Mean filtering is a fundamental digital signal processing technique commonly used for image and signal denoising. This article will detail how to implement a simple yet efficient mean filter using the Verilog hardware description language.
Basic Principles of Mean Filtering
The core idea of mean filtering is to replace the value of a pixel with the average value of its surrounding neighborhood. For a 3×3 neighborhood, the calculation formula is as follows:
 This method can effectively reduce random noise but may cause slight blurring of image edges.Implementation Method
This method can effectively reduce random noise but may cause slight blurring of image edges.Implementation Method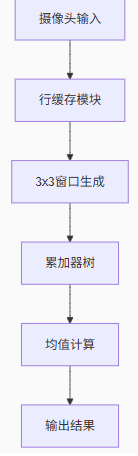
Design Description
This mean filter implementation includes the following key components:
Row Buffer Mechanism:Two row buffers are used to store the previous two rows of data, along with the current row data to form a 3×3 window.
-
3×3 Window Construction:Using pixel buffers and row buffers, extract the 9 pixel values surrounding the currently processed pixel.
-
Summation and Average Calculation:Add the 9 pixel values and divide by 9 to obtain the average. Here, a right shift of 3 bits (dividing by 8) is used as an approximation to dividing by 9 to improve hardware efficiency.
-
Pipelined Design:To enhance processing speed, a pipelined structure is adopted, ensuring that one pixel can be processed per clock cycle.
Processing Results:
Original Image

Image After Mean Filtering

Follow our public account to join the QQ group
To obtain the source code for the filtering module, please join the QQ group!