Introduction
The MX9008 is a dual-channel power management IC suitable for applications powered by USB or 5V DC adapters. It employs a high-efficiency synchronous buck architecture, and the internal compensation network simplifies circuit design. The buck converter operates in current mode control, supporting a constant switching frequency.The dual-channel 5.5V DC/DC buck power management unit (PMU) provides low dropout operation at 100% duty cycle, extending the battery life of portable systems.
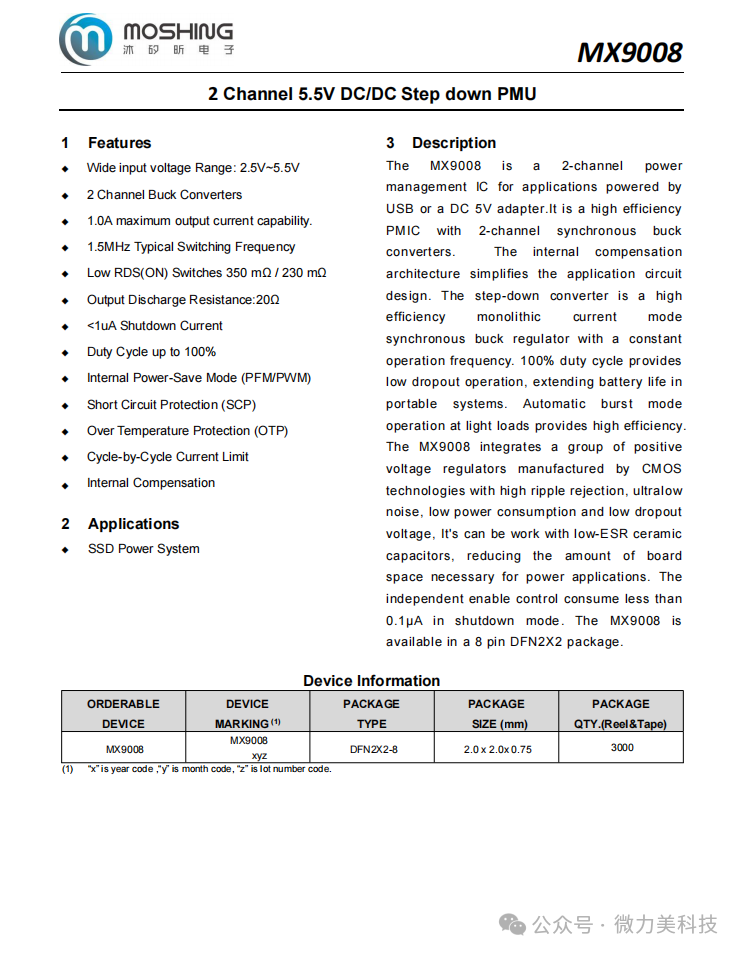
In light load conditions, it automatically enters burst mode to enhance efficiency. The MX9008 is built using CMOS technology, featuring high ripple rejection, ultra-low noise, low power consumption, and low dropout characteristics, supporting low ESR ceramic capacitors to reduce PCB space usage. The independent enable control function allows for power consumption below 0.1μA in shutdown mode. The MX9008 comes in an 8-pin DFN2X2 package.
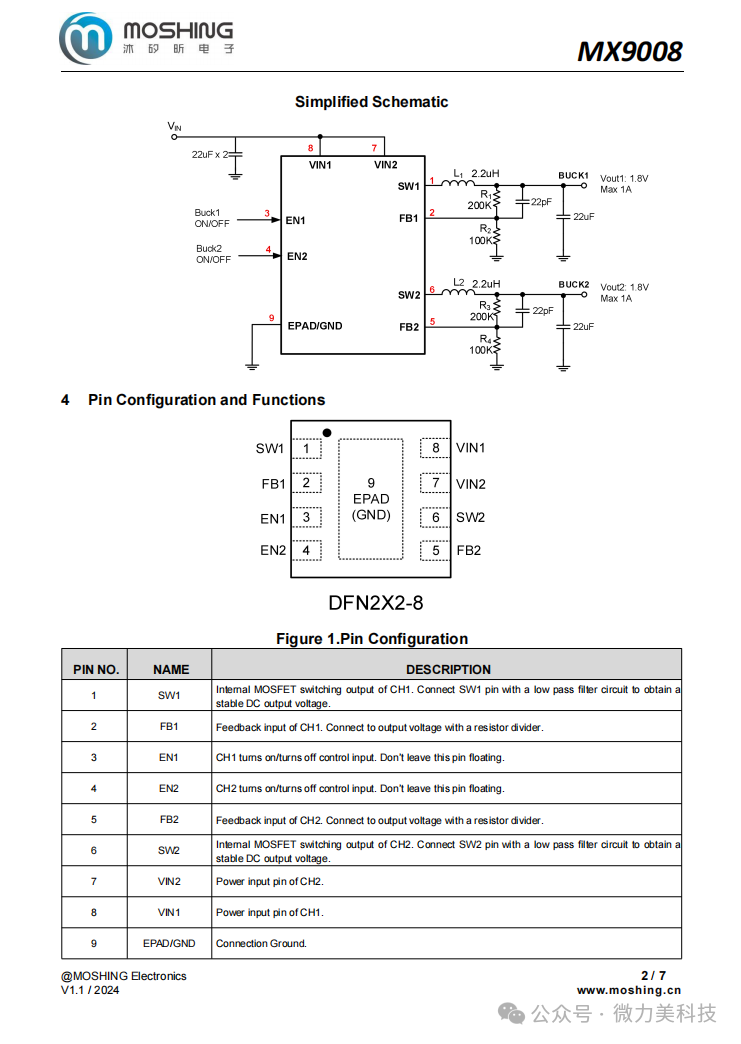
Features
-
Wide input voltage range: 2.5V~5.5V
-
Dual-channel synchronous buck converter
-
Maximum output current capability: 1.0A
-
Typical switching frequency: 1.5MHz
-
Low on-resistance (RDS(ON)): PMOS 350 mΩ / NMOS 230 mΩ
-
Output discharge resistance: 20Ω
-
Shutdown current <1μA
-
Duty cycle up to 100%
-
Internal power-saving mode (PFM/PWM)
-
Short-circuit protection (SCP)
-
Over-temperature protection (OTP)
-
Cycle-by-cycle current limiting
-
Internal compensation network
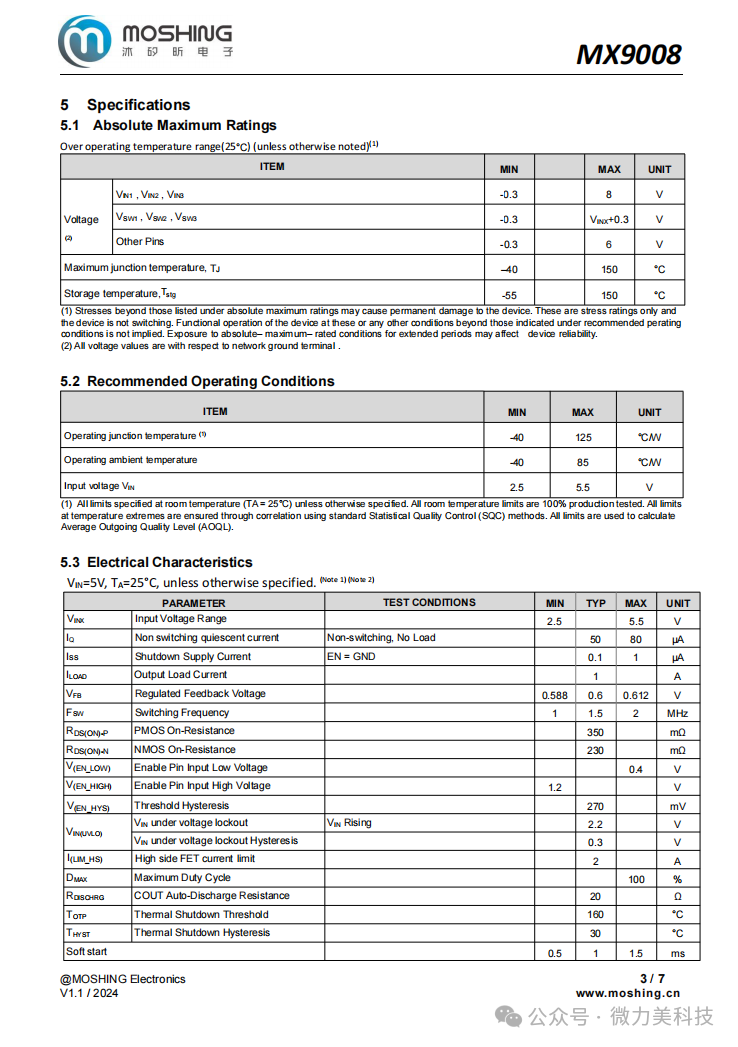
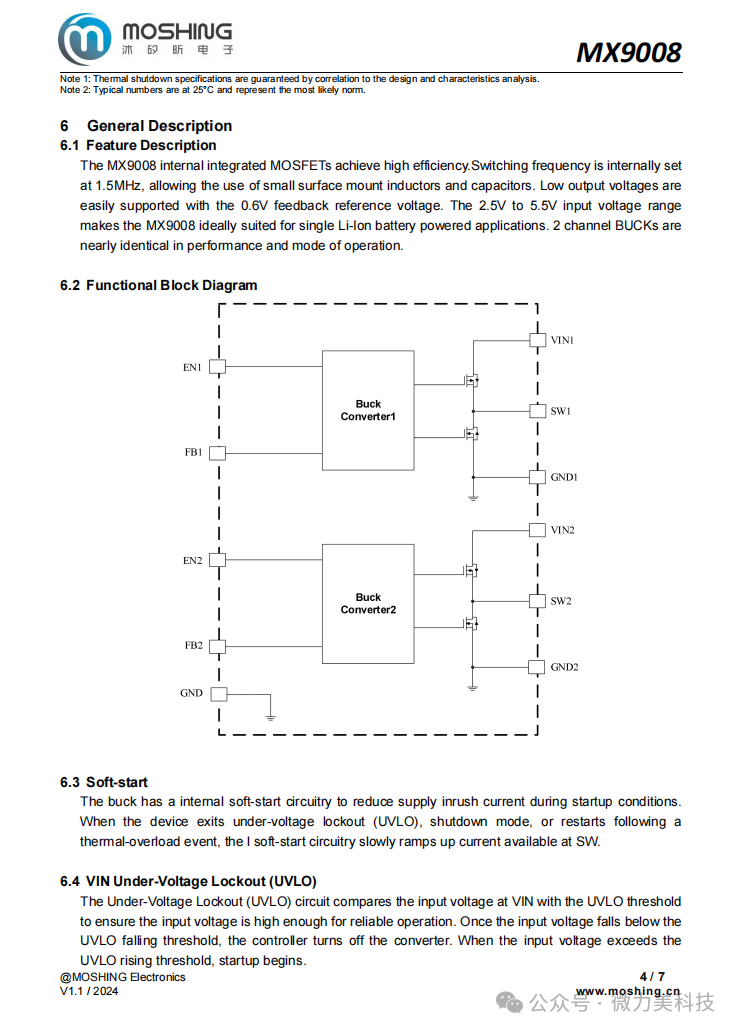
Functional Description
-
Soft Start; The buck converter has a built-in soft start circuit to reduce inrush current during startup. When the device exits under-voltage lockout (UVLO), shutdown mode, or thermal overload recovery, the soft start circuit gradually increases the current at the SW pin.
-
Input Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO); The UVLO circuit monitors the input voltage, and if it falls below the threshold (typical value 2.2V), the controller turns off the converter; if it exceeds the threshold (typical value 2.5V), the converter is activated.
-
High Efficiency and Low Power Consumption; Low on-resistance: PMOS 350mΩ / NMOS 230mΩ, reducing switching losses and improving conversion efficiency (typical value >90%). Power-saving mode: automatically switches to PFM mode under light load to reduce power consumption; shutdown current <1μA, extending battery life.
-
High-frequency switching (1.5MHz): Supports small size inductors and ceramic capacitors, reducing component size and optimizing space utilization.
-
High integration and simplified design; internal compensation network: no external compensation components required, simplifying circuit design.
-
Dual-channel independent control: supports two independent buck outputs, flexibly adapting to multiple voltage requirements (e.g., 3.3V and 1.8V).

-
100% Duty Cycle: Low dropout (LDO-like) characteristics, suitable for battery-powered scenarios.
-
Comprehensive protection features; Short-circuit protection (SCP): cycle-by-cycle current limiting to prevent overcurrent damage. Over-temperature protection (OTP): threshold 160°C (hysteresis 30°C), ensuring safe operation at high temperatures. Under-voltage/over-voltage lockout (UVLO/OVLO): automatically shuts down during abnormal input voltage to protect system stability.
-
Wide input voltage range (2.5V~5.5V); compatible with USB power (5V), single-cell lithium-ion batteries (3.7V), and other power sources, providing strong adaptability.
-
Compact package (DFN2X2-8); package size is only 2.0×2.0mm, suitable for space-sensitive applications such as wearable devices and miniature modules.

Applications
Power systems for solid-state drives (SSD).
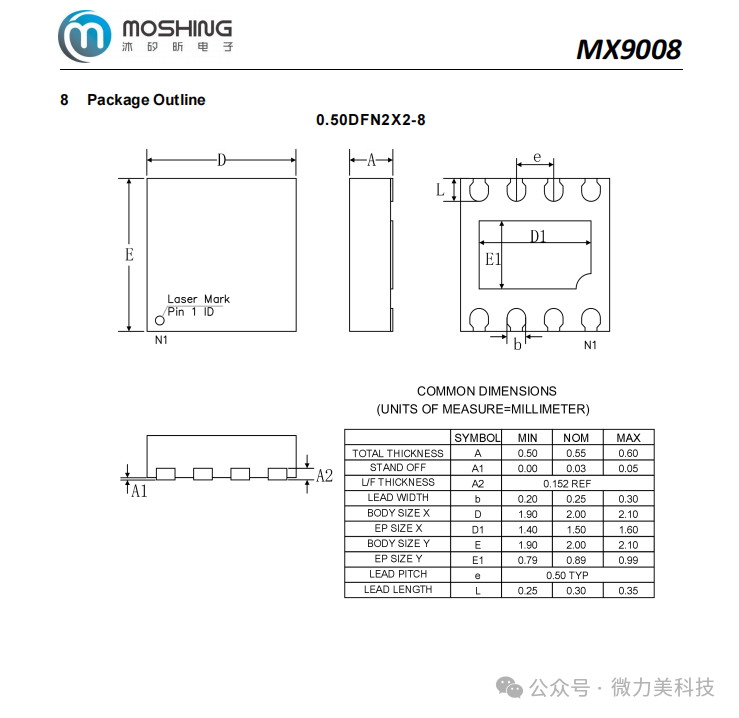
Conclusion; The MX9008, with its high efficiency, high integration, robust protection, and flexible multi-channel design, has wide applicability in storage, portable devices, industrial control, consumer electronics, and more. Its compact package and low power characteristics particularly meet the urgent demand for miniaturization and long battery life in modern electronic devices, making it an ideal choice for high-performance power management.
