
MLNLP community is a well-known machine learning and natural language processing community both domestically and internationally, covering NLP graduate students, university professors, and corporate researchers.The vision of the community is to promote communication and progress between the academic and industrial sectors of natural language processing and machine learning, especially for beginners.Research | Multi-Agent SystemsEditor | PaperAgentIn multi-agent systems (MAS: multi-agent systems), designing effective prompts and topologies poses challenges, as individual agents may be sensitive to prompts, and manually designing topologies requires extensive experimentation.
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2502.02533
Paper title: Multi-Agent Design: Optimizing Agents with Better Prompts and Topologies
To automate the entire design process, Google & Cambridge University first conducted an in-depth analysis of the design space to understand the factors that contribute to building effective MAS. It was found that: prompt design has a significant impact on downstream performance, while effective topologies only occupy a small portion of the entire search space.In mathematical problems, Gemini 1.5 Pro compared agents that only used self-consistency (SC), self-refinement (reflect), and multi-agent debate (debate) for expansion, demonstrating the relationship between the accuracy of prompt-optimized agents and the total number of labels for each problem. The error bars represent one standard deviation. We show that with more effective prompts, utilizing more computational resources can achieve higher accuracy.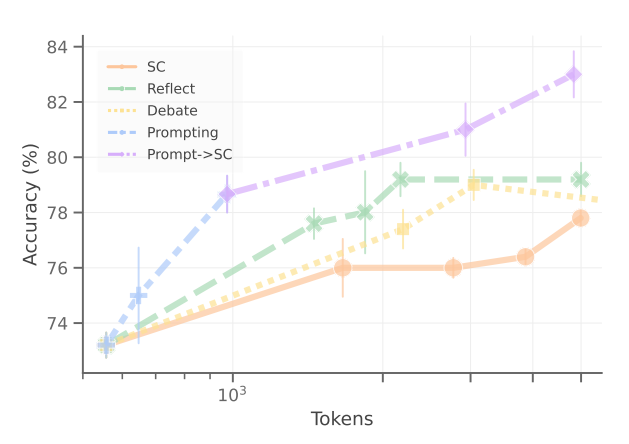 Performance of different topologies using Gemini 1.5 Pro compared to baseline agents, each topology was optimized through APO, where “Sum.” (summary) and “Exe.” (executor) are task-specific topologies as shown in Figure 4. We observed that not all topologies positively impact multi-agent system (MAS) design.
Performance of different topologies using Gemini 1.5 Pro compared to baseline agents, each topology was optimized through APO, where “Sum.” (summary) and “Exe.” (executor) are task-specific topologies as shown in Figure 4. We observed that not all topologies positively impact multi-agent system (MAS) design.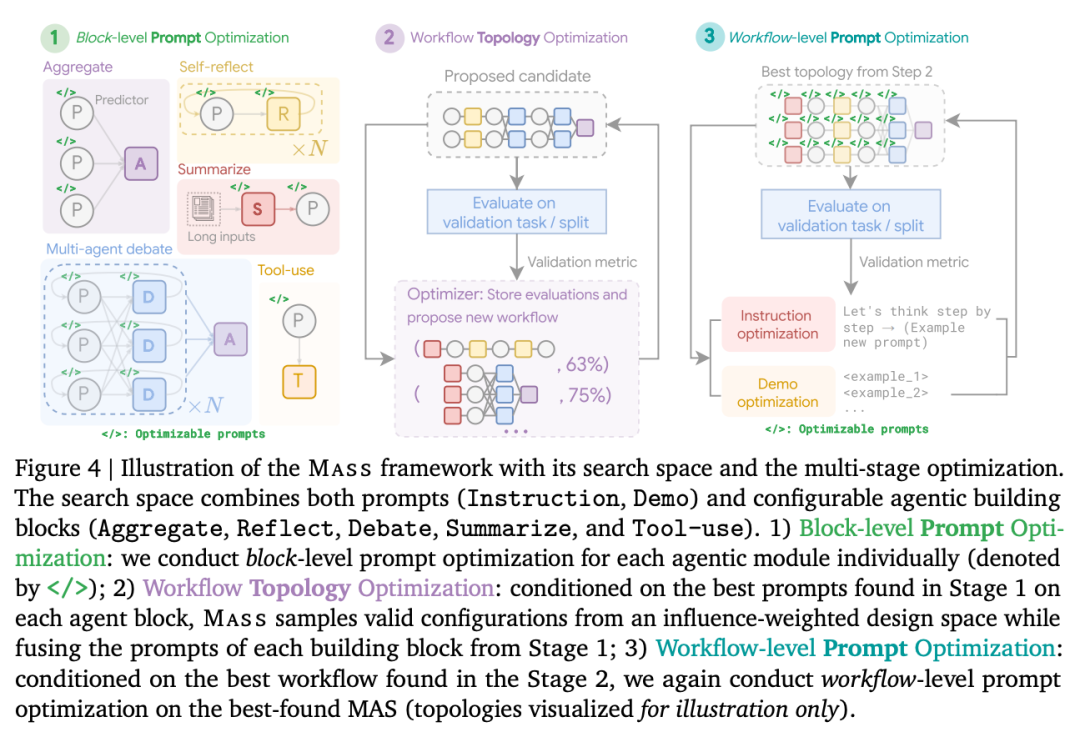
Based on these findings, Google & Cambridge University proposed the Mass framework, which optimizes MAS through three stages:
-
Block-level (local) prompt optimization: Optimizing prompts for agents within each topology block.
-
Workflow topology optimization: Optimizing workflow topologies within the pruned topology space.
-
Workflow-level (global) prompt optimization: Conducting global prompt optimization on the identified best topology.

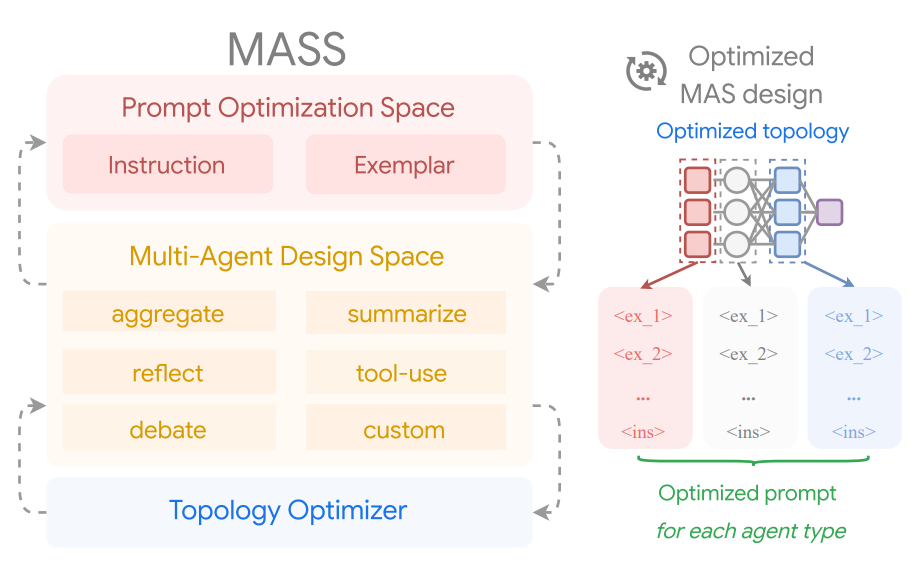 The proposed multi-agent system search (Mass) framework discovers effective multi-agent system designs by interleaving prompt optimization and topology optimization within a customizable multi-agent design space (the right side shows optimized topologies and optimized prompts, with key components shown on the left).
The proposed multi-agent system search (Mass) framework discovers effective multi-agent system designs by interleaving prompt optimization and topology optimization within a customizable multi-agent design space (the right side shows optimized topologies and optimized prompts, with key components shown on the left).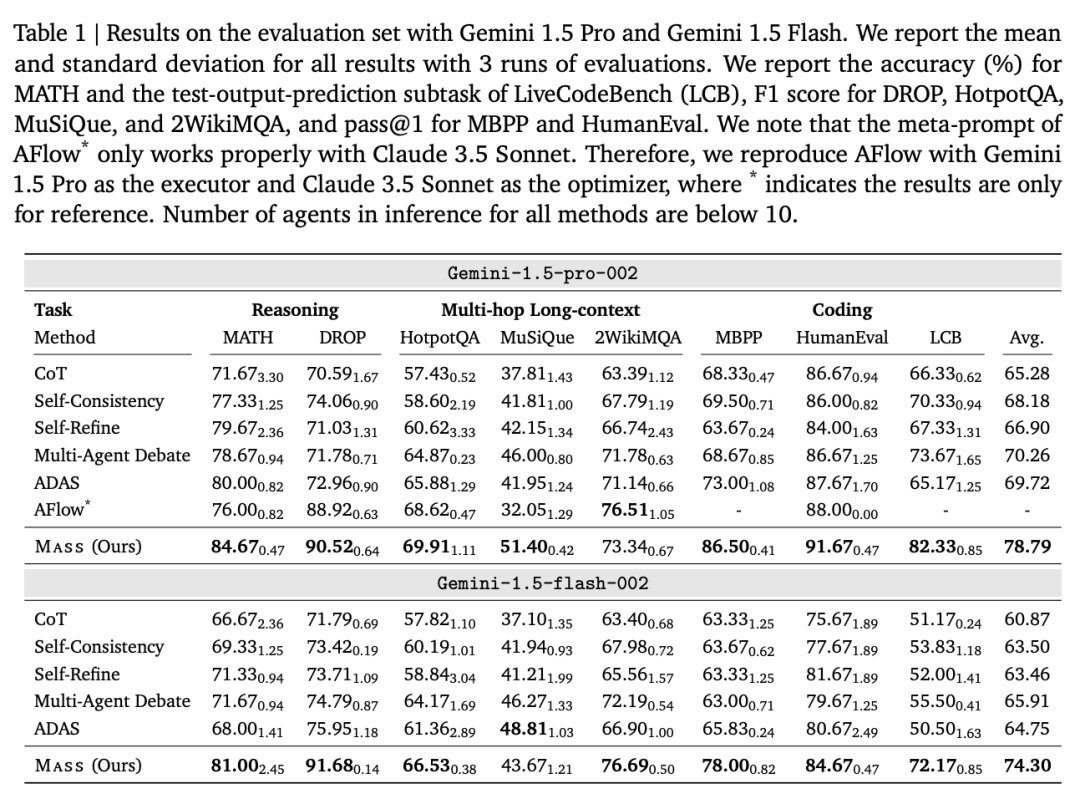
The experiments used Gemini 1.5 Pro and Flash models and compared them with various existing methods, including chain-of-thought (CoT), self-consistency (SC), self-refinement (Self-Refine), multi-agent debate (Multi-Agent Debate), ADAS, and AFlow.

-
Performance improvement: Mass significantly outperformed existing methods on multiple tasks, with an average performance improvement of over 10%.
-
Importance of optimization stages: Through phased optimization, Mass achieved performance improvements at each stage, demonstrating the necessity of optimization from local to global.
-
Co-optimization of prompts and topologies: Mass achieved better performance by simultaneously optimizing prompts and topologies compared to optimizing them separately.
-
Cost-effectiveness: Mass demonstrated stable and effective performance improvements during optimization, showing higher sample efficiency and cost-effectiveness compared to existing automated design methods.


Technical Group Invitation

△ Long press to add the assistant
Scan the QR code to add the assistant on WeChat
Please note:Name – School/Company – Research Direction(e.g., Xiao Zhang – Harbin Institute of Technology – Dialogue Systems)to apply for joining Natural Language Processing/Pytorch and other technical groups
About Us
MLNLP community is a grassroots academic community jointly built by scholars in machine learning and natural language processing from both domestic and international backgrounds. It has developed into a well-known community for machine learning and natural language processing, aiming to promote progress between the academic and industrial sectors of machine learning and natural language processing.The community provides an open communication platform for practitioners in further education, employment, and research. Everyone is welcome to follow and join us.