On October 5, 2022, the Intelligent Processor Team of the Institute of Computing Technology, Chinese Academy of Sciences, received the Runner-up award for Best Paper for their paper titled Cambricon-P: A Bitflow Architecture for Arbitrary Precision Computing at the MICRO 2022 conference (CCF Class A), a flagship event in computer architecture.

Cambricon-P is a novel processor architecture designed for Arbitrary Precision Computing (APC). APC involves computations on data ranging from thousands to millions of bits, serving as a fundamental computational model for various scientific applications in fields such as mathematics, physics, chemistry, and biology. Current processors performing APC computations require breaking down the original high-bit-width data into smaller chunks to fit the low-bit-width arithmetic units of the hardware. This fine-grained decomposition inevitably introduces a large amount of intermediate data, leading to intensive on-chip data movement and long, complex computation dependency chains, resulting in very low hardware utilization.
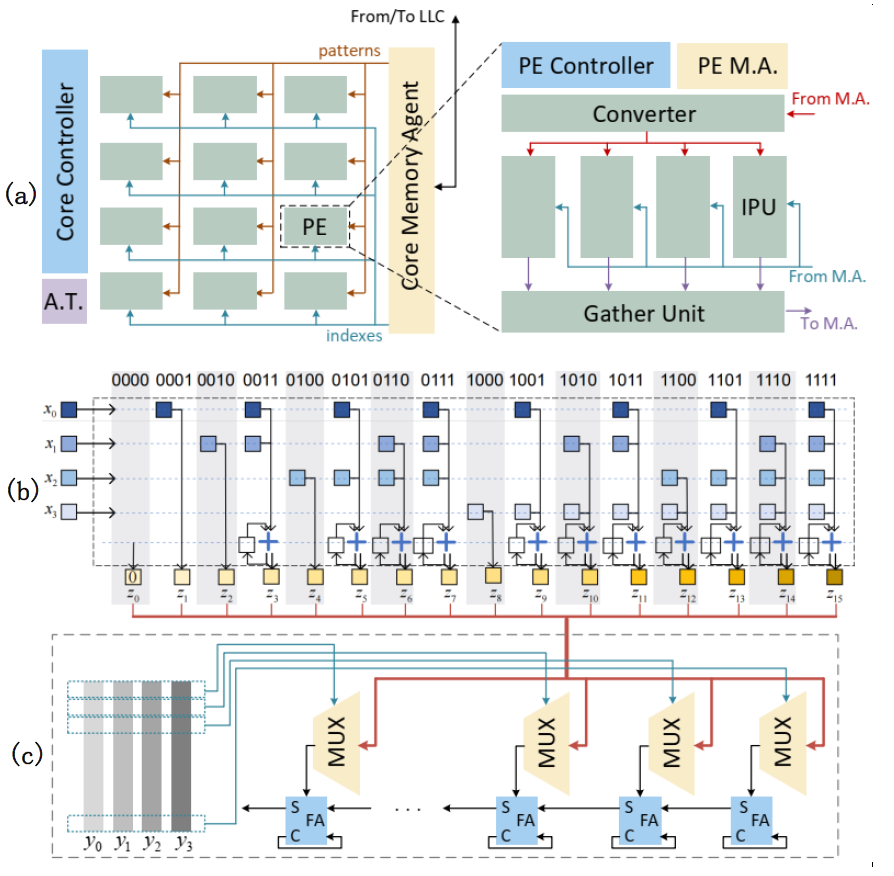
The Cambricon-P architecture proposed by the Institute of Computing Technology achieves flexible and efficient support for high-bit-width APC computations through serial bitstream processing. Cambricon-P employs a bit-indexed inner product unit, eliminating redundancy while enhancing parallel computation efficiency. Compared to general-purpose processors, Cambricon-P achieves at least an order of magnitude acceleration and hundreds of times improvement in energy efficiency for practical APC applications.
The Intelligent Processor Team of the Institute of Computing Technology has been deeply engaged in architecture research for many years, proposing the world’s first deep learning processor architecture (in collaboration with Inria, France) and developing the world’s first deep learning processor prototype chip. The Cambricon-P architecture proposed by the team showcases new opportunities for the integration of architecture and a wide range of scientific computing scenarios in the context of a new golden age of architecture.
Background: MICRO, ISCA, ASPLOS, and HPCA are recognized as the four major international academic conferences in the field of computer architecture, all classified as CCF Class A. MICRO is the oldest of these conferences. Since its inception in 1968, the 55 editions of the MICRO conference have published over 1900 papers. Historically, institutions from mainland China have only received the Best Paper award at these four conferences twice, specifically at ASPLOS 2014 (DianNao) and MICRO 2014 (DaDianNao), both awarded to the Intelligent Processor Team of the Institute of Computing Technology.
