
Recently, Xiaopeng Motors officially launched a new round of OTA upgrades for the P7 model, with the NGP automatic navigation assistance (public beta version) also being opened to users for the first time. The core of the NGP automatic navigation function is high-precision maps and high-precision positioning, but many people are unclear about what high-precision maps are. Today, we will unveil these sophisticated and professional terms and see what high-precision maps really are.

Previously, our colleagues conducted a detailed experience of the Xiaopeng P7 NGP function. Interested friends can click the image below to jump to the article.

Before understanding high-precision maps, I think it is necessary to first understand the history and iterations of electronic map navigation. We classify electronic map navigation into three generations based on functionality and usage.
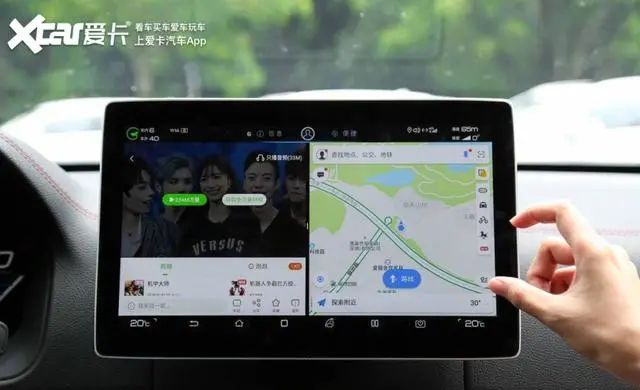
The first generation of electronic navigation mainly presents 2D flat maps. Some friends may remember that when using the initial navigation software, it was necessary to download the map data of various cities to the local device, and route planning was calculated by the local chip. It could complete the journey from point A to point B, but the calculation logic only considered distance and road attributes (national roads, provincial roads, ring roads, toll highways, etc.).
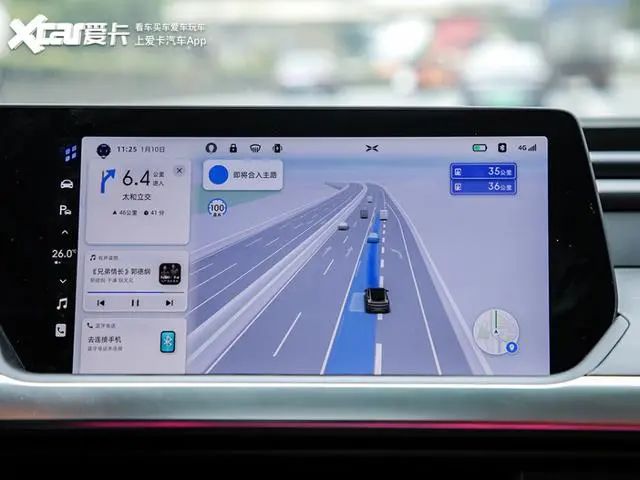
When electronic map navigation reached its second generation, which is widely used today, local data began to connect to the internet and gradually introduced big data and cloud computing. Similarly, when navigating from point A to point B, the navigation system considered more factors, such as whether the road was congested and whether to choose the shortest distance or the shortest time route. With the improvement of map accuracy, the navigation would also pop up road images and guide routes when passing junctions.

When electronic navigation reached the third generation, we began to talk about high-precision maps, which will be increasingly used in the automatic driving functions of vehicles.
Currently, most vehicles equipped with mainstream automatic driving functions are at the L2 level. Most vehicles use a front-mounted camera and millimeter-wave radar to confirm whether there are vehicles in the passable area directly in front of the vehicle. If there are vehicles, they will follow at a safe braking distance; if there are no vehicles, they will accelerate to the set cruising speed. This function cannot be achieved with existing ordinary low-density maps, as the current low-density map’s coordinate accuracy is about 5-10 meters, which cannot perfectly accommodate this.
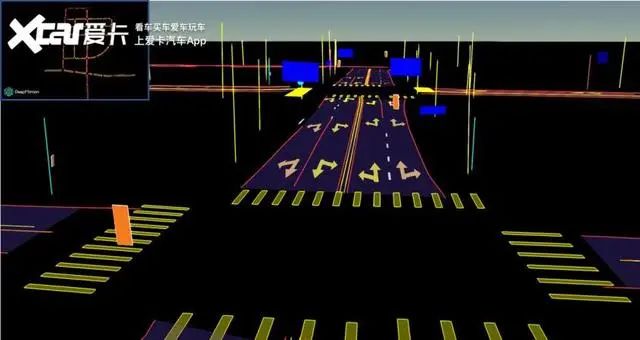
However, the absolute accuracy of high-precision maps is generally at the sub-meter level. Taking Gaode Map as an example, the absolute accuracy can reach within 10 centimeters, and the lateral relative accuracy is often even higher. High-precision maps not only have high-precision coordinates but also accurate road shapes, including data on each lane’s slope, curvature, heading, elevation, and tilt.

In addition, the lane markings between each lane, whether dashed, solid, or double yellow lines, the color of the lines, the road’s isolation belt, and even the arrows and text on the road will all be described. For automatic driving considerations, speed limits and recommended speeds for each lane also need to be provided. Elements such as pedestrian crossings, roadside billboards, isolation belts, speed limit signs, traffic lights, and roadside telephone stops, which we generally refer to as traffic participants, will also have their absolute geographic coordinates, physical dimensions, and characteristics included in the high-precision data.
How is this collected?
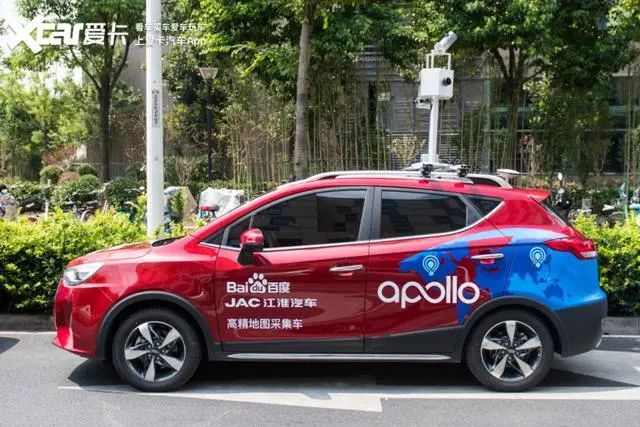

In some cities, you may have seen collection vehicles with large cameras and collection devices on top. These vehicles are responsible for the current mainstream high-precision map collection work. In addition to the visible wide-angle cameras, the collection devices on the roof also include gyroscopes and other equipment to detect road slope, curvature, heading, elevation, and tilt data.
After the collection vehicle gathers information, it draws vector maps, which undergo a series of accuracy overlay processes to be completed. In addition to conventional road collection, drone collection has also started to join the ranks of high-precision map creation. Previously, Zhonghaida and Jifei, along with Tianji Aviation, launched an integrated solution for aerial surveying and mapping called “Yitu,” which uses drones for surveying. Zhonghaida has the backing of Beidou satellites and had previously invested 36 million yuan to establish a joint venture with Wuhan Guangting (which has high-precision mapping qualifications) in 2016. However, currently, Zhonghaiting is 51% owned by SAIC. Moreover, SAIC has also partnered with Gaode to collaborate on high-precision maps, so in the future, SAIC has no worries regarding high-precision map applications.
What is the impact of high-precision maps on autonomous driving?
There was a story circulating online that Ford discovered during an autonomous driving test that each self-driving test vehicle in the same batch would slightly veer at a certain point on the lane, as if avoiding uneven ground. After research and physical inspection of the vehicles, it was found that the issue did not originate from the cars but from the map. The problem arose after the map had just been updated, and an incorrect value on the map caused a raised parameter at that avoidance point, while the ground was actually completely flat. Therefore, the accuracy of high-precision maps greatly affects the safety of future equipped autonomous driving and the richness of autonomous driving functions.
What are high-precision maps?
After discussing the principles and roles of high-precision maps, let’s take a look at which companies are currently involved in high-precision mapping and what their specialties are. We have compiled five companies, both domestic and international, listed in no particular order.
1. Waymo

Waymo is a self-driving company under Google, definitely one of the companies with the most advanced autonomous driving technology in the world. Waymo started creating maps for autonomous driving as early as 2009, and Alphabet officially spun it off on December 13, 2016, with John Krafcik as CEO. The name “Waymo” represents “A new way forward in mobility.” Currently, it meets the L4 level of autonomous driving in several cities in the United States.
Waymo’s high-precision map foundation is developed from Google Maps, with a strong data and technology background. Currently, the high-precision maps it produces are known to be used only for its self-driving and not as a commercial product. Its map collection method is through laser radar combined with navigation positioning systems, and it has a large fleet of mapping vehicles to create high-precision maps.
2. DeepMap

DeepMap was founded in 2016 in the United States, with a founding team that has strong backgrounds in Google Maps, Google Earth, Apple Maps, and Baidu’s autonomous vehicles. DeepMap’s technical route is to provide complete solutions for high-precision maps. Its map and positioning modules have been applied to various vehicle models and fleets for autonomous driving training. In July 2018, it received approximately $60 million in investments from Alibaba, Didi, and BAIC.
DeepMap’s main method of collecting map data is through multi-sensor fusion solutions using laser radar and combined navigation positioning systems, employing a crowdsourcing model for data collection. Its developed software can convert data collected from crowdsourced vehicle sensors into detailed maps. DeepMap also provides software that can be embedded in vehicles to solve issues related to positioning, data updates, route planning, and data collection. Its high-precision maps have three-dimensional centimeter-level road information and can provide real-time road dynamic information.
3. Four-Dimensional Map New

Four-Dimensional Map New currently belongs to the first tier of high-precision map companies in China. In 2013, it began technical research and exploration in the field of autonomous driving maps. In 2015, it established the intelligent map division, officially starting the product development and commercialization of autonomous driving maps aimed at Level 3 and above. Now, Four-Dimensional Map New has mastered a complete product capability solution for autonomous driving maps from data collection, automated mapping to crowdsourced updates and rapid iteration.
At the beginning of 2019, it signed a license agreement for autonomous driving maps and related services with BMW, which will provide autonomous driving map products and services for the new platform of BMW Group brands to be mass-produced and launched in China from 2021 to 2024. It has since collaborated with a series of OEMs, including Aiways and Great Wall Motors, to provide them with hardware and software services and solutions for autonomous driving.
4. Gaode Map

Gaode Map was acquired by Alibaba in 2014 and began research and development of autonomous driving maps in the same year. In October 2016, Gaode announced that it would provide autonomous driving map data free of charge to partners in the automotive industry during the development and testing of autonomous vehicles. In August 2017, Gaode collaborated with Qianxun Location to develop autonomous driving maps and high-precision positioning.
Currently, Gaode has completed the collection of over 320,000 kilometers of high-precision autonomous driving maps. The vehicles specifically used for HAD-level autonomous driving map collection mainly collect road information through two laser radars and four cameras, with an accuracy of up to 10 cm. Gaode collaborates with precision location service provider Qianxun Location to provide a comprehensive solution of “autonomous driving maps + high-precision positioning.” Gaode has cooperated with Bosch, NVIDIA, and Cadillac to develop positioning layers and data update solutions for autonomous driving maps. Its high-precision autonomous driving maps have been applied in Cadillac’s SuperCruise system.
5. Ditu Technology

Unlike other BAT-acquired mapping companies, Ditu is a wholly-owned subsidiary of Beijing Xiaojun Technology Co., Ltd. After obtaining a testing license in 2017, this company began low-profile mapping work.
Unlike other companies, in addition to the crowdsourcing model, Ditu relies on Didi’s operational vehicles to collect road information from various places, resulting in an unimaginable amount of data. The configuration of crowdsourced vehicles will determine which data is returned and which map elements are updated. In the future, Didi will have the capability to participate in defining vehicles, combining autonomous driving functions with map surveying to achieve the ultimate ideal update model.
Summary: Faced with limited testing licenses, many internet companies and car manufacturers in China are participating through self-research or acquisition. Even overseas mapping companies can find traces of Chinese enterprises investing, highlighting the importance of high-precision maps for the future of automobiles. After all, autonomous driving technology is no longer just a concept and trend; it is gradually transitioning to a basic configuration for future models. Therefore, whoever possesses high-precision maps will be able to enhance autonomous driving technology. Fortunately, currently, China’s participation in high-precision maps and autonomous driving business exceeds 80%, so in the future, we can expect more intelligent and advanced autonomous driving technology in Chinese brand vehicles.
>> Recent News
-
Regarding the online reporting of the 2020 annual data for the economic operation monitoring of the geographic information industry.
-
Notice on the application for the top 100 enterprises in the geographic information industry and the most dynamic small and medium-sized enterprises in 2021.
-
Two Sessions | Zhao Dachun: Promote the 5G + Beidou high-precision positioning system to better empower various industries.
-
List of universities offering the national-level first-class undergraduate program in Geographic Information Science.
-
Shandong establishes a monthly release mechanism for remote sensing imagery.
-
The General Office of the CPC Central Committee and the General Office of the State Council issued the “Action Plan for Building a High-Standard Market System.”
-
The new path for the surveying and mapping geographic information industry in the new era.

China Geographic Information Industry Association WeChat Official Account
—— Follow the industry highlights and understand the association dynamics ——
WeChat ID: dixinxiehui
Email:[email protected]
Website:www.cagis.org.cn