cloud platform, effectively improving testing efficiency.
ESIPro-Sivic
ESI Group’s sensor simulation analysis solution Pro-SiVIC can help manufacturers in the transportation industry conduct virtual testing of the operating performance of various onboard or airborne perception systems, accurately reproducing factors such as lighting conditions, weather, and other road users.
Pro-SiVIC can be used to establish high-fidelity, realistic 3D scenes and achieve real-time interaction in the scenes for simulation analysis, reducing the need for physical prototypes. Customers can quickly and accurately simulate the performance of various embedded systems under typical and extreme operating environments. It can provide sensor models based on various technologies, such as cameras, radar, LiDAR (laser scanners), ultrasonic sensors, GPS, odometers, and communication devices. For example, in the automotive industry, Pro-SiVIC provides multiple environmental directories, offering representative different roads (urban roads, highways, and rural roads), traffic signs, and lane markings.

NVIDIADrive Constellation
NVIDIADrive Constellation is an autonomous driving simulation platform launched by NVIDIA, primarily consisting of two parts in hardware: one is the DGX server running the DriveSim software system, relying on the powerful graphical computing capabilities of DGX to realistically simulate lighting, nighttime, and various weather changes in real environments; the other server is equipped with the DRIVE AGX Pegasus onboard computer, used to run the full-stack algorithms for autonomous driving, forming a complete HIL simulation closed loop.

PanoSim
PanoSim is a simulation software platform that integrates complex vehicle dynamics models, three-dimensional driving environment models, automotive traffic models, onboard environmental sensor models (cameras and radar), wireless communication models, GPS and digital map models, automatic generation of Matlab/Simulink simulation environments, and graphical and animation post-processing tools. It is based on physical modeling and numerical simulation principles that balance precision and efficiency, realistically simulating various environments and conditions for automotive driving, and establishing high-precision camera, radar, and wireless communication models based on geometric and physical modeling concepts to support the R&D, testing, and validation of automotive dynamics and performance, automotive electronic control systems, intelligent driving assistance and active safety systems, environmental sensing and perception, and autonomous driving technologies and products.
PanoSim not only includes complex vehicle dynamics models, chassis (brakes, steering, and suspension), tires, drivers, and powertrains (engines and transmissions) models but also supports modeling and simulation analysis for large, medium, and small passenger cars with various typical drive types and suspension forms. It provides three-dimensional digital virtual testing scene modeling and editing functions, supporting modeling and editing of road and road textures, lane markings, traffic signs and facilities, weather, and nighttime conditions for automotive driving environments.
AAI
AAI (Automotive Artificial Intelligence) is a startup founded in Berlin in 2017. AAI constructs a complex high-fidelity virtual environment based on high-precision maps, integrating traffic participants into the virtual simulation environment using artificial intelligence technology, and utilizing driving behavior data from real life to train participant behaviors using machine learning algorithms, thus generating profiles of aggressive drivers, mild drivers, and defensive drivers, aiming to replicate the real world and realistically simulate all road users and environmental factors. AAI supports various sensor simulations and also provides analyzers for in-depth analysis of data generated from simulations.

AirSim
AirSim is an open-source research project developed by Microsoft Research, based on the Unreal Engine, for drones and autonomous driving simulation. AirSim is implemented as a plugin for Unreal Engine, fully utilizing Unreal Engine’s capabilities to create highly realistic virtual environments, simulating shadows, reflections, and other real-world conditions, while the virtual environment can conveniently produce a large amount of labeled data, and it provides a simple and convenient interface for drones and autonomous driving algorithms to conduct extensive training. The main goal of AirSim is to serve as a platform for AI research, testing deep learning, computer vision, and end-to-end reinforcement learning algorithms for autonomous vehicles. The latest version of AirSim also provides a version for the Unity engine, adding support for LiDAR.

CARLA
CARLA is an open-source simulator developed under the guidance of the Computer Vision Center at the Autonomous University of Barcelona, designed for the development, training, and validation of autonomous driving systems. Like AirSim, CARLA is also developed based on Unreal Engine, using a server and multi-client architecture. In terms of scenes, CARLA provides open-source digital resources for creating scenes for autonomous driving (including city layouts, buildings, and vehicles) and several scenes built with these resources for autonomous driving testing and training. At the same time, CARLA can also use VectorZero’s road construction software RoadRunner to create scenes and accompanying high-precision maps, and provides a simple map editor. CARLA supports flexible configuration of sensors and environments, supporting multiple cameras, LiDAR, GPS, and other sensors, and can adjust lighting and weather conditions. CARLA provides simple automatic behavior simulation for vehicles and pedestrians, and also provides a complete set of Python interfaces to control vehicles, traffic lights, etc., for convenient co-simulation with autonomous driving systems, completing decision-making systems and end-to-end reinforcement learning training.

LGSVL Simulator
LGSVL Simulator is an open-source autonomous driving simulator developed by LG’s Silicon Valley lab based on the Unity engine. It integrates with the open-source autonomous driving platforms Autoware and Baidu Apollo. Users can annotate and export high-precision map formats that match the autonomous driving system based on 3D scenes created in Unity. It also provides support for sensor simulations, including LiDAR, millimeter-wave radar, GPS, IMU, and cameras, and can synchronously output raw results and ground truth of sensors.
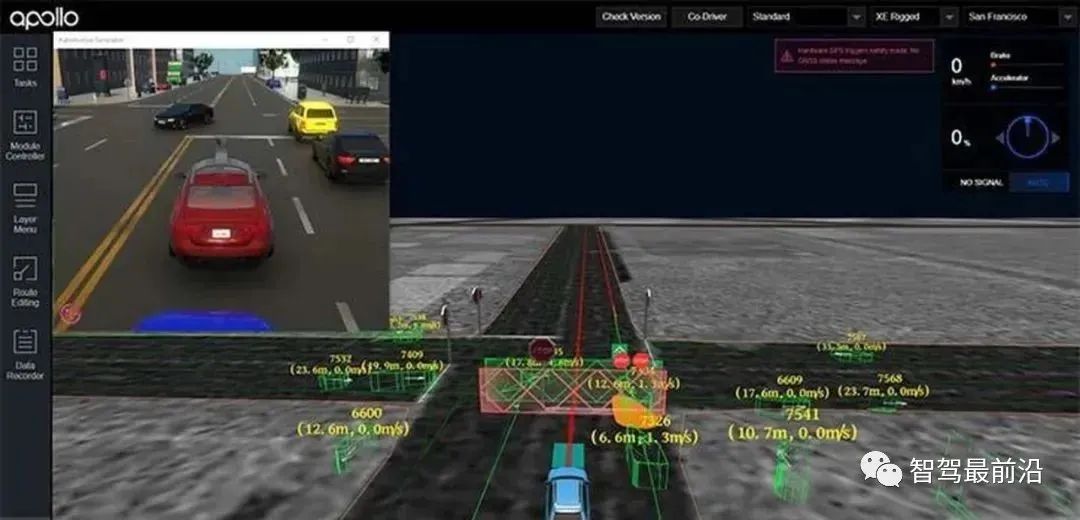
Baidu Apollo
The Baidu Apollo simulation platform is an important component of the Baidu Apollo platform, serving both to support the internal development and iteration of the Apollo system and to provide cloud-based decision system simulation services for developers in the Apollo ecosystem. The Apollo simulation platform is built on Baidu Cloud and Azure cloud services, allowing simulation testing using user-specified Apollo versions in the cloud. Apollo simulation scenes can be divided into Worldsim and Logsim. Worldsim consists of predefined roads and obstacles, serving as a simple and efficient unit test for autonomous driving vehicles, while Logsim consists of scenes extracted from road test data, reflecting the complex and variable obstacles and traffic conditions in actual environments. The Apollo simulation platform also provides a relatively complete scene discrimination system, evaluating autonomous driving algorithms from aspects such as traffic rules, dynamic behavior, and comfort.
Apollo has also established a partnership with Unity, developing a realistic virtual environment simulation based on Unity, providing a 3D virtual environment, and variations in roads and weather. Recently, Baidu has proposed a new data-driven approach for end-to-end simulation of autonomous driving: Enhanced Autonomous Driving Simulation (EADS). This method uses simulated traffic flow to enhance real-world images, creating photorealistic simulated scenes that resemble real-world renderings. Specifically, it suggests using LiDAR and camera scans of street scenes. The input data is decomposed into background, scene lighting, and foreground objects. At the same time, a new view synthesis technique is proposed, allowing viewpoint changes on static backgrounds. Foreground vehicles are equipped with computer-generated 3D models. Through accurately estimated outdoor lighting, 3D vehicle models, computer-generated pedestrians, and other movable entities can be repositioned and rendered back to the background image, creating realistic street scene images. Additionally, simulated traffic flow, synthesized object placement and movement, and capturing real-world vehicle trajectories that look natural and capture the complexity and diversity of real-world scenes are also proposed.

Waymo Carcraft
Representing the world’s leading level of Waymo’s autonomous vehicle, one of the core secrets is its Carcraft simulator, which is key to Waymo’s ability to drive billions of miles each year. At the beginning of Carcraft’s development, this system was only used visually to replay the situations of roadside vehicles on the road; later, it played an increasingly important role. Carcraft can test each new software version using replay data from real-world driving to verify algorithm improvements, discover new issues, and construct entirely new virtual scenes for testing. Every day, 25,000 virtual Waymo autonomous vehicles drive over 8 million miles in the simulator to solidify existing autonomous driving skills and test new skills. The greatest advantage of simulation testing is the ability to quickly repeat tests of scenarios that are rare but important in reality, such as five-way intersections and merging into roundabouts. The simulator allows the autonomous driving system many opportunities to practice specific scenarios to master corresponding skills. Additionally, in the simulator, modifications can be made to specific participants or traffic signals in a particular test scenario, adding extra pedestrians, thereby constructing a large number of derivative scenarios for more thorough testing of autonomous driving algorithms.
23. Tencent TAD Sim Simulation Platform
Tencent’s autonomous driving virtual simulation platform TAD Sim was designed from the outset to differ from traditional simulation systems, specifically designed and developed for autonomous driving testing and validation, with built-in centimeter-level high-precision maps, constructing a true digital twin system containing dynamic and static elements, testing the completeness of autonomous driving algorithms with ever-changing scenarios.

