1: What are the approaches to achieving robot lightweighting?
Lightweighting mainly falls into two directions: structural lightweighting and material lightweighting. Structural lightweighting primarily involves design optimization, including increasing integration, improving topology, morphology, and parameters; material lightweighting focuses on using new lightweight materials to achieve weight reduction.
2. Besides polycarbonate, what other lightweight materials are worth noting?
Magnesium alloys and engineering plastics like nylon are also noteworthy lightweight materials. Magnesium alloys, due to their good strength, ductility, and electromagnetic interference resistance, have mature applications in the automotive industry, achieving weight reduction and cost savings. Nylon (PA) is characterized by good flexibility and mature applications, also used in automotive and robotic shell structural components. However, both have relatively limited market space, around several hundred million.
3. Among lightweight materials, which is the most important?
Polycarbonate (PCT) is the most important lightweight material due to its excellent mechanical properties, heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and processing characteristics, widely used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics. Although its current market size and price are relatively small, it has high potential as a quality lightweight material in material applications.
4. What is the market outlook for polycarbonate?
The demand for polycarbonate at the million-unit level is about 2 billion. If considering larger growth (e.g., in tens of millions), the market space will reach 20 billion. Additionally, due to high barriers, strong profitability, and the relatively small market capitalization of domestic listed companies, the polycarbonate sector has significant market capitalization elasticity.
5. How can lightweight materials be applied to reduce the weight of components?
The application of materials is not only aimed at external component lightweighting but also crucially involves core components. Joint modules, structural parts, and shells are significant portions of the whole machine. By applying lightweight materials such as polycarbonate, magnesium alloys, and nylon, significant performance improvements can be achieved. There is also exploration of lightweight solutions for components like ball screw plastics and frameless motors.
6. What are the main advantages of material lightweighting and the specific paths for lightweighting? What are the main technical paths for structural and material lightweighting?
The advantages of material lightweighting lie in its flexibility, not constrained by specific technical paths. The paths for lightweighting mainly include structural lightweighting and material lightweighting. Structural lightweighting needs to converge on a specific path, and currently, there are no obvious signs in the industry; while material lightweighting starts from the overall weight distribution, optimizing by selecting suitable materials for components like joint modules and structural parts. The main paths for structural lightweighting include parameter optimization, topology optimization, and morphological integration. Material lightweighting can be divided into metal-to-metal replacement and plastic-to-metal replacement. Specifically, parameter optimization achieves zero-cost optimal matching through changes in size and component layout; topology optimization further reduces volume through hollow or specific structural designs; morphological integration involves the integrated design of joint modules and structural parts, reducing connectors and structural components to lighten weight.
7. In which specific components does material lightweighting have significant application space?
Material lightweighting has significant application space in multiple components. For example, in the ball screw field, carbon fiber or glass fiber modifications are used to meet performance requirements, but currently, humanoid robots use this technology less, so the short-term market space is limited. Frameless motors mainly rely on material selection and magnetic circuit design optimization. In terms of shells and structural parts, magnesium alloys and nylon are favored due to mature processing technology and outstanding cost-performance ratio. In the short term, magnesium alloys are expected to see good application, while modified nylon is believed to have greater long-term development potential.
8. What material substitution trends have emerged in the application of industrial robots?
In industrial robots, there is a trend of magnesium alloys replacing aluminum alloys, and in the humanoid robot field, magnesium alloys may be the first to be applied to shells and other structural parts.
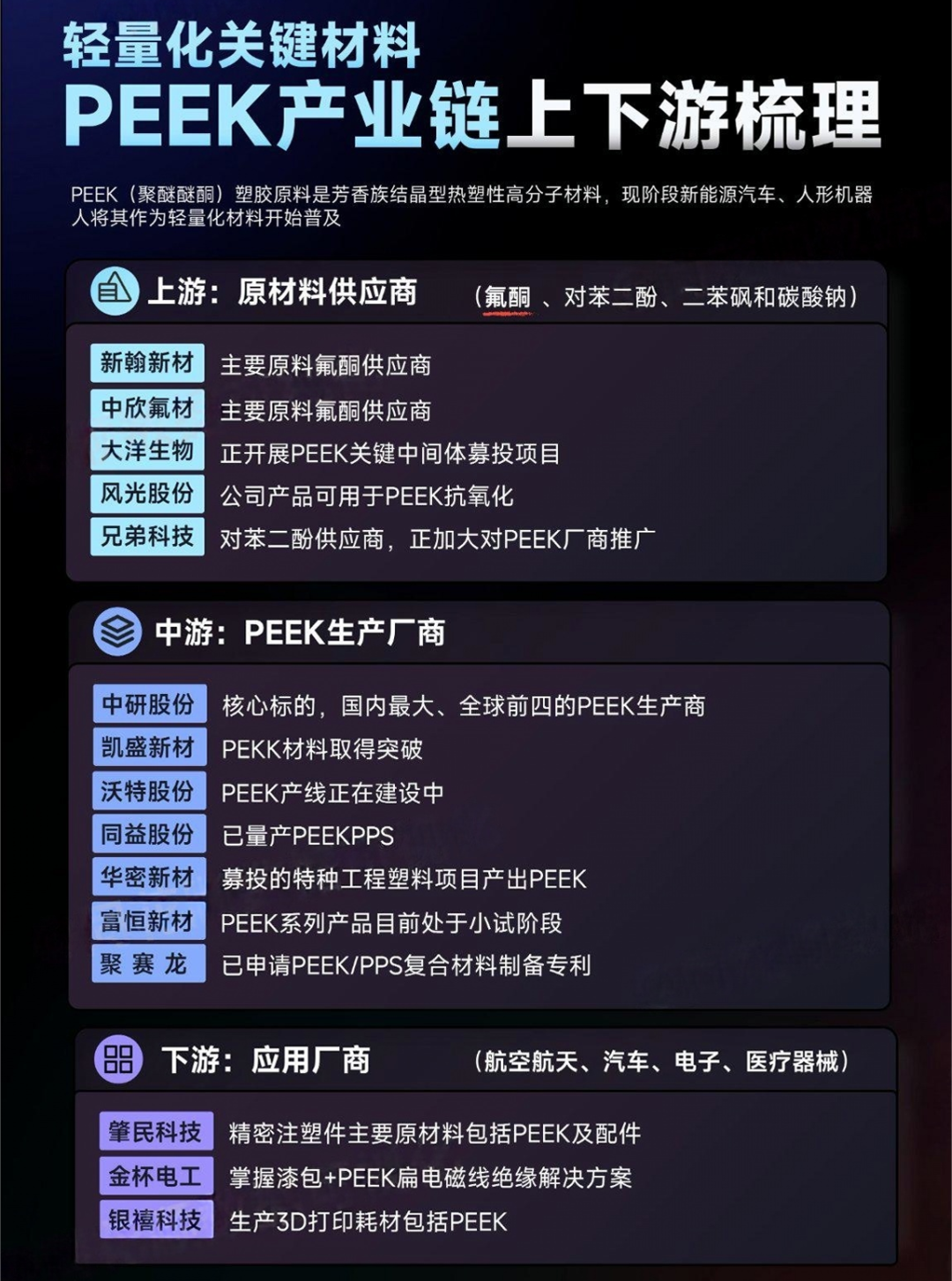
9. Why is PEEK considered the pinnacle of engineering plastics, and what are its cost issues?
PEEK material ranks first among engineering plastics in rigidity, toughness, wear resistance, corrosion resistance, and processing performance, but its cost is high, mainly due to the price of raw material fluorides reaching 120,000 yuan per ton, and limited production capacity. The processing process is complex, requiring operation in flammable and explosive environments, and generates harmful gases and wastewater, thus limiting processing.
10. What are the main barriers to PEEK material? Which companies have competitive advantages in material production?
The main barriers to PEEK material include:
1) High difficulty in production processes, requiring high-temperature polycondensation reactions for up to 12 hours under specific conditions;
2) Consistency control of batches; large reactors can enhance stability but are not absolute;
3) Balancing various indicators, such as solubility and viscosity, crystallinity, etc., all requiring strict control of the production process;
4) Adaptability of modified enhancements and downstream application scenarios, requiring mastery of composite modification technology and energy consumption advantages. UK Victrex and China’s Zhongyuan Co. have the production capacity of 5000-liter reactors, enabling batch stability and high efficiency in the production process, thus occupying a leading position in the market. Meanwhile, Zhongyuan Co. shows strong R&D capabilities and energy consumption advantages in purification processes and the performance balance of final products.
11. What barriers exist for PEEK material at the application end?
The application barriers of PEEK material mainly lie in long verification cycles; for example, in high-pressure motor applications, it takes about 8 years from development to product launch. Additionally, PEEK material has certain advantages in medical applications due to its compatibility with the human body, and its application in humanoid robots may be faster and more rapid than in the automotive sector.
12. What is the global market structure for PEEK materials?
In the global PEEK material market, UK Victrex occupies the first tier, possessing full industry chain capabilities, with a market share of about 70%; the second tier includes overseas companies Solvay and Ensinger; the third tier is domestic Zhongyan Co., which performs well in the domestic substitution field, comparable to international giants in technology level, and has significant cost advantages. Currently, the market share of the three overseas companies accounts for 86%.
13. What are the future global and Chinese market size forecasts for PEEK?
It is expected that by 2027, the global PEEK market size will reach 8.5 billion, and the Chinese market will reach 2.8 billion. Compared to the current demand in the automotive and aerospace sectors, the future growth in the automotive sector and humanoid robot sector will jointly drive the market size growth of PEEK materials.
14. How will Zhongyan Co.’s market share change in the automotive and humanoid robot sectors in the future?
With the acceleration of domestic substitution and the increase in demand for humanoid robots, Zhongyan Co.’s market share is expected to increase significantly. In terms of production capacity construction, the current actual production capacity in China is about 1200 tons, and it is expected that by 2027, the actual domestic PEEK production capacity will reach 5400 tons per year, sufficient to cover the demand growth in the humanoid robot sector.
15. What technological and commercial progress has been made regarding nylon applications in the motor sector? What are the advantages of nylon in shell material selection?
In the motor sector, using nylon materials can significantly reduce weight and improve insulation performance, especially in bases and external rings. Some manufacturers, such as Keda Li and Mengli, have achieved a 71% shock absorption effect, enhanced mechanical strength, and relatively reduced processing difficulty. Although the processing process requires high equipment standards, considering cost and performance advantages, nylon has good application prospects in the motor sector. Given that shells require toughness, engineering plastics like nylon are more suitable than magnesium alloys, as they have high wear resistance, high impact resistance, and flexibility. After adding glass fiber or carbon fiber modifications, nylon can meet the demands for shell materials. Although magnesium alloys have promotional advantages in the short term due to mature processing technology, nylon solutions are expected to achieve large-scale promotion in the C-end humanoid robot market due to their comprehensive performance advantages in the long term.
16. How is nylon applied in the automotive and robot sectors? What is the specific application of nylon in humanoid robots?
Nylon is widely used in automotive manufacturing and electronics due to its impact resistance and flexibility, such as in engine fuel supply systems and electrical systems. In the robotics sector, nylon has been applied in industrial and collaborative robots, such as in harmonic steel wheels and parts of planetary roller screws, where modifications can reduce friction coefficients and improve strength. In humanoid robots, nylon is mainly used for outer shell coverings to achieve a more skin-like and humanized effect. Additionally, nylon materials can be applied in lightweight design for joint modules and structural parts through weaving processes, especially in reducers and motors, by replacing some metal components with carbon fiber modified engineering plastics to achieve weight reduction while maintaining rigidity and wear resistance.
17. In pure rotary joint solutions, what is the market space for magnesium alloys and nylon pure materials for PPSP? How does the comprehensive solution enhance the effectiveness for humanoid enterprises?
In pure rotary joint solutions, the market space for magnesium alloys and nylon pure materials for PPSP is 100 million, 1.2 billion, and 300 million respectively. In the comprehensive solution, considering both rotary and linear joints, the effectiveness for humanoid enterprises significantly increases, reaching a level of 2 billion yuan, referring to the pure material market space.
18. After comprehensive consideration, what is the order of attention for components? In terms of material selection, which is the optimal choice?
The attention for components is ranked as follows: ramp steel wheels > shells > ball screws, based on a comprehensive consideration of weight reduction effects, technical difficulty, and cost-performance ratio. Considering market space, competitive landscape, and technical difficulty, PEEK is the optimal choice, followed by magnesium alloys, and lastly nylon.
19. What related targets are recommended for attention?
First, Keda Li is recommended, as its structural component business is steadily growing, with an annual growth rate of over 10%, and it has early layout and positioning advantages in lightweight materials. Secondly, Zhaomin Technology is recommended, as it has mature applications in automotive injection parts, deep binding with downstream customers, and has good application expansion in humanoid robot plastic parts injection. Additionally, Hongbo Co. is recommended, as the company has excellent performance in automotive and motorcycle intake cooling system components, has launched products in the humanoid robot sector, and collaborates with leading overseas customers while actively extending into the materials themselves, such as sensory and pure resin production fields.
20. What are the focus points for Xusheng Group and Baowu Magnesium Industry?
Xusheng Group, as a leading aluminum die-casting enterprise, has developed magnesium alloy products and collaborates with downstream customers for sample delivery. It has significant barriers and scale advantages in the magnesium alloy field. Baowu Magnesium Industry is the largest specialized magnesium alloy producer in China, with a complete layout of the magnesium alloy industry chain, from raw materials to recycling, successfully applied in high-end fields such as aerospace and new energy vehicles.
21. Which domestic companies in the technology field need to be focused on?
First, Zhongyuan Co. should be focused on, as its technology level and production capacity layout are in the domestic first tier, successfully applied in fields such as new energy vehicles, possessing high-end product production know-how, and expected to ensure sustained and stable growth through domestic substitution.
22. What is the status of Xinxin New Materials in the field of special engineering plastics?
Xinxin New Materials focuses on core raw materials for special engineering plastics, with a rich product variety, widely applied in pharmaceuticals, pesticides, cosmetics, and special engineering plastics, possessing strong industry chain capabilities, good customer binding and stickiness, and new production capacity has been put into operation. With the growth of applications in the robotics field, it will bring profit elasticity.
23. What are the views on Zhongxin Fluorine Materials and Nanshan Zhishang?
Zhongxin Fluorine Materials, as a company with a full industry chain layout in fluorochemical, has industry advantages in cost control, and other fluorochemical products can be used as raw materials for robot batteries and other electronic components. With the large-scale implementation of robots, it will benefit from the growth in demand for core raw materials. Nanshan Zhishang is a leader in the textile and clothing industry, with important applications of high molecular polyvinyl chloride and nylon in the robotics field. With new material substitution and technological advancements, the company is expected to perform well.