Why is a Software Version Number Important?
Generating a software version number is a crucial task in the software development and maintenance process. It has many meanings and benefits, as well as various common methods.
-
Identification and Tracking: A software version number serves as a unique identifier to distinguish different versions of the software. This helps developers and users identify and track different release versions of the software. When issues arise, it becomes easier to pinpoint bugs or improvements in a specific version.
-
Communication and Documentation: Version numbers provide a simple and clear way to communicate with team members, users, and other stakeholders. Through version numbers, people can clearly understand which version of the software is being discussed, making collaboration and problem-solving easier.
-
Release Planning: Version numbers can be used to formulate and execute software release plans. By setting version numbers, teams can plan which features and improvements will be included in specific versions and when these versions will be released.
-
User Expectation Management: Version numbers can be used to manage user expectations. Users can understand new features, improvements, and bug fixes based on the version number. This helps users know whether they need to upgrade or take other actions.
-
Software Stability: A well-designed version number system can distinguish between major versions, minor versions, and revision versions. This helps users quickly identify whether significant changes that may introduce instability have occurred.
Common Methods for Generating Software Version Numbers
-
Semantic Versioning (SemVer): SemVer is a popular versioning scheme typically composed of three parts: major version, minor version, and patch number, for example, 1.2.3. An increase in the major version indicates incompatible changes, an increase in the minor version indicates backward-compatible feature additions, and an increase in the patch number indicates backward-compatible bug fixes.
-
Date Versioning: Using the date as part of the version number, such as 2023.09.11, allows people to easily know the release date of the software. This is useful for working on or testing versions before or after a specific date.
-
Custom Versioning: Some teams and organizations use custom versioning schemes tailored to their needs. This may include project identifiers, build numbers, branch information, etc.
-
Pre-release Versions and Metadata: Sometimes, version numbers may include pre-release versions and metadata to further detail the software’s status and features. For example, 1.2.3-beta1 indicates a pre-release version, while 1.2.3+build456 indicates a version with a build number.
-
Language-Specific Versioning: Certain programming languages and tools have their own versioning specifications that developers should follow to ensure compatibility with related tools.
How to Generate Date Version Numbers in Microcontrollers
First, Introduce Two Common Macro Definitions in C Language
In C language, there are some special macro definitions used to obtain information such as the current compilation date and time. Here are two common macro definition examples:
-
__DATE__ Macro:
printf("Compilation Date: %s\n", __DATE__);This macro is replaced at compile time with a string representing the date the source code was compiled. Typically, its format is similar to “Sep 11 2023”, indicating the month, day, and year.
-
__TIME__ Macro:
printf("Compilation Time: %s\n", __TIME__);This macro is replaced at compile time with a string representing the time the source code was compiled. Typically, its format is similar to “12:34:56”, indicating hours, minutes, and seconds.
These macros can be used to log the compilation date and time in the code, which is very useful for debugging and version management.
Specific Implementation
#include "version.h"
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void Get_Compile_Date_Base(uint8_t *Year, uint8_t *Month, uint8_t *Day)
{
//Sep 11 2023
const char *pMonth[] = {"Jan", "Feb", "Mar", "Apr", "May", "Jun", "Jul", "Aug", "Sep", "Oct", "Nov", "Dec"};
const char Date[12] = __DATE__;//Get compilation date
uint8_t i;
for(i = 0; i < 12; i++)if(memcmp(Date, pMonth[i], 3) == 0)*Month = i + 1, i = 12;
*Year = (uint8_t)atoi(Date + 9); //Date[9] is the two-digit year, Date[7] is the full year
*Day = (uint8_t)atoi(Date + 4);
}
void Get_Compile_Time_Base(uint8_t *HH, uint8_t *MM, uint8_t *SS)
{
//15:40:23
const char Time[10] = __TIME__;//Get compilation time
*HH = (uint8_t)atoi(Time + 0);
*MM = (uint8_t)atoi(Time + 3);
*SS = (uint8_t)atoi(Time + 6);
}
char g_date_buf[10];
char g_time_buf[10];
char g_version_buf[20];
char* Get_Compile_Date(void)
{
uint8_t Year, Month, Day;
Get_Compile_Date_Base(&Year, &Month, &Day);//Get compilation date
sprintf(g_date_buf, "20%02d-%02d-%02d", Year, Month, Day);//Format arbitrarily
return g_date_buf;
}
char* Get_Compile_Time(void)
{
uint8_t HH, MM, SS;
Get_Compile_Time_Base(&HH, &MM, &SS);//Get compilation time
sprintf(g_time_buf, "%02d:%02d:%02d", HH, MM, SS);//Format arbitrarily
return g_time_buf;
}
char* Get_Compile_Ver(void)
{
uint8_t Year, Month, Day;
uint8_t HH, MM, SS;
Get_Compile_Date_Base(&Year, &Month, &Day);//Get compilation date
Get_Compile_Time_Base(&HH, &MM, &SS);//Get compilation time
sprintf(g_version_buf, "20%02d-%02d-%02d-%02d-%02d-%02d",Year, Month, Day, HH, MM, SS);//Format arbitrarily
return g_version_buf;
}#ifndef _VERSION_H_
#define _VERSION_H_
#include "stm32f4xx.h"
char* Get_Compile_Date(void);
char* Get_Compile_Time(void);
char* Get_Compile_Ver(void);
#endifImplementation Results
printf("RI QI:%s\r\n",__DATE__);
printf("SHI JIAN:%s\r\n",__TIME__);
printf("#############################Test#########################\r\n");
printf("RI QI:%s\r\n",Get_Compile_Date());
printf("SHI JIAN:%s\r\n",Get_Compile_Time());
printf("Soft Version:%s\r\n",Get_Compile_Ver());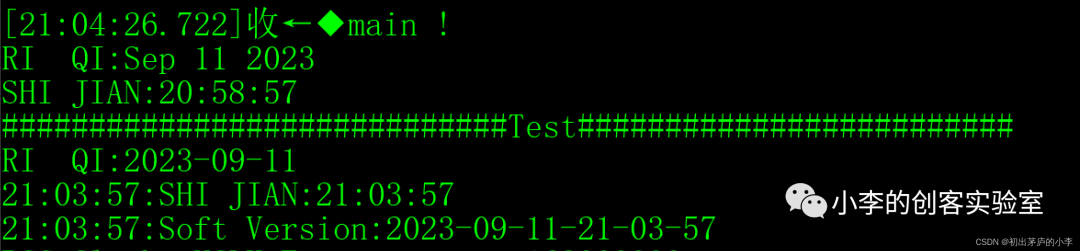 The compilation time is: September 11, 2023, 21:03:57 (just now)
The compilation time is: September 11, 2023, 21:03:57 (just now)
Other Methods (Direct Macro Definition Implementation)
Reference Blog: http://t.csdn.cn/BNv0F
Previous Articles: Basic Knowledge of Embedded Systems: Number Systems and Encoding, Introduction to USB Basics, Implementing Color Effects with WS2812B Using STM32CubeMx (Detailed), Domestic Microcontroller (Qin Heng Micro WCH) CH32V307 Evaluation Board Serial Port Usage