Skip to content
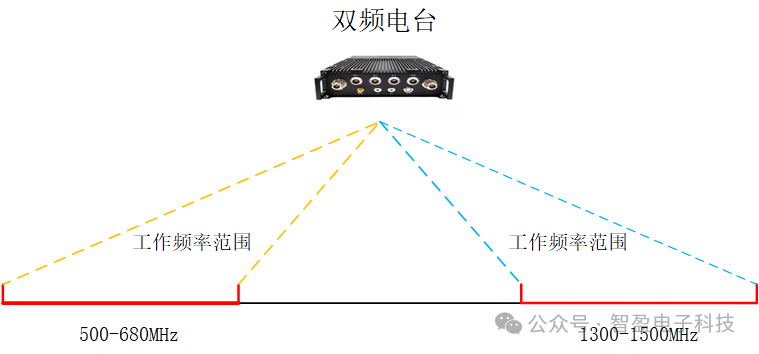
The dual-band broadband self-organizing network station is based on a general SDR platform (divided into non-domestic and domestic) that employs COFDM, diversity reception, MIMO, dynamic TDMA, intelligent routing, and intelligent anti-jamming technologies. The operating frequencies are 500~680MHz and 1300~1500MHz. (Utilizing a single baseband board, not two radios combined together)
It innovatively adopts unique and excellent RF filtering technology, focusing on the following aspects:
High Selectivity Filtering: Effectively suppresses out-of-band interference signals, enhancing the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR).
Low Insertion Loss Design: Minimizes signal power loss while ensuring filtering performance.
Band Optimization: Designs specialized filters for the different characteristics of the U band and L band to achieve optimal communication performance.
Band Selectivity: The station can operate in the 500~680MHz and 1300~1500MHz bands, requiring the RF filter design to ensure good passband characteristics within these two bands while effectively suppressing interference signals from other bands.
Dynamic Adjustment Capability: The station uses intelligent anti-jamming technology, allowing it to dynamically adjust operating frequencies based on real-time channel conditions. The RF filter must have a rapid response capability to adapt to quick frequency switching.
High Performance Requirements: In complex electromagnetic environments, RF filters must possess high selectivity and low insertion loss to ensure signal clarity and stability, enhancing communication reliability.
Integrated Design: With the trend towards miniaturization of devices, the integrated design of RF filters has become an important consideration. The RF filter in the dual-band broadband self-organizing network station must minimize size while ensuring performance to fit compact device designs.
After adopting this technology, it is possible to select appropriate frequency points for different application environments, leveraging the strong diffraction and penetration capabilities of the U band radio while utilizing the cleaner spectral characteristics of the L band to achieve higher transmission rates. At the same time, it can implement adaptive frequency selection and cross-band fast hopping anti-jamming technology in the U and L bands, further enhancing the anti-jamming capabilities of the communication network.

