1.Self-Propelled, Light-Controlled, Magnetically Navigated Micro Robots for Polymer Degradation
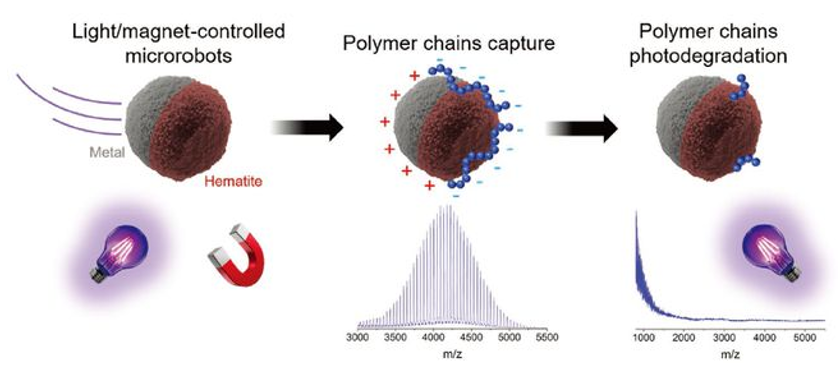
Professor Martin Pumera’s team at Brno University of Technology has designed and developed self-propelled, light-driven, magnetically navigated hematite/metal dual-sided micro robots capable of degrading polymer chains in water. These micro robots exhibit fuel-free self-propulsion characteristics under UV light and feature programmable control for on/off switching and movement direction. Researchers also evaluated and explained the speed differences of the micro robots under varying fuel concentrations and metal coatings through electrochemical measurements, demonstrating the micro robots’ ability to photodegrade polymer materials using high molecular weight (Mw 4000) polyethylene glycol (PEG). The active motion, electrostatic capture capability, excellent charge separation at the hematite/metal interface, and catalyzed photo-Fenton reaction of the micro robots enable effective photodegradation of PEG chains.

2.Electro-Controlled Adhesive Hydrogels for Climbing Robots by Professor Dai Lizong’s Team at Xiamen University
Professor Dai Lizong’s team at Xiamen University has proposed a new approach to electrochemical strategies for controlling polymer adhesion performance, based on the interdisciplinary integration of polymers and electrochemistry, as well as materials and mechanical engineering. By applying a stimulus voltage between 3.0 and 4.5 V, they achieved rapid, reversible, cyclic adhesion/detachment of borate ester polymer hydrogels to conductive substrates, establishing a new mode of programmable climbing for robots on inverted and vertical surfaces. This innovation allows walking and wheeled robots to perform controlled movements on vertical and inverted stainless steel or copper surfaces, marking a significant advancement in climbing robot design that overcomes the limitations of high engineering technical barriers.

3.Georgia Tech’s “Aggregated Particle Robots”
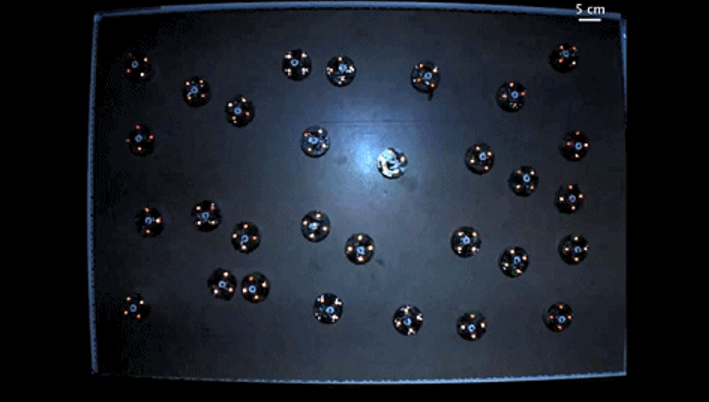
The research team at Georgia Tech recently proposed a new control system where autonomous, self-braking entities derive macroscopic behavior solely from local interactions, without requiring strong hardware or traditional computational methods based on local interaction physics. The findings were published in Science Advances under the title “Programming Studies of Active Viscoelastic Particle Materials with Mechanically Induced Phase Transitions.” The researchers first designed a theoretical abstraction of a “self-organizing particle system (SOPS)” and rigorously analyzed specific and simple distributed algorithms to achieve specific goals while ensuring system robustness and error tolerance. Based on this, they constructed a new system that includes “aggregated particle robots” with basic activity capabilities, equipped only with fundamental light sensors to test whether theoretical predictions can be realized in real-world damping-driven systems.
 4.Soft Robot Control System with Adjustable Stiffness
4.Soft Robot Control System with Adjustable Stiffness
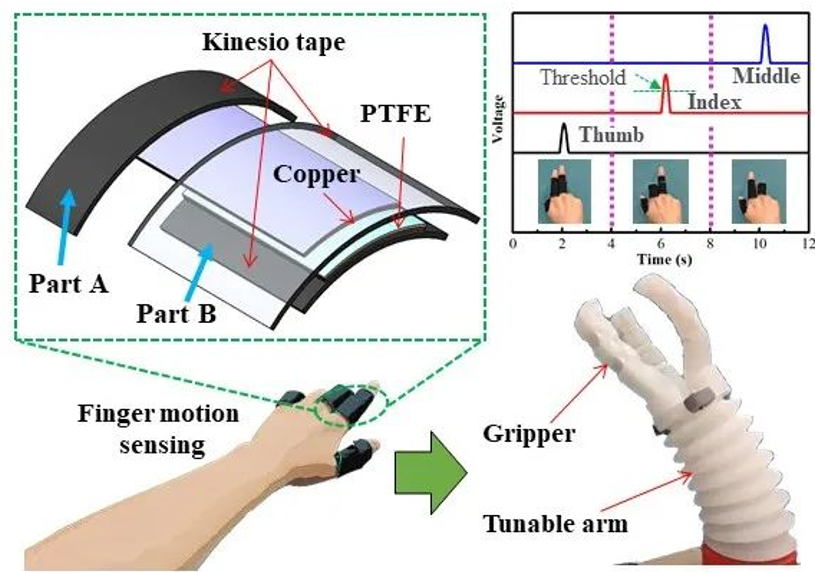
Professor Cao Changyong’s team at Michigan State University has designed a control system for soft robots that enables safe human-robot interaction with variable stiffness. This system employs multi-material and biomimetic design, utilizing tendon (cable) drive methods combined with the phase change principles of low melting point alloys to achieve rapid response, precise control, multi-degree-of-freedom movement, and adjustable stiffness. The soft robotic arm can flexibly bend in all directions under the traction of three evenly distributed cables. The arm is uniformly equipped with low melting point alloy tubes, where the coils wrapped under electrical current generate Joule heat to control the liquid-solid state change of the alloy, thereby altering the overall stiffness of the soft arm. The soft robot fingers are designed with a dual-side flexible hinge structure, allowing for bidirectional bending through a single micro motor. The flexible hinge is filled with soft porous silicone to effectively prevent interference between the driving cables and the external environment, without affecting its bending performance.

5.Garbage Sorting Robot, Sorting 100 Times Per Second with 95% Accuracy
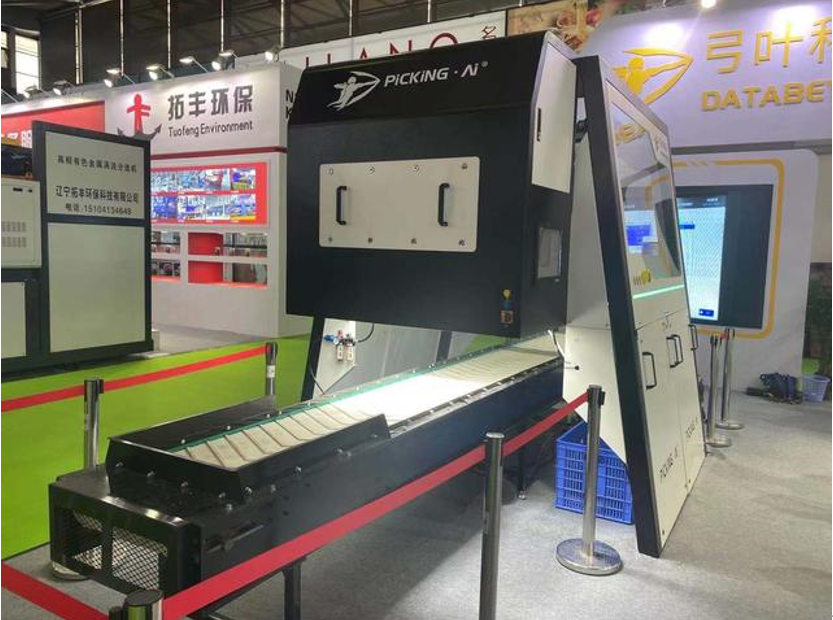

Recently, Guangdong Gongye Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Gongye Technology) showcased its AI garbage sorting robot PiCKiNGAi at the 22nd China Environmental Protection Expo. According to Gongye Technology, this fully self-developed garbage sorting robot can operate continuously 24/7, sorting at a speed of 90-100 times per minute, making it the fastest garbage sorting robot in the world. Founder Mo Zhuoya stated that the company’s image recognition database has reached hundreds of millions of images. This robot can pick out recyclable metals, plastics, paper, etc., from sorted dry waste, achieving an accuracy rate of over 95%. Mo Zhuoya claims that one garbage sorting robot can replace about eight workers and can categorize waste into six to eight categories, making it more detailed and accurate than manual sorting.

6.Saab Seaeye Underwater Robot to be Used in Taiwan Wind Farm
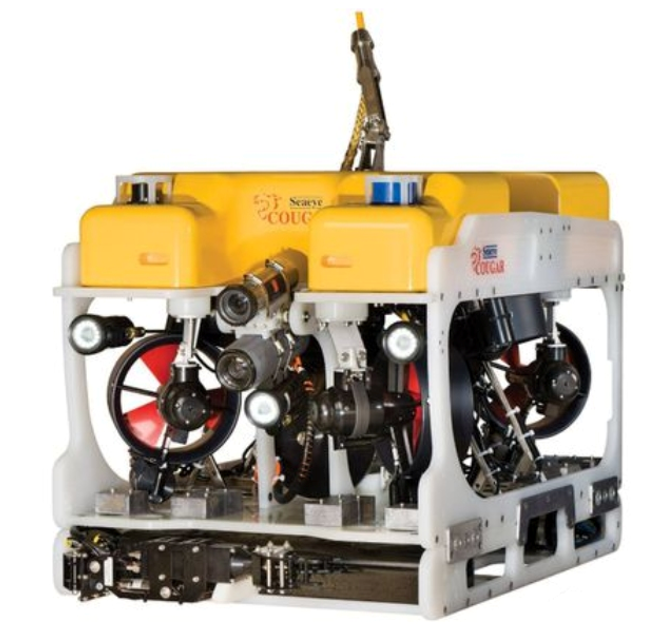

The Metal Industry Research and Development Center (MIRDC) in Taiwan will use underwater remotely operated robots to assist in the development and maintenance of turbine underwater structures. The Seaeye small 300m Cougar XT compact robot is specifically designed for harsh shallow water operating environments, minimizing the impact of ocean currents while reducing frame size, buoyancy, and weight. Additionally, the device uses a lighter 17mm tether cable to reduce drag. The Cougar is equipped with six thrusters, a design that helps the device maintain stability in strong cross currents and allows for precise maneuverability around underwater structures, while also handling various equipment, including cameras, sonar, tracking systems, and controllers. The robot is equipped with a Kongsberg color zoom camera, Blueview multibeam sonar, Tritec SeaKing side-scan sonar, Cygnus ultrasonic thickness gauge, CP contact probe, and a mechanical arm with four functions. It can also swim freely and has a dedicated 16-foot control cabin.

7.Baido Partners with International Water Association to Release White Paper on “AI Empowering Digital Water Management”

As a global leader in artificial intelligence, Baido has collaborated with the International Water Association (IWA), a top global industry association in the water sector, to co-author the white paper “AI Empowering Digital Water Management” (hereinafter referred to as the “white paper”), deeply researching the digital transformation path of the water industry. On April 29, 2021, the white paper release conference, hosted by Baido and IWA, and co-organized by the Jiangsu Nanjing Ecological Technology Island Economic Development Zone, was held in Nanjing, themed “Digital Water Management, Smart Future,” gathering top researchers, experts, scholars, and entrepreneurs from home and abroad to explore innovative technologies and management methods of AI in water resource management.
The content of this article is reproduced from Interface News, China Robotics Network, Frontiers in Polymer Science, 36Kr
END
More Exciting Content
*A Brief Discussion on the Development Direction of Robots and Related Industries in the 14th Five-Year Plan
*Future Robots: Visual AI Empowering Smart Logistics, Flexible Solutions Leading Industry Transformation
*Opening the Door to Robot Operations, What Key Did Yijiahe Take?
*Industry | Digitalization? Intelligence? What is the Current Status of Intelligent Manufacturing in Chinese Enterprises?
*Why Did Jiekai Robot Win the Toyota Order?
*The New Internet Celebrity in Hotels – “No. 9 Sugar Cube” Makes a Cute Appearance, Winning Fans with Strength
*Industry | The Future of Robot Technology in Production and Work
*Hot Topics | Candela Secures 375 Million Yuan in Series B Financing, Enhancing Service Robots for Smart Living in Multiple Scenarios
*Industry | Six Major Application Trends of AI Changing Manufacturing in 2021
*Industry | A 10,000-Word Paper: How the Rise of Robots Affects the Chinese Labor Market?
*The Nuclear Industry Market Welcomes New Developments, Silicon Step Promotes Nuclear Radiation Inspection Robots to Maintain Nuclear Safety!
*Under Flexible Manufacturing, AI + Software Brings New Opportunities for the Chinese Robot Industry!


Join the Community
Welcome to join the 【Robot Lecture Hall】 reader discussion group, to discuss topics related to the field of robotics and share cutting-edge technology and industry dynamics.
Discussion groups on educational robots, medical robots, legged robots, industrial robots, service robots, special robots, drones, soft robots, etc. are recruiting, follow the Robot Lecture Hall public account and send “Group Chat” to get the joining method!
Recruiting Authors
The Robot Lecture Hall is recruiting 【part-time content creators】. If you are interested in writing articles on 【technology】 or 【industry】 related to robots, you cansend your resume and original works to the email:[email protected]
We have no requirements for profession, location, etc., and welcome friends to join!


Feeling tired? Tap “Looking” to support us!