 WeChat Official Account:Electromagnetic Compatibility Home
WeChat Official Account:Electromagnetic Compatibility Home
Issue 2778
1.Problem Description
An industrial display screen experienced blue screen issues and system crashes during ESD (Electrostatic Discharge) testing, with ±6kV contact discharge applied to the network port, USB, and serial port. The system could recover after a power cycle, but the tests failed.
This issue has persisted for six months, during which the client company and the solution provider have made four revisions (from V1.0 to V1.31), investing significant resources without resolution. Time is of the essence.
2.Troubleshooting
Considering that previous modifications focused on grounding, filtering, and isolation without improvement, we suspect that the single board has ESD vulnerabilities. Therefore, we decided to adopt a sensitive source diagnosis and remediation approach to address the issue at its root.
Based on the experimental phenomena, we determined that the CPU functional unit was being interfered with. Analyzing the signal pins of the core sub-board (CPU module circuit) from practical experience and signal functionality, we identified that the signals listed in Table 1 are particularly sensitive and prone to electrostatic interference.
Table 1: Sensitive Signals Prone to ESD Interference
|
Index |
Network Name |
Signal Function |
ESD Sensitive |
|
1 |
LCD_HSYNC |
LCD horizontal sync signal |
YES |
|
2 |
LCD_VSYNC |
LCD vertical sync signal |
YES |
|
3 |
I2C_SDA |
I2C bus bidirectional data signal |
YES |
|
4 |
I2C_CLK |
I2C bus clock signal |
YES |
|
5 |
LCD_EN |
LCD enable signal |
YES |
|
6 |
LCD_CLK |
LCD clock signal |
YES |
|
7 |
VCC_3V3_MPU |
3.3V power supply for MPU unit |
YES |
|
8 |
eDP_RESET |
eDP interface reset signal |
YES |
We adjusted the ESD gun voltage to 100V, 300V, 600V, and 1000V, applying contact discharge to the signal pins listed in Table 1 of the core sub-board to identify ESD sensitive signals, as shown in Figure 1.
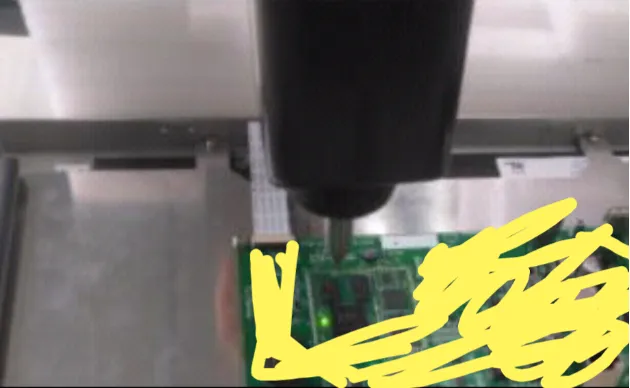
Figure 2: Contact Discharge on IC Pins
During the experiment, the issue did not recur, thus ruling out problems with these signals. The test records are shown in Table 2.
Table 2: ESD Sensitive Signal Verification Results
|
Index |
Network Name |
100V |
300V |
600V |
1000V |
|
1 |
LCD_HSYNC |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
2 |
LCD_VSYNC |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
3 |
I2C_SDA |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
4 |
I2C_CLK |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
5 |
LCD_EN |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
6 |
LCD_CLK |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
7 |
VCC_3V3_MPU |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
|
8 |
eDP_RESET |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Normal |
Continuing to analyze the sensitive circuits on the core sub-board, we found that when applying contact discharge of 100V to the sensitive signal DDR_CLK, the issue recurred, and it could be reproduced with each discharge.
The DDR_CLK trace is 4 mil, and there are no reserved pads for the trace, limiting our remediation options. To determine if the electrostatic radiation electromagnetic field affects the DDR_CLK clock signal, we used a metal grounding wire placed directly above the DDR_CLK trace and discharged the ESD gun onto the copper terminal of the grounding wire, as shown in Figure 3.
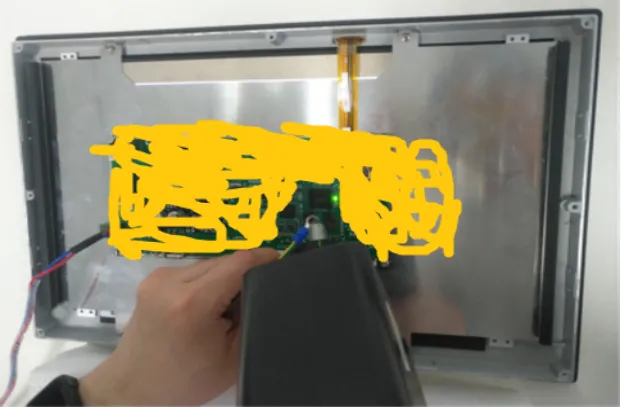

Figure 3: Contact Discharge on Grounding Wire Copper Terminal
Using the method shown in Figure 3, during 6kV contact discharge, the issue could be reproduced in all five discharges. Therefore, we confirmed that the electrostatic electromagnetic field radiation affects the DDR_CLK signal and DDR devices. At this point, we used copper foil to shield the core board area and ground it to protect the sensitive DDR signals and modules, as shown in Figure 4.
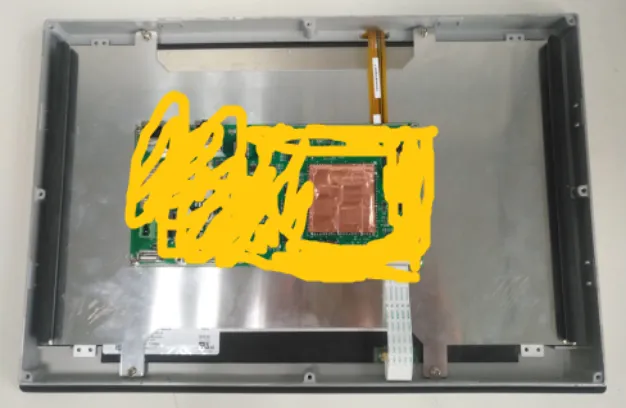

Figure 4: Core Board Module Shielding
After shielding the core board module area, we performed contact discharge tests at ±6kV, 8kV, and 10kV on the I/O interfaces, with each series of 40 discharges, and the system operated normally, resolving the issue. Thus, we determined that the core board was affected by electrostatic interference, causing the entire system to crash.
3.Cause Analysis
We continued to verify whether the entire system ESD was due to radiation coupling or capacitive coupling. Analysis showed that the system’s electrostatic discharge leakage path was I/O interface — single board PGND — metal chassis — chassis cover — grounding wire, as shown in Figure 5.
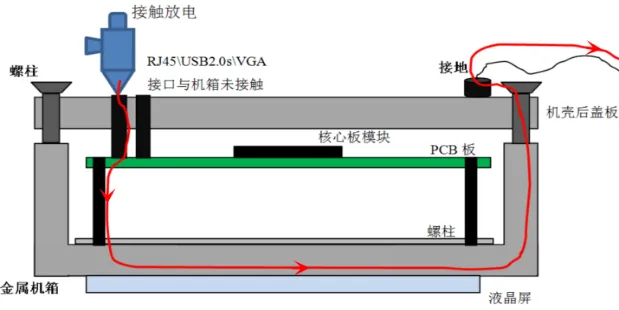
Figure 5: Entire System Electrostatic Discharge Leakage Path
When the chassis cover is not screwed to the metal chassis or is left uncovered, we found that there were no issues with electrostatic discharge, thus ruling out radiation coupling. At this point, the electrostatic leakage path was I/O interface — single board PGND — metal chassis, indicating that there was no capacitive coupling between the sensitive parts of the core board DDR and the chassis cover (the two are very close), as shown in Figure 6.
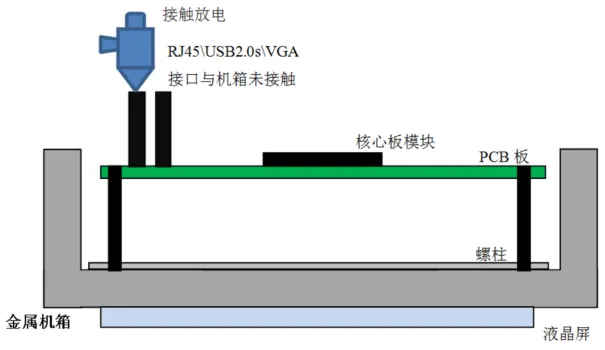
Figure 6: Electrostatic Leakage Path Without the Back Cover
Based on the above, the simplified model of the electrostatic coupling of the core sub-board is shown in Figure 7.
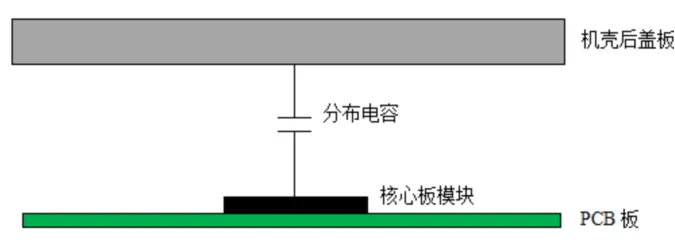
Figure 7: Core Sub-Board Electrostatic Coupling Model
During diagnosis, after adding a shielding cover to the core sub-board, the electrostatic coupling model is shown in Figure 8.
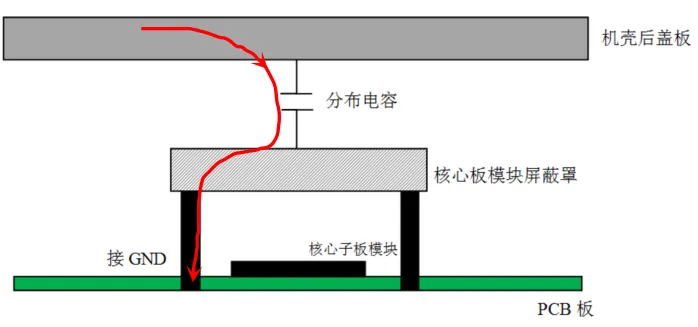
Figure 8: Core Sub-Board Electrostatic Coupling Model
From Figure 8, it can be seen that after adding a shielding cover to the core sub-board, the electrostatic energy from the chassis back cover is directly coupled to the metal shield and grounded through the shield’s grounding pin to GND, thus preventing ESD from directly coupling to the sensitive DDR module, resolving the issue. Therefore, based on the above analysis, the electrostatic interference from the chassis back cover is capacitively coupled to the DDR module circuit, leading to the ESD problem.
4.Remediation Measures
Since the core sub-board is a platform product of the client company, and the DDR circuit on the module is particularly sensitive, we recommend that the mainboard adopt a shielding cover to shield the sensitive core sub-board module for mass production. This solution is simple and feasible, with a cost increase of less than 0.5 yuan, and is reliable in effect. After communicating with the client, there is currently sufficient space on the mainboard for this solution to be produced. The shielding cover is shown in Figure 9.
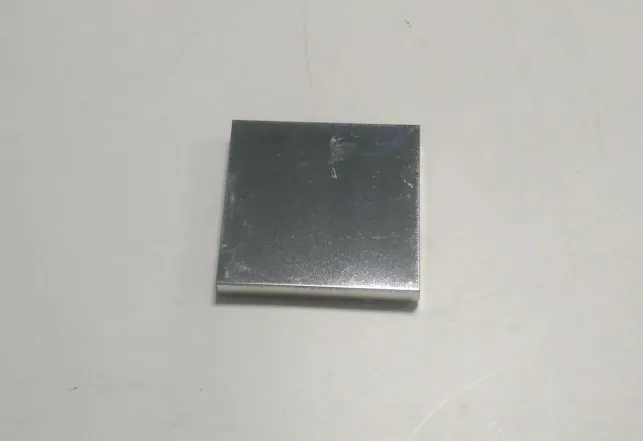

Figure 9: Core Board Shielding Cover
5.Practical Results
After the board modification, we conducted electrostatic tests again, and the system crash issue has not recurred, and the tests passed.
Summary
During ESD experiments, engineers often encounter issues where a single discharge causes a crash, and despite numerous PCB modifications, the problem remains unresolved, leading to frustration and self-doubt. Why? Because there are extremely sensitive weak points in the circuit regarding ESD. Without targeting the root cause, how can one conquer the problem? In this case study, the ESD issue was diagnosed and analyzed meticulously, identifying sensitive sources and coupling paths, and successfully resolved through shielding the sensitive sources. This article’s remediation methods and thought process remind us that to strike effectively, one must aim for the critical point; if one takes action, it must be decisive and impactful, with the first battle determining the outcome.



Some Electronic Book Screenshots

Complete Set of Hardware Documentation Collection
