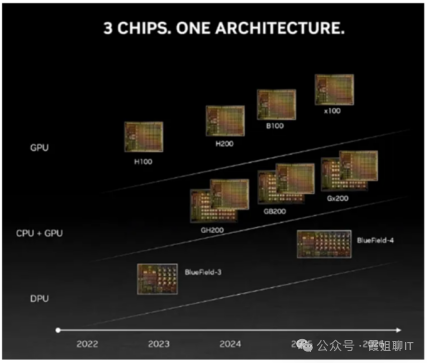
BlueField The DPU is developed based on SmartNIC technology after NVIDIA acquired the Israeli network chip company Mellanox.
The latest version is theBlueField-3 DPU, which began full production in 2023.The next generationBlueField-4 is expected to be released in 2025. Compared to theBlueField-3 DPU, the AI acceleration will use an ARM processor, while theBlueField-4 DPU will integrate a GPU for AI acceleration.
The key specifications of the BlueField-3 DPU are as follows:
|
Network Interface |
1 or 2 ports, 400Gb/s, Ethernet or IB |
|
Host Interface |
PCIe 5.0 x32 |
|
Processor |
16 ARM Cortex-A78 cores, 8MB L2 cache, 16MB LLC system cache |
|
Memory |
Dual DDR5 5600MT/s DRAM ECC memory, Memory Capacity32GB |
The hardware architecture of the BlueField-3 DPU is shown in the figure below:
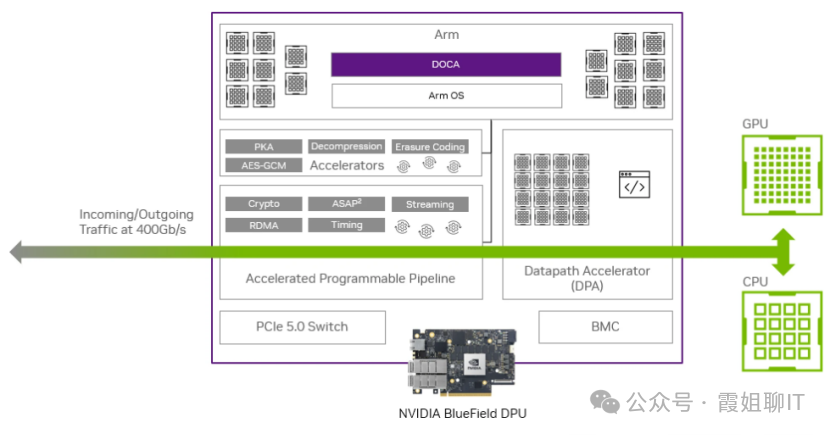
Among them, the DPA (Datapath Accelerator) is a separate embedded system that does not occupy the computational power of the 16 ARM cores. It can accelerate workloads that require high-performance access to the NIC engine for certain packet and I/O processing workloads.
The BlueField-3 DPU provides the following acceleration features:
1.Security
Platform security, secure boot using hardware root of trust, onboard flash encryption, device authentication, regular expression (RegEx) matching processor, IPsec/TLS/MACSec 128/256 bit dynamic data encryption, public key accelerator (PKA), true random number generator (TRNG), etc.
2.Storage
NVMe and VirtIO-blk, NVMe-oF and NVMe/TCP acceleration, decompression engine, and erasure coding for RAID implementation.
3.Networking
RoCE, zero-touch RoCE, accelerated switching and packet processing, SR-IOV, VirtIO acceleration, overlay network acceleration, user-defined data flow classification, stateless TCP offload, etc.
4.HPC/AI Acceleration
HPC/AI All-to-All engine, GPUDirect, GPUDirect Storage (GDS), HPC MPI tag matching.
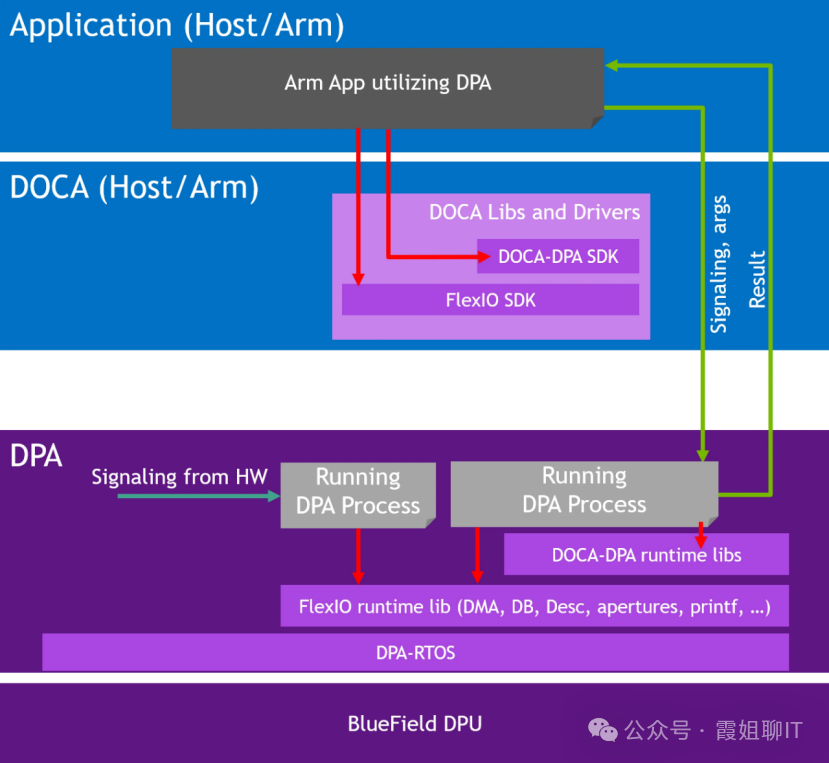
Just like NVIDIA’s GPUs come with CUDA, the BlueField-3 DPU also has its own software framework, DOCA.
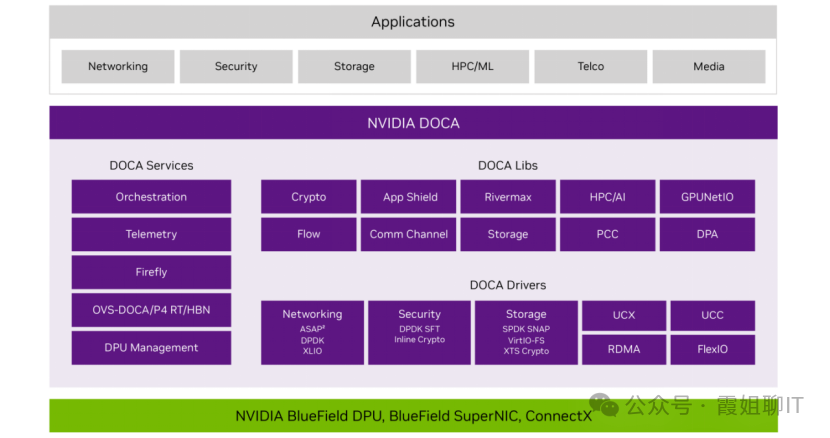
DOCA consists of two parts:
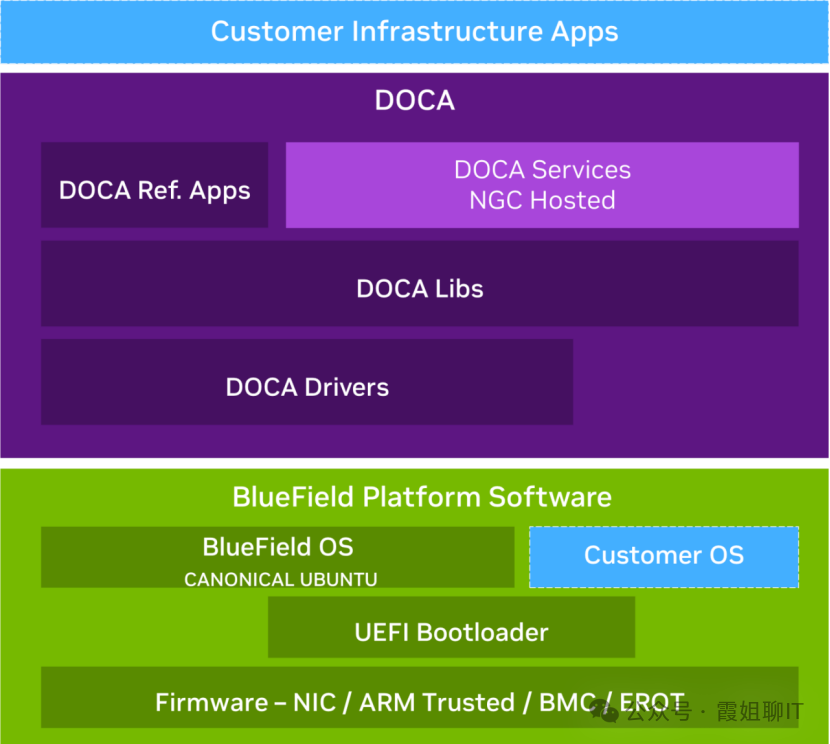
1: DOCA-Host: This software package is installed on the Host and includes libraries and drivers.
2: BlueField Software Package: This package is located on the DPU device and includes firmware, OS, DOCA runtime drivers, and libraries.
DOCA drivers provide the necessary interfaces to run within the host OS kernel, enabling the device to communicate and interact with the host system, thus offloading, accelerating, and isolating infrastructure services such as networking, storage, and security.
DOCA Libraries are built on top of the DOCA drivers, providing developers with higher-level programming interfaces and function calls. The DOCA libraries are pre-optimized for performance, feature rich scenarios, and guided examples, allowing developers to easily leverage the DPU’s acceleration capabilities to develop various high-performance, secure, and reliable data center applications without needing to delve into the underlying hardware details. For example, the DOCA Flow library can be used to define and control network traffic, implementing network policies and management functions; the DOCA App Shield library focuses on host monitoring and threat detection, providing advanced container monitoring features, etc.
DOCA also comes with a series of toolkits for users:
lDOCA Bench: Can evaluate the performance of DOCA applications.
lCapabilities Print: Can print the available and visible devices in the DPU, their capabilities, and the available DOCA libraries.
lDPA Tools: A set of executables that can be used to manage and monitor DPA resources and debug DPA applications.
lFlow Tune: Provides visibility and analysis capabilities for DOCA Flow programs.
lDOCA Ngauge: Can be used to probe NIC hardware counters and store collected data and related metadata in HDF5 format.
lPCC Counter: Used to print hardware counters related to PCC.
lSocket Relay: Allows unloading Unix domain socket (AF_UNIX series) server applications to the DPU, with communication between both parties handled by the DOCA Comch agent.
lDOCA Telemetry Utils: Can display all available counters and generate counter IDs that can be used in other DOCA tools. It helps understand the various performance metrics and status data currently supported by the network device, such as packet counts, throughput, latency, etc., providing a comprehensive grasp of the device’s operational status.
Refer to the official DOCA SDK documentation and development community for DPU programming.
Additionally, NVIDIA Technical Services has published a book titled “Data Processors: An Introduction to DPU Programming.” This book is the official guide covering DPU technology, NVIDIA DPU technology, DPU development and practice, ecosystem, and deployed products. Interested readers can purchase it for further insights.