01Basic Understanding Model:HS-S10PName:Fog SensorSeries:SensorDescription:This is a sensor device designed for detecting fog concentration. It has a built-in fog-sensitive element that converts the fog concentration signal into an electrical signal output by sensing the condensation state of water vapor in the air. It can monitor the fog level in real-time, providing environmental humidity and visibility perception capabilities for devices.Usage Scenarios:Linking street lights and traffic signals to automatically enhance brightness or trigger warnings in foggy weather(Smart Traffic), monitoring fog concentration in greenhouses to control ventilation equipment and adjust humidity to prevent crop mold(Agricultural Greenhouses), automatically switching to night vision mode when visibility is affected by fog in conjunction with cameras(Security Systems), etc.;Aligning withAI Education in Primary and Secondary Schools, compliant with“Guidelines for Artificial Intelligence General Education in Primary and Secondary Schools (2025 Edition),”by building fog monitoring devices and other projects to cultivate students’ understanding and practical skills in environmental perception technology.Disciplinary Integration:Physics, Chemistry, Labor, Information TechnologyEthical Education:Discussing sensor misjudgments(such as false triggers caused by high humidity non-fog environments)and their impact on traffic systems;analyzing the responsibility boundaries of fog monitoring data in public travel safety(such as decision biases caused by data delays);exploring technical limitations(such as detection failure in extreme fog conditions)and the risks to systems relying on this technology.
Model:HS-S10PName:Fog SensorSeries:SensorDescription:This is a sensor device designed for detecting fog concentration. It has a built-in fog-sensitive element that converts the fog concentration signal into an electrical signal output by sensing the condensation state of water vapor in the air. It can monitor the fog level in real-time, providing environmental humidity and visibility perception capabilities for devices.Usage Scenarios:Linking street lights and traffic signals to automatically enhance brightness or trigger warnings in foggy weather(Smart Traffic), monitoring fog concentration in greenhouses to control ventilation equipment and adjust humidity to prevent crop mold(Agricultural Greenhouses), automatically switching to night vision mode when visibility is affected by fog in conjunction with cameras(Security Systems), etc.;Aligning withAI Education in Primary and Secondary Schools, compliant with“Guidelines for Artificial Intelligence General Education in Primary and Secondary Schools (2025 Edition),”by building fog monitoring devices and other projects to cultivate students’ understanding and practical skills in environmental perception technology.Disciplinary Integration:Physics, Chemistry, Labor, Information TechnologyEthical Education:Discussing sensor misjudgments(such as false triggers caused by high humidity non-fog environments)and their impact on traffic systems;analyzing the responsibility boundaries of fog monitoring data in public travel safety(such as decision biases caused by data delays);exploring technical limitations(such as detection failure in extreme fog conditions)and the risks to systems relying on this technology.
02Technical Parameters
Water Vapor Sensing:
The fog-sensitive element of the sensor(such as a humidity-sensitive resistor or capacitor)changes its resistance or capacitance value when it comes into contact with fog, as the surface adsorbs water vapor;Signal Processing:The circuit converts the resistance/capacitance changes into electrical signals, which are amplified and processed by a comparator to output analog signals(which vary linearly with fog concentration)and digital signals(which trigger alarms at threshold levels).
Parameter Analysis:
G(GND): Power input negative/ground
V(VCC):Power input positive/positive terminal
S(Signal):Signal output interface
Detection Range: 0-100% relative fog concentration (corresponding visibility 10-1000 meters)Response Time: ≤5s, Recovery Time: ≤10s03Code Example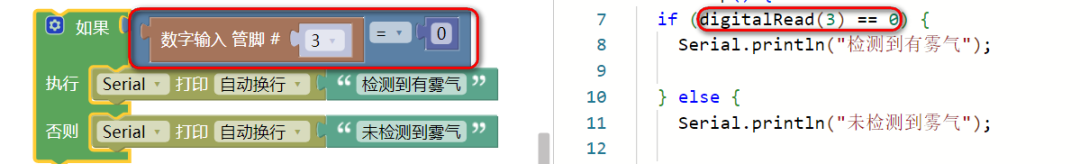
The connection pin is digital D3.
Note: Students should observe the two codes in the red box and compare the differences between the two equal signs by researching.
04Safety Measures
1.Always disconnect power when wiring, and confirm the polarity of VCC and GND; reversing connections can damage the internal circuit.;
2.Avoid using near high voltage environments to prevent electromagnetic interference from affecting detection accuracy.;
3.Operating temperature range 0℃~60℃; do not use in frosting or icing environments (must defrost first).;4.Avoid oil, corrosive gases to prevent contamination and failure of sensitive elements.;5.The sensor surface has a protective mesh; avoid touching or wiping the sensitive area with hands.;6.Regular calibration is required after long-term use to ensure detection accuracy.;7.Do not place liquids on the desktop to prevent seepage into the sensor and causing short circuits..05Expansion
Students can add an LED light that lights up when fog is detected.
 Arduino Sensor: HS-S01A Infrared SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S02P Infrared Sensor (Obstacle Avoidance)Arduino Sensor: HS-S03P Ultraviolet SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S05P Sound SensorArduino Sensor: HS-F07P Active BuzzerArduino Sensor: HS-S08P Flame SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S09LB Raindrop SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S09PC Soil Moisture Sensor
Arduino Sensor: HS-S01A Infrared SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S02P Infrared Sensor (Obstacle Avoidance)Arduino Sensor: HS-S03P Ultraviolet SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S05P Sound SensorArduino Sensor: HS-F07P Active BuzzerArduino Sensor: HS-S08P Flame SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S09LB Raindrop SensorArduino Sensor: HS-S09PC Soil Moisture Sensor
Arduino Sensor: HS-S11-L Gas Sensor
Arduino Sensor: HS-S26A Temperature and Humidity Sensor — Previous Recommendations —
— Previous Recommendations —