Obstacle Avoidance Car Based on 51 Microcontroller PART 010151 Minimal System Board
PART 010151 Minimal System Board
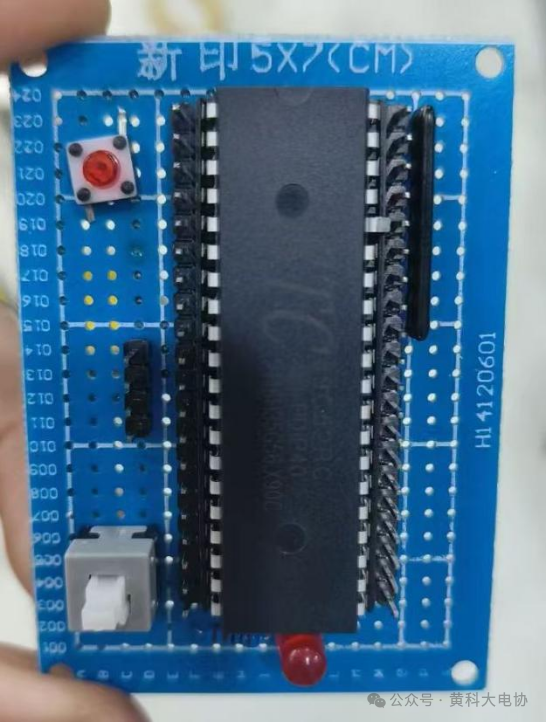 For the 51 microcontroller, simply add a crystal oscillator between XTAL1 and XTAL2, and connect a capacitor to ground on each side of the crystal. The microcontroller has an inverter inside, and with the capacitor and crystal, it can oscillate. Reset is done through a switching power supply, and the microcontroller’s serial port can be connected to a TTL to USB module for programming.
For the 51 microcontroller, simply add a crystal oscillator between XTAL1 and XTAL2, and connect a capacitor to ground on each side of the crystal. The microcontroller has an inverter inside, and with the capacitor and crystal, it can oscillate. Reset is done through a switching power supply, and the microcontroller’s serial port can be connected to a TTL to USB module for programming.
 02L298N
02L298N
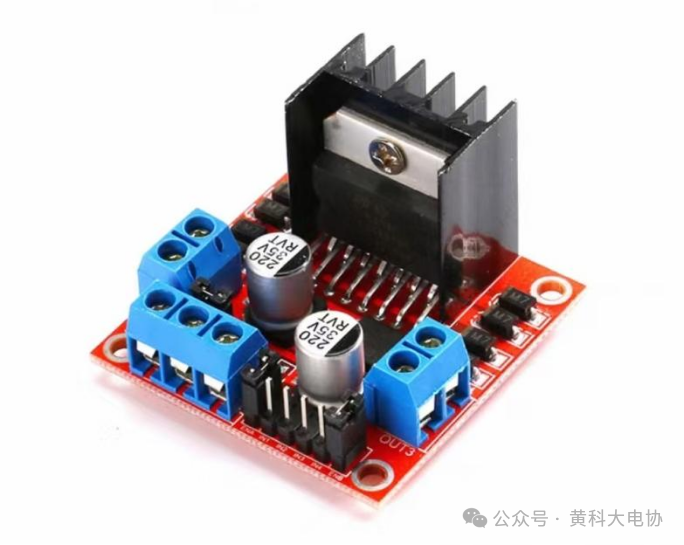 The L298N is a dedicated driver integrated circuit that can increase output current and enhance output power. Its output current is 2A, with a maximum current of 4A and a maximum operating voltage of 12V. Its input can be directly connected to the microcontroller, making it easy to control. When driving a DC motor, it can directly control a stepper motor and achieve both forward and reverse rotation. By inputting PWM signals to the ENA and ENB pins, the motor speed can be controlled, and this functionality can be achieved by changing the logic levels at the input.
The L298N is a dedicated driver integrated circuit that can increase output current and enhance output power. Its output current is 2A, with a maximum current of 4A and a maximum operating voltage of 12V. Its input can be directly connected to the microcontroller, making it easy to control. When driving a DC motor, it can directly control a stepper motor and achieve both forward and reverse rotation. By inputting PWM signals to the ENA and ENB pins, the motor speed can be controlled, and this functionality can be achieved by changing the logic levels at the input.
 03
03
Infrared Module

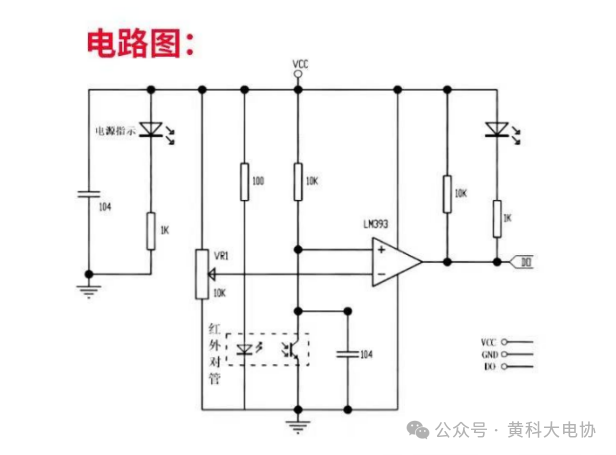 This sensor module has strong adaptability to ambient light. It features a pair of infrared emitters and receivers. The emitter emits infrared light at a certain frequency, and when the detection direction encounters an obstacle (reflective surface), the infrared light is reflected back and received by the receiver. After processing through a comparator circuit, the green indicator light will turn on, and the signal output interface will output a digital signal (a low-level signal). The detection distance can be adjusted using a potentiometer, with an effective range of 2~30cm and a working voltage of 3.3V-5V. The detection distance of this sensor can be adjusted via the potentiometer, and it has characteristics such as low interference, easy assembly, and convenient use, making it widely applicable in robot obstacle avoidance, obstacle avoidance cars, assembly line counting, and many other scenarios.
This sensor module has strong adaptability to ambient light. It features a pair of infrared emitters and receivers. The emitter emits infrared light at a certain frequency, and when the detection direction encounters an obstacle (reflective surface), the infrared light is reflected back and received by the receiver. After processing through a comparator circuit, the green indicator light will turn on, and the signal output interface will output a digital signal (a low-level signal). The detection distance can be adjusted using a potentiometer, with an effective range of 2~30cm and a working voltage of 3.3V-5V. The detection distance of this sensor can be adjusted via the potentiometer, and it has characteristics such as low interference, easy assembly, and convenient use, making it widely applicable in robot obstacle avoidance, obstacle avoidance cars, assembly line counting, and many other scenarios.
 PART 02
PART 02
0
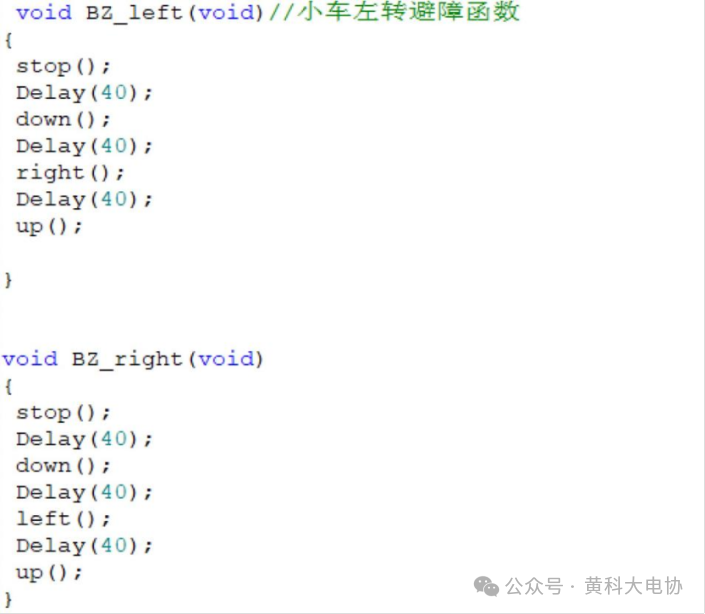
1Defining Wheel Movement and Steering


 02
02
Controlling the Speed Levels of the Car


 03
03
Timer Module


 04Car Obstacle Avoidance
04Car Obstacle Avoidance

 05Calling the Main Function
05Calling the Main Function
 END
END
Scan to follow
Electronic Association
Editor: Li Siqian Hou Ruixue
Typesetting: Wu Baohui
Review: Zhang Bin
