The role of sensors in automobile automatic control is becoming increasingly important and widely applied. In this issue, we will introduce various types of sensors that may be used in cars and their functions.
The function of the air flow sensor is to convert the amount of air inhaled by the engine into an electrical signal, which is provided to the Electronic Control Unit (ECU). It is the main basis for determining the basic fuel injection amount.
Vane Type:The vane type air flow sensor belongs to the volumetric flow type. This sensor has a simple structure and low cost, but due to its moving part, the vane occupies a large area of the intake duct, thus reducing the flow capacity of the intake system and increasing intake resistance, so it is rarely used now.
Karman Vortex Type:The Karman vortex type air flow sensor belongs to the volumetric flow type and is widely used in Toyota and Mitsubishi cars. This sensor is small in size, lightweight, non-wearing, has a simple intake duct, low intake resistance, high detection accuracy, and fast response, but its cost is relatively high and is often used in high-end cars.
Hot Wire Type:The hot wire type air flow sensor belongs to the mass flow type and can directly detect the mass flow of intake air without needing to correct for intake temperature and atmospheric pressure. Because this sensor has no moving parts, it has low intake resistance and good response characteristics, and can accurately detect the intake air volume during rapid deceleration, thus it is widely used.
Hot Film Type:The hot film type air flow sensor belongs to the mass flow type, developed by General Motors, and is widely used in vehicles produced by GM and Japan’s Isuzu. The working principle of this sensor is fundamentally the same as that of the hot wire type sensor, except that it replaces the hot wire with a hot film (made of heating metal platinum fixed on a thin resin film). This structure allows the heating element to not directly bear the resistance generated by the airflow, thus increasing its strength and reliability during operation.
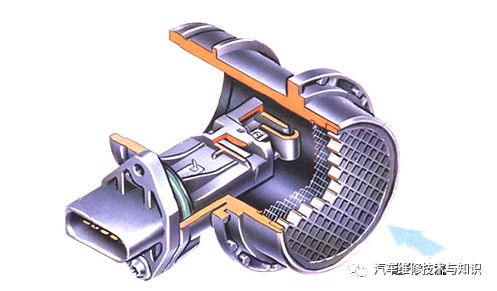
Engine Temperature Sensor
The function of the engine temperature sensor is to convert the temperature changes of gases or liquids into electrical signals to provide to the ECU.
Water Temperature Sensor:Installed on the cylinder block, it is used to detect the temperature of the engine cooling water and converts this information into an electrical signal to provide to the engine’s ECU.
Intake Temperature Sensor:The engine intake temperature sensor is installed on the air flow sensor in the L-type EFI system, while in the D-type EFI system, it is installed inside the air filter housing or pressure regulator to provide the engine ECU with information on the intake temperature.

Fuel Temperature Sensor:Used in the fuel injection system of the diesel engine electronic control distribution pump, it provides the engine ECU with information on fuel temperature for precise control of injection quantity.
Position and Speed Sensors
The throttle position sensor, crankshaft position sensor, vehicle speed sensor, and accelerator pedal position sensor are used to provide various position information to the ECU.
Throttle Position Sensor:Installed on the throttle body, the throttle position sensor can convert information such as throttle opening, idle, and full load into electrical signals for the ECU. There are linear output and switch output types of throttle position sensors. Comparatively, the latter has poorer detection performance but is simpler and cheaper. Some EFI systems are equipped with both types of throttle position sensors, using the switch output type sensor to detect engine idle and full load status, while using the linear output type sensor to detect the full range of throttle openings.

Crankshaft Position Sensor:Used to provide the ECU with the crankshaft angular position signal, piston stroke position signal, and engine speed signal. There are three types: magnetic, photoelectric, and Hall effect. The first two are usually installed inside the distributor and rotate with it, while the latter is installed at the front end of the crankshaft. Due to the strong anti-interference ability of magnetic and Hall effect sensors and good recognition capability at high speeds, they are widely used.
Vehicle Speed Sensor:Installed on the transmission output shaft or main reducer, it provides the ECU with vehicle speed signals. The structure and principle of this sensor are very similar to that of the crankshaft position sensor.
Accelerator Pedal (Throttle Pedal) Position Sensor:Usually used in direct injection engines, it provides the ECU with information on load size, load range, acceleration, and deceleration. The ECU uses this information to determine the fuel injection quantity for the combustion layer area (the combustion forms of direct injection engines include stratified combustion and homogeneous combustion).
Exhaust Purification Sensors
Exhaust purification sensors convert relevant information from the exhaust into electrical signals to provide to the ECU.
Oxygen Sensor:Oxygen sensors are classified into zirconia and titanium types, installed in the exhaust pipe, used to feedback the actual air-fuel ratio signal to the ECU, thus converging the actual air-fuel ratio to a narrow range near the theoretical value, forming closed-loop control. Comparatively, titanium oxygen sensors have a simple structure, small size, and low cost, but their resistance varies greatly with temperature changes, so certain temperature compensation measures are usually taken when used at high temperatures.
Exhaust Gas Recirculation Displacement Sensor:Mainly used to provide the electronic control system with the opening information of the exhaust gas recirculation control valve to facilitate corresponding control of the exhaust treatment system’s working conditions.
Pressure Differential Sensor:Installed downstream of the particulate filter, it provides the electronic control system with pressure differential information of the particulate filter to timely burn off the particulates in the filter at high temperatures, preventing an increase in exhaust back pressure.
NOx Sensor:Used to provide the electronic control system with the concentration information of NOx in the exhaust after-treatment system to facilitate corresponding control of the after-treatment SCR system’s working conditions.
Exhaust Temperature Sensor:Usually installed near the three-way catalytic converter to detect its working temperature and convert this signal into an electrical signal to provide to the electronic control system.
EGR Temperature Sensor:Usually installed downstream of the EGR valve to detect the temperature of the EGR and convert this signal into an electrical signal to provide to the electronic control system.
Automatic Air Conditioning System Sensors
The sensors used in the automatic air conditioning system, besides temperature sensors, also include some other sensors.
Interior Temperature Sensor:Usually installed on the underside of the dashboard, it is a thermistor temperature sensor with a negative temperature coefficient, used to provide the air conditioning ECU with the temperature signal inside the cabin.
Exterior Environment Temperature Sensor:The exterior environment temperature sensor is also a thermistor temperature sensor with a negative temperature coefficient, usually installed on the lower side of the vehicle’s front bumper, to provide the air conditioning ECU with the temperature signal outside the cabin.
Evaporator Temperature Sensor:Usually installed on the evaporator housing, it detects the temperature changes inside the refrigeration unit and provides the detected signal to the air conditioning ECU.

Sunlight Radiation Sensor:The sunlight radiation sensor is a light-sensitive diode sensor, usually installed below the front windshield of the car, used to convert the degree of sunlight radiation into electrical signals to provide to the air conditioning ECU.
Coolant Flow Sensor:The coolant flow sensor is usually installed between the liquid storage dryer and expansion valve, used to detect the flow of refrigerant and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to the air conditioning ECU.
Compressor Lock Sensor:The compressor lock sensor is a type of magnetic sensor, usually installed inside the compressor, used to detect the compressor’s speed and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to the air conditioning ECU.
Smoke Concentration Sensor:Used to detect the smoke level inside the cabin and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to the air conditioning ECU. The ECU will automatically open or close the air exchanger based on this information to maintain fresh air inside the cabin.
Humidity Sensor:Used to detect the fogging of the car windshield and the humidity inside the cabin, converting this change into an electrical signal to provide to the air conditioning ECU.
The structural forms of level sensors mainly include float type, reed switch type, thermal switch type, variable resistor type, and electrode type (for battery measurement), among others.
Fuel Level Sensor:Used to detect the amount of fuel storage and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or fuel gauges, allowing the system to display whether the fuel level is below the set value.
Coolant Level Sensor:Used to detect the amount of coolant storage and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or water level display systems, allowing the system to display whether the coolant level is below the set value.
Brake Fluid Level Sensor:Used to detect the amount of brake fluid storage and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or brake fluid level display systems, allowing the system to display whether the brake fluid level is below the set value.
Battery Liquid Level Sensor:Used to detect the amount of electrolyte storage in the battery and convert this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or alarm circuits, allowing the system to display whether the electrolyte level is below the set value.
The function of the oil pressure sensor is to convert the changes in oil pressure into electrical signals to provide to the ECU.
Rail Fuel Pressure Sensor:Usually installed on the rail of the diesel engine common rail electronic control fuel injection system, it detects the pressure of fuel inside the rail and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to the ECU.
Fuel Tank Pressure Sensor:Usually installed inside the fuel tank, it detects the pressure of the fuel inside the tank and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or alarm circuits.
Oil Pressure Sensor:Usually installed in the main oil passage of the engine, it detects the oil pressure and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or alarm circuits.
Transmission Oil Pressure Sensor:Usually installed inside the automatic transmission oil pump (or output oil passage), it detects the oil pressure of the transmission and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to relevant electronic control systems or alarm circuits.
Electronic Control Suspension and Steering System Sensors
Electronic control suspension is used to improve vehicle stability, while electronic control steering is used to improve steering strength.
Front and Rear Suspension Height Sensors:Primarily installed in the electronic control suspension system, they detect the deformation of the front and rear suspensions and convert this change into electrical signals to provide to the suspension ECU.
Vehicle Body Acceleration Sensor:Primarily installed in the electronic control suspension system, it detects the vibration of the vehicle body and converts this change into electrical signals to provide to the suspension ECU, indirectly providing information about the road conditions while the car is driving.
Vehicle Body Displacement Sensor:Primarily installed in the electronic control suspension system, it detects the displacement of the vehicle body relative to the axle and converts this change into electrical signals to provide to the suspension ECU, reflecting the smoothness of the vehicle body and changes in vehicle body height.
Steering Wheel Angle Sensor:Primarily installed in the vehicle’s electronic control steering system, it detects the angle of the steering wheel and converts this change into electrical signals to provide to the steering ECU, used to calculate the degree of body tilt.
Torque Sensor:Mainly installed in the vehicle’s electronic control steering system to detect the steering wheel’s steering load torque signal and convert this change into electrical signals to provide to the steering ECU.
Yaw Rate Sensor:Used to detect and record the vehicle’s movement around the vertical axis and convert this change into electrical signals to provide to the steering ECU, to determine whether the vehicle is skidding.
Yaw Rate Sensor:Used to detect the centrifugal force generated when the vehicle is turning and convert this change into electrical signals to provide to the steering ECU, to determine whether the vehicle is skidding while navigating turns.
Airbag and Collision System Sensors
Both the airbag and collision systems are part of the vehicle’s safety protection system, with the former protecting the human body and the latter protecting the vehicle and pedestrians.
Collision Sensor:Common collision sensors include mechanical collision sensors, magnetic collision sensors, piezoelectric collision sensors, strain gauge collision sensors, piezoresistive collision sensors, and mercury switch collision sensors. The collision sensor detects signals during a car collision and provides this signal to the airbag ECU.
Safety Sensor:Used to detect the severity of a car (collision) impact and provide this signal to the airbag ECU, acting as insurance to prevent the airbag from deploying incorrectly.
Ultrasonic Distance Sensor:Usually installed on the rear bumper of the vehicle, it emits ultrasonic waves towards the rear of the vehicle and converts the reflected ultrasonic waves into electrical signals to provide to the collision control ECU.
Corner Radar Sensor:Usually installed on the bumper to compensate for the detection blind spots of ultrasonic sensors and convert the detected signals into electrical signals to provide to the collision control ECU.
Knock Sensor:Knock sensors include magnetostrictive, resonant piezoelectric, and non-resonant piezoelectric types. This type of sensor is usually installed on the engine body to convert the engine vibration signals into electrical signals to provide to the engine ECU, to detect the occurrence time and amplitude of knock.
Braking, Cruise, and Navigation System Sensors
Braking is part of the vehicle’s safety protection system, while cruise control and navigation belong to the vehicle’s comfort systems.
Brake Pressure Switch Sensor:Used to detect the pressure of brake fluid in the brake line and convert the detected signal into an electrical signal to provide to the electronic control system or alarm control circuit.
Brake Light Switch Sensor:Used to detect the on/off status of the brake light circuit and convert the detected signal into an electrical signal to provide to the electronic control system or relevant control circuit.
Distance Sensor:Used to detect obstacles in front and behind the vehicle and the distance between the vehicle and other vehicles, converting the detected signal into an electrical signal to provide to the collision electronic control system or relevant control circuit.
Compass Sensor:Used to detect the condition of the geomagnetic field and convert the detected signal into an electrical signal to provide to the navigation electronic control system or relevant control circuit for determining driving direction.
Gyroscope Sensor:Used to detect the direction of the vehicle’s travel and convert the detected signal into an electrical signal to provide to the navigation electronic control system or relevant control circuit for automatic data recording.
Pressure and Speed Sensors
Pressure sensors mainly include semiconductor pressure-sensitive resistors, capacitive sensors, membrane box-driven variable inductance sensors, and surface acoustic wave sensors. The first two are widely used, featuring small size, high precision, low cost, good response performance, strong versatility, and a wide detection range.
Intake Manifold Absolute Pressure Sensor:Used in D-type EFI systems. Unlike the air flow sensor, the intake manifold absolute pressure sensor adopts an indirect measurement method, measuring the relative value of the absolute pressure inside the intake manifold based on engine load changes, thus calculating the engine’s intake volume.
Boost Pressure Sensor:Usually installed on turbocharged engines, it detects the working conditions of the turbocharger and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to the ECU, allowing the ECU to control the fuel injection pulse and the size of boost pressure.
Cylinder Combustion Pressure Sensor:There are two types of cylinder combustion pressure sensors: one is a direct type sensor with the pressure surface on the side of the combustion chamber, abbreviated as PDS; the other is a washer-type pressure sensor fastened to the spark plug, abbreviated as PGS. The former can achieve linear detection of combustion chamber pressure, while the latter has good assembly properties and is suitable for higher precision knock control and misfire detection.Cylinder combustion pressure sensors provide the ECU with cylinder combustion pressure signals. The control system can obtain a lot of information from the combustion pressure sensor, thus enabling timely control of the engine, such as determining the optimal ignition timing and valve timing.
Tire Pressure Monitoring Sensor:The tire pressure monitoring sensor adopts temperature difference compensation correction, which can generate a series of electronic signals based on changes in tire pressure, tire temperature, and battery voltage, providing timely tire pressure readings. Its maximum working pressure can reach 1380kPa, with a working temperature range of -40~125°C and an accuracy of no less than 1%.Tire speed sensors are used to detect wheel speeds and provide this signal to the ABS ECU, which processes it to obtain vehicle speed signal parameters. Tire speed sensors are usually installed on the wheel, reducer, or transmission, typically using electromagnetic induction or photoelectric sensing principles to obtain signals. The number of installations depends on the system layout and control methods.

Deceleration Sensor:The commonly used deceleration sensors mainly include differential voltage type deceleration sensors and switch type deceleration sensors. The former detects the deceleration signal through the movement of sliding components during vehicle deceleration, while the latter senses the magnitude of deceleration through the movement of inertial components during vehicle deceleration. Deceleration sensors are also known as G sensors, used to detect wheel acceleration or braking deceleration, serving as auxiliary signals for threshold control and detecting and controlling braking processes on low-friction surfaces.
Oil Quality Sensor:The oil quality sensor uses ceramic capacitance to detect the stability of the oil medium to remind timely oil changes, reducing engine wear and extending its service life.
Electric Seat Sensor:Usually installed around the bottom of the seat, it provides the seat electronic control system with signals for seat position adjustments in terms of front and rear and height, and has a memory function. It generally consists of four sensors, including sliding position sensor, front vertical position sensor, rear vertical position sensor, and tilt position sensor.
Headlight High/Low Beam Control Sensor:Used during nighttime oncoming vehicles, it senses the intensity of light from oncoming vehicles and converts this change into an electrical signal to provide to the headlight electronic control system, allowing timely adjustment of light to prevent glare.
Fingerprint Sensor:Mainly applied in the vehicle’s security and anti-theft system, used to identify legitimate drivers, with a detection error rate of less than 0.01%.
Welcome to Angel Round,ARound Companies Join the Group (Friendly connections including top institutions among 500 automotive investment institutions; several companies have already completed); There are many groups for communication in the automotive industry, including whole vehicles, automotive semiconductors, key components, new energy vehicles, intelligent connected vehicles, aftermarket, automotive investment, autonomous driving, vehicle networking, etc. To join the group, please scan the administrator’s WeChat (Please indicate your company name)











