Welcome FPGA engineers to join the official WeChat technical group.
Clickthe blue textto follow us at FPGA Home – the best and largest pure FPGA engineering community in China
During debugging, you will always encounter various interfaces and conversion boards, and the feeling of not fully understanding can be very frustrating!
First, serial ports, UART ports, COM ports, and USB ports refer to physical interface forms (hardware). TTL, RS-232, and RS-485 refer to level standards (electrical signals).
Serial Port: The serial port is a general term; UART, TTL, RS232, and RS485 all follow similar communication timing protocols, so they are collectively referred to as serial ports.
UART Interface: Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, UART is the logical circuit for serial communication. This part can be a standalone chip or embedded as a module in other chips. Microcontrollers, SOCs, and PCs all have UART modules.
COM Port: Specifically refers to the D-SUB shaped (a type of connector structure, the connector for VGA interfaces is also D-SUB) serial communication port on desktop computers or some electronic devices, which applies serial communication timing and RS232 logical levels.
USB Port: Universal Serial Bus, which is a completely different concept from the serial port. Although it also communicates in a serial manner, the communication timing and signal levels of USB are entirely different from those of the serial port, hence there is no relation. USB is a high-speed communication interface used for PCs to connect various peripherals, USB flash drives, mice, keyboards, external hard drives, and of course, it also includes “USB to Serial” modules. (The USB to Serial module is a USB interface UART module)
TTL, RS232, and RS485 are all representations of logical levels.
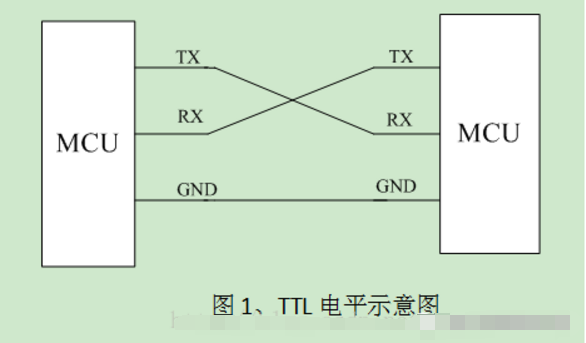
TTL: TTL refers to Transistor-Transistor Logic. Many “USB to TTL” modules on the market are actually “USB to TTL level serial” modules. In such signals, 0 corresponds to 0V, and 1 corresponds to 3.3V or 5V. It is compatible with the IO levels of microcontrollers and SOCs. However, it may not always be TTL levels because most digital logic is now made using CMOS technology, just continuing to use the term TTL. When we perform serial communication, the output from the microcontroller is basically TTL level.
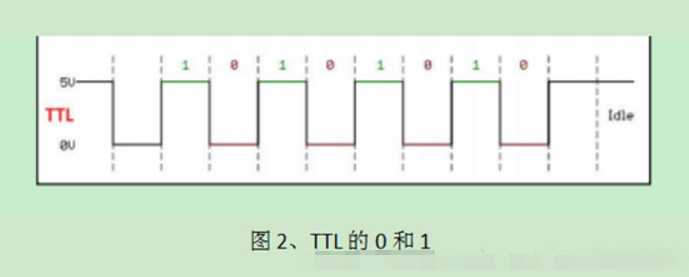
TTL Level: Full duplex (logic 1: 2.4V–5V logic 0: 0V–0.5V)
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows, TTL is used for communication between two MCUs.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
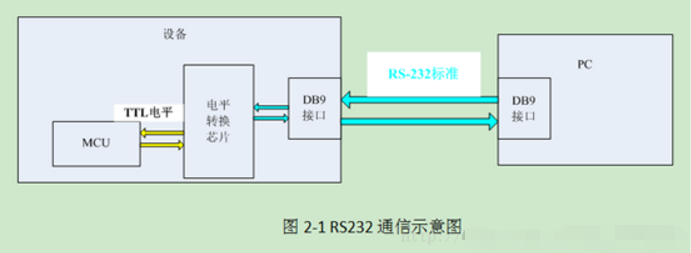
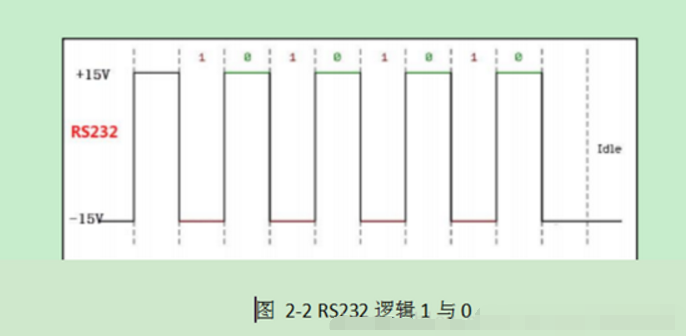
RS232: is an asynchronous transmission standard interface established by the Electronic Industries Association (EIA), which corresponds to both level standards and communication protocols (timing). The level standard is: +3V~+15V corresponds to 0, -3V~-15V corresponds to 1. The logical levels of RS232 differ from TTL, but the protocol is the same.
RS-232 Level: Full duplex (logic 1: -15V–5V logic 0: +3V–+15V)
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows, TTL is used for communication between MCU and PC.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
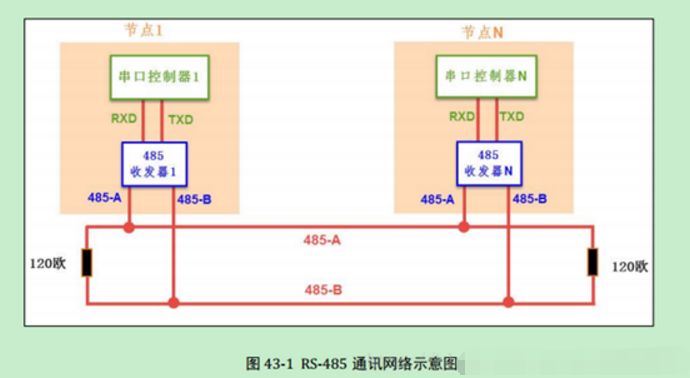
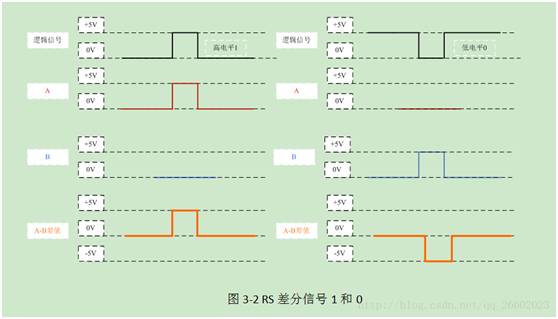
RS485: RS485 is a serial interface standard that uses differential signaling for long-distance transmission, which has much stronger anti-interference capability than RS232. A differential voltage of -(2~6)V represents 0, and + (2~6)V represents 1.
RS-485: Half duplex (logic 1: +2V–+6V logic 0: -6V—2V) here the level refers to the voltage difference between wires A and B.
1. The hardware block diagram is as follows.
2. ‘0’ and ‘1’ representation.
COM port refers to the serial communication port, abbreviated as serial port. This is different from USB’s “Universal Serial Bus” and the hard disk’s “SATA”.
Generally, we see two types of physical standards. D-type 9-pin connectors and 4-pin Dupont connectors.
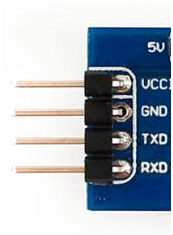
This is a common 4-pin serial port, often seen on circuit boards, and often has Dupont pins on top. Sometimes there is a fifth pin for the 3.3V power supply.
Since this is reserved on the circuit board, the protocol can vary, depending on the specific device.
In embedded systems, the serial port usually refers to the UART port, but we often confuse it with the COM port, as well as the relationships with RS232, TTL, etc. In fact, UART and COM refer to physical interface forms (hardware), while TTL and RS-232 refer to level standards (electrical signals).
UART has 4 pins (VCC, GND, RX, TX), using TTL levels, with low level as 0 (0V) and high level as 1 (3.3V or above).
The following is the D-type 9-pin serial port (commonly referred to). You can see it behind desktop computers. Remember, the protocols for this type of interface are only two: RS-232 and RS-485. It will not be TTL level (unless for special applications). The definition of the 9-pin serial port can be referred to here:
http://wenku.baidu.com/view/5c170c6925c52cc58bd6be6e.html
We generally only connect RXD and TXD pins, plus GND.
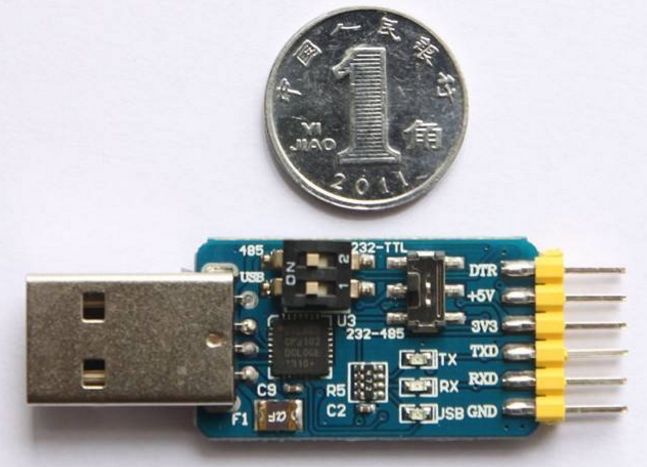
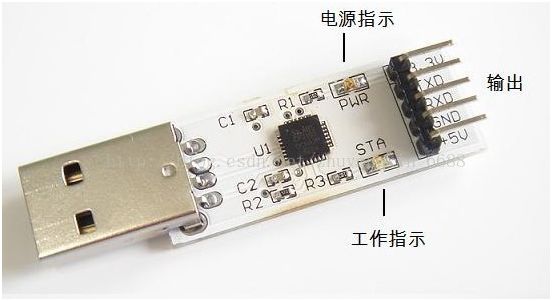
Below is a small board for USB to TTL serial, which can extend a serial port via USB. The chip is PL2303HX. Various serial ports are often confused online, but this one can indeed download programs to STC microcontrollers.
This is another type, the CP2102 chip, also a USB to TTL serial. It is said to be better than PL2303, but in actual use, I haven’t felt the difference. This small board also has a +3.3V power supply pin to accommodate different target circuits. The following image shows a USB to RS-232 serial:
‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧ END ‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧‧

Welcome communication engineers and FPGA engineers to follow our public account
The largest FPGA WeChat technical group in the country
Welcome everyone to join the national FPGA WeChat technical group, which has tens of thousands of engineers, a group of engineers who love technology, where FPGA engineers help and share with each other, creating a strong technical atmosphere! Hurry up and invite your friends to join!!
Press and hold to join the FPGA national technical group!
FPGA Home Components City
Advantageous components services, please scan to contact the group owner: Jin Juan Email: [email protected] Welcome to recommend to procurement
ACTEL, AD part advantageous ordering (operating the full series):
XILINX, ALTERA advantageous stock or ordering (operating the full series):
(The above components are part of the models, for more models please consult group owner Jin Juan)
Service concept: FPGA Home components self-operated city aims to facilitate engineers to quickly and conveniently purchase components services. After years of dedicated service, our customer service is spread across major listed companies, military research units, and small and medium-sized enterprises. Our greatest advantage is emphasizing a service-first concept and achieving fast delivery with favorable prices!
Direct-operated brands: Xilinx ALTERA ADI TI NXP ST E2V, Micron and more than a hundred component brands, especially skilled in dealing with components banned by the US and Europe. We welcome engineering friends to recommend us to procurement or consult us directly! We will continue to provide the best service in the industry!
Official thanks to brands of the FPGA technical group: Xilinx, intel (Altera), microsemi (Actel), Lattice, Vantis, Quicklogic, Lucent, etc.