Skip to content


During debugging, various interfaces and conversion boards are encountered, and the feeling of not fully understanding can be quite frustrating!
First, serial ports, UART ports, COM ports, and USB ports refer to physical interface forms (hardware). TTL, RS-232, and RS-485 refer to level standards (electrical signals).
Serial Port: The term serial port is a general term; UART, TTL, RS232, and RS485 all follow similar communication timing protocols, thus they are collectively referred to as serial ports.
UART Interface: Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter (UART) is the logical circuit for serial transmission. This part can be a standalone chip or embedded as a module within other chips; microcontrollers, SOCs, and PCs all have UART modules.
COM Port: Specifically refers to the D-SUB shaped serial communication port on desktop computers or some electronic devices, applying serial communication timing and RS232 logic levels.
USB Port: Universal Serial Bus, completely a different concept from serial ports. Although it also communicates in a serial manner, the communication timing and signal levels of USB are entirely different from those of serial ports, thus they have no relation. USB is a high-speed communication interface used for connecting various peripherals to PCs, including USB drives, mice, keyboards, external hard drives, and of course, the “USB to Serial” module (the USB to Serial module is a UART module for USB).
TTL, RS232, and RS485 are all representations of logical levels.
TTL: TTL refers to Transistor-Transistor Logic. Many “USB to TTL” modules on the market are actually “USB to TTL level serial” modules. In this case, the signal 0 corresponds to 0V, and 1 corresponds to 3.3V or 5V. It is compatible with the IO levels of microcontrollers and SOCs. However, it may not necessarily be TTL level, as most digital logic today is made with CMOS technology, only retaining the TTL nomenclature. When we communicate via serial, the levels coming directly from the microcontroller are generally TTL levels.
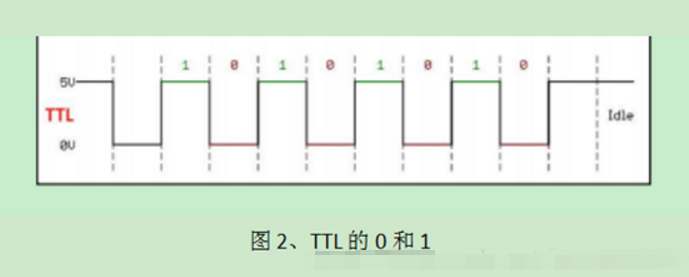
TTL Level: Full duplex (logic 1: 2.4V–5V, logic 0: 0V–0.5V)
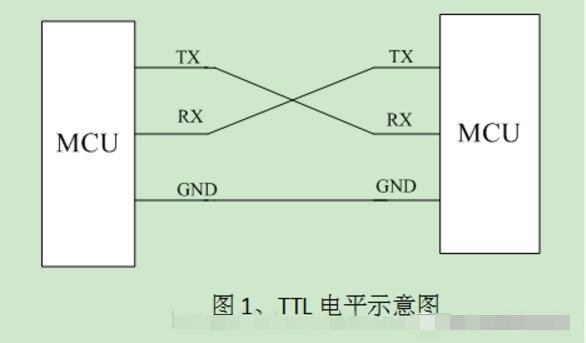
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows, TTL used for communication between two MCUs.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
RS232: This is an asynchronous transmission standard interface established by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA), which corresponds to both level standards and communication protocols (timing). The level standard is: +3V~+15V corresponds to 0, -3V~-15V corresponds to 1. The logic levels of RS232 differ from TTL, but the protocol is the same.
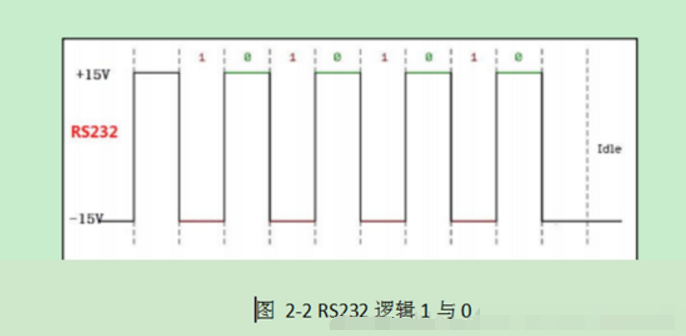
RS-232 Level: Full duplex (logic 1: -15V–5V, logic 0: +3V–+15V)
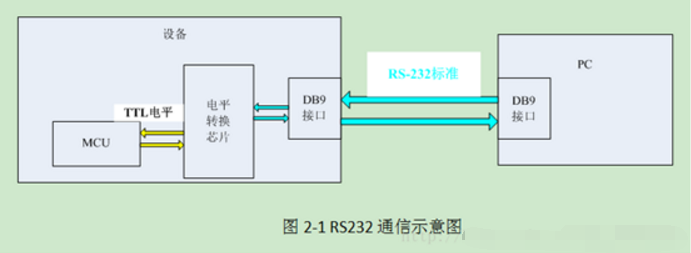
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows, TTL used for communication between MCU and PC.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
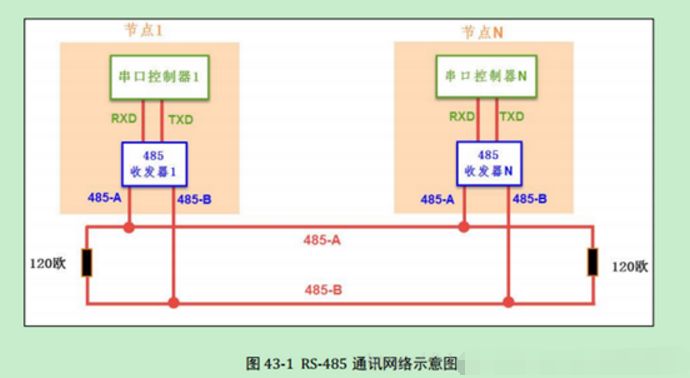
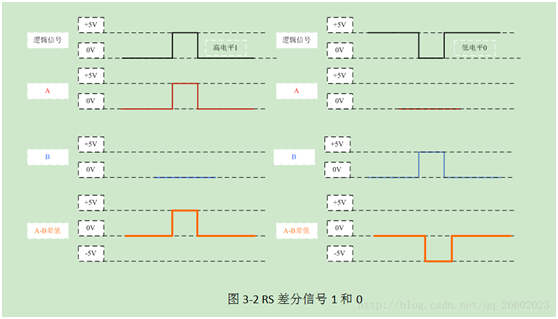
RS485: RS485 is a serial interface standard that uses differential signaling for long-distance transmission, providing much better noise immunity than RS232. A differential voltage of -(2~6)V indicates 0, while a differential voltage of +(2~6)V indicates 1.
RS-485: Half duplex (logic 1: +2V–+6V, logic 0: -6V—2V), where the level refers to the voltage difference between lines A and B.
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
COM port refers to the serial communication port, commonly known as the serial port. This is distinct from USB’s “Universal Serial Bus” and the hard drive’s “SATA”.
Generally, we see two physical standards: the D-type 9-pin connector and the 4-pin DuPont connector.
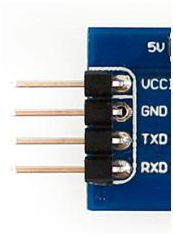
This is a common 4-pin serial port, often found on circuit boards, sometimes with DuPont pins. Occasionally, there might be a fifth pin for a 3.3V power supply.
Since this is reserved on the circuit board, there can be many types of protocols depending on the specific device.
In embedded systems, the term serial port generally refers to the UART port, but we often confuse it with the COM port, as well as the relationships with RS232, TTL, etc. In fact, UART and COM refer to physical interface forms (hardware), while TTL and RS-232 refer to level standards (electrical signals).
UART has 4 pins (VCC, GND, RX, TX), using TTL levels, where low level is 0 (0V) and high level is 1 (3.3V or above).
The following is a D-type 9-pin serial port (colloquial term). You can see this at the back of desktop computers. Remember, the protocol for this type of interface is only two: RS-232 and RS-485. It will not be TTL level (unless for special applications). The definition of the 9-pin serial port can be referenced here:
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/5c170c6925c52cc58bd6be6e.html
We generally only connect RXD and TXD pins, plus GND.
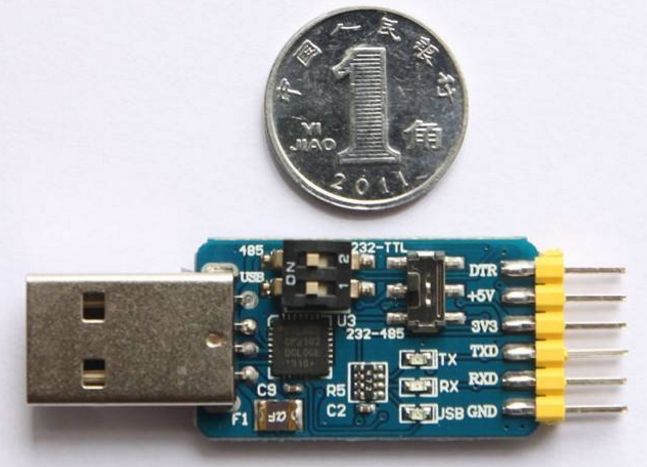
The following image shows a USB to TTL serial board, which can expand a serial port via USB. The chip is PL2303HX. Various serial ports are often confused online, but this one can indeed be used to download programs to STC microcontrollers.
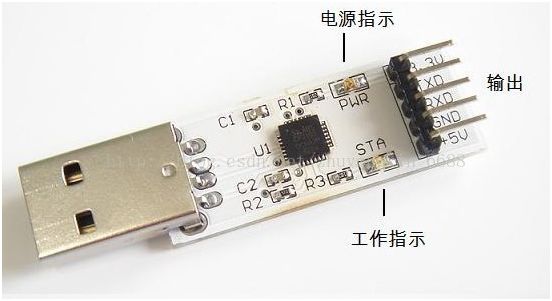
This is another type, the CP2102 chip, which is also a USB to TTL serial port. It is said to be better than PL2303, but in practical use, I haven’t felt much difference. This small board also has a +3.3V power supply pin to accommodate different target circuits. The following image shows a USB to RS-232 serial port:
‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧ END ‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧