| In this issue, the author introduces the entire process of design to application of microrobots in medical systems, discussing the current technological level and the challenges faced. Microrobots, ranging in size from a few micrometers to several millimeters, can access complex anatomical areas within the human body that are difficult to reach, enabling targeted drug delivery, localized treatment, and precise monitoring. These robots possess excellent mobility, low invasiveness, and minimal tissue damage. By navigating through complex biological environments, microrobots can deliver therapies with unprecedented precision, improving treatment outcomes and patient prognosis. Furthermore, their small size allows for minimally invasive procedures, reducing recovery time and increasing patient comfort. |
Follow our official account and reply “microrobots” to obtain related papers
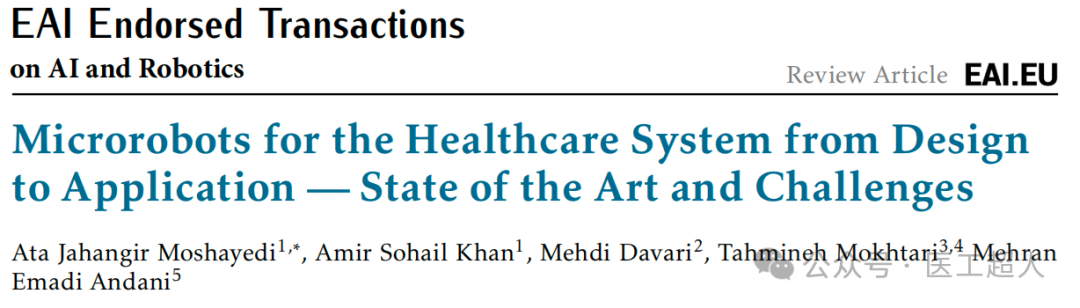
This article comprehensively explores the applications of microrobots in the medical field, from technological evolution, design requirements to specific cases and future development trends. It details various types of microrobots and their specific applications in diagnosis, treatment, and surgery, highlighting the potential of these advanced devices in improving disease management efficiency and patient treatment quality.
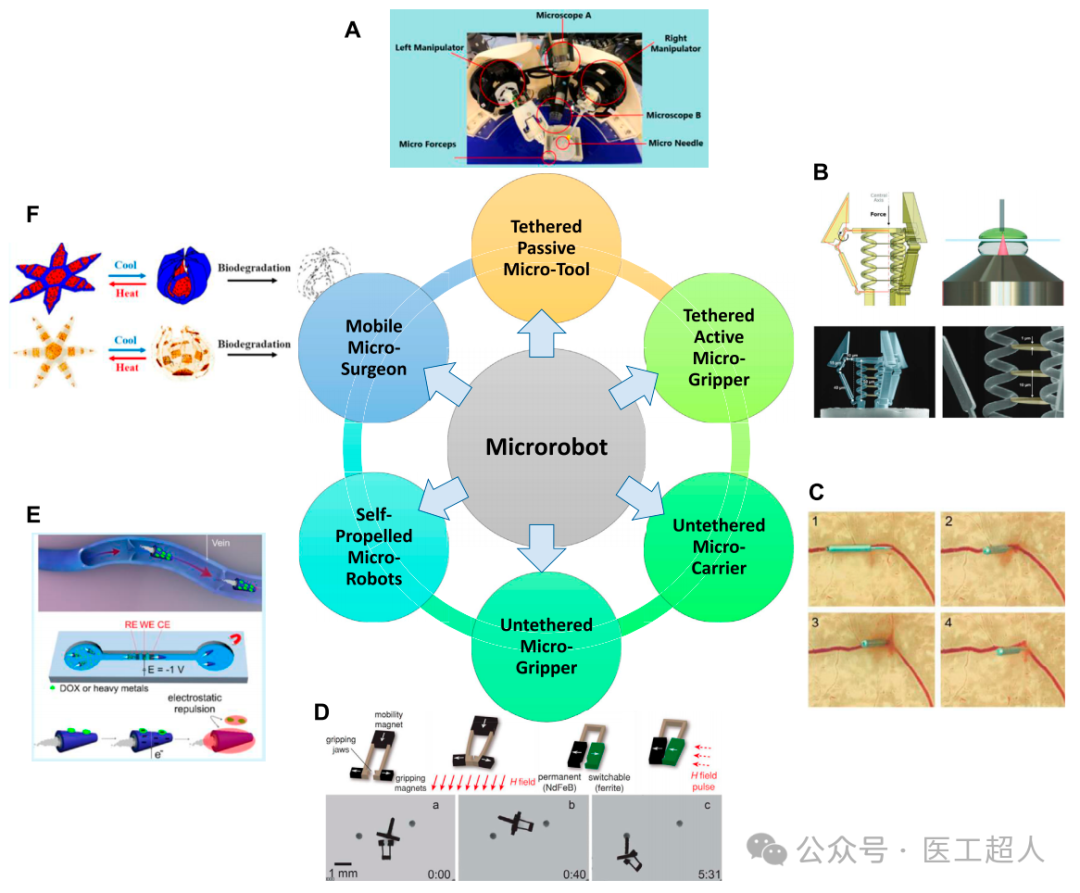
Overview of six categories of microrobots: (A) Tethered passive microrobots (B) Tethered active microrobots (C) Untethered microrobots (Chatzipirpiridis et al., 2015a), (D) Untethered micromanipulators (E) Self-propelled microrobots (F) Mobile microsurgeons
Technological Evolution and Historical Background:
The technology of microrobots originated from preliminary conceptual explorations in the 1950s, evolving through stages of Micro-Electro-Mechanical Systems (MEMS), nanotechnology development to smart materials and biomechanical systems. In particular, the development of MEMS technology has provided the technical foundation for the precise control and miniaturization of microrobots.
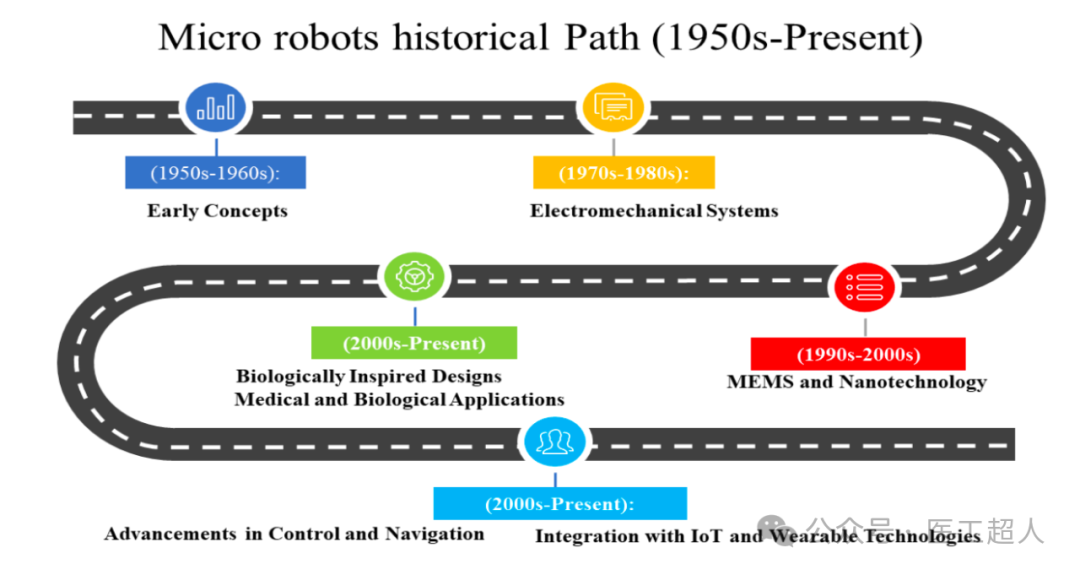
The development history of microrobots
Classification and Applications of Microrobots:
-
Biological microrobots: Made from biological materials, such as DNA robots, which have shown high specificity and effectiveness in targeted drug delivery experiments.
-
Synthetic microrobots: Typically made of metal or plastic, widely used in minimally invasive surgeries and precise operations.
-
Functional microrobots: Combine sensors and actuators, capable of performing more complex tasks such as biological detection and environmental monitoring.
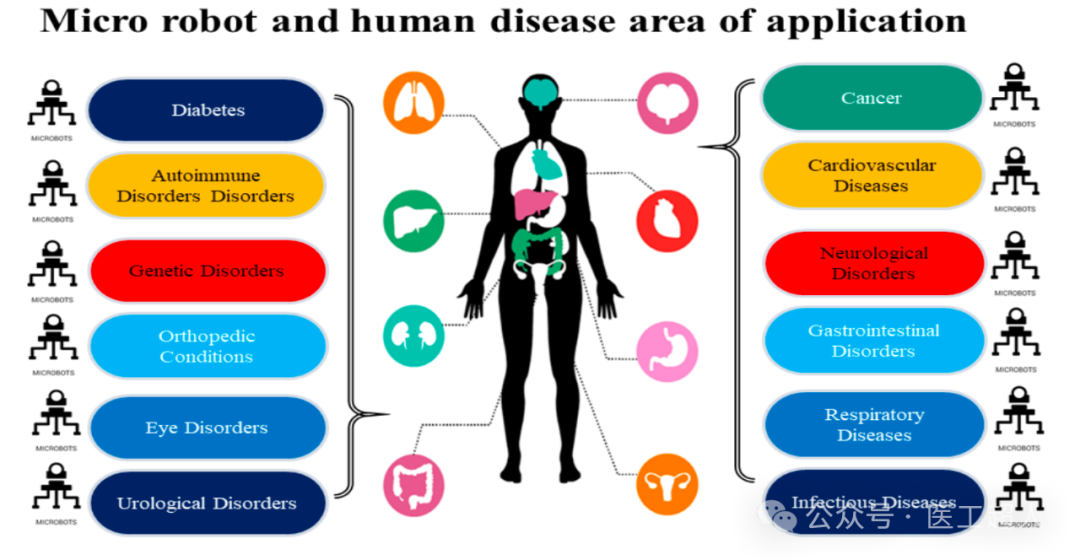
Classification and applications of microrobots
Successful Cases and Data Support:
-
Clinical trial data: A DNA robot in a clinical trial for cancer drug delivery successfully delivered drugs directly to tumor cells, reducing the impact on normal cells, improving treatment targeting and reducing side effects.
-
Surgical application cases: In minimally invasive heart surgery, the use of microrobots for precise operations increased the success rate by 20% and reduced recovery time by 50%.
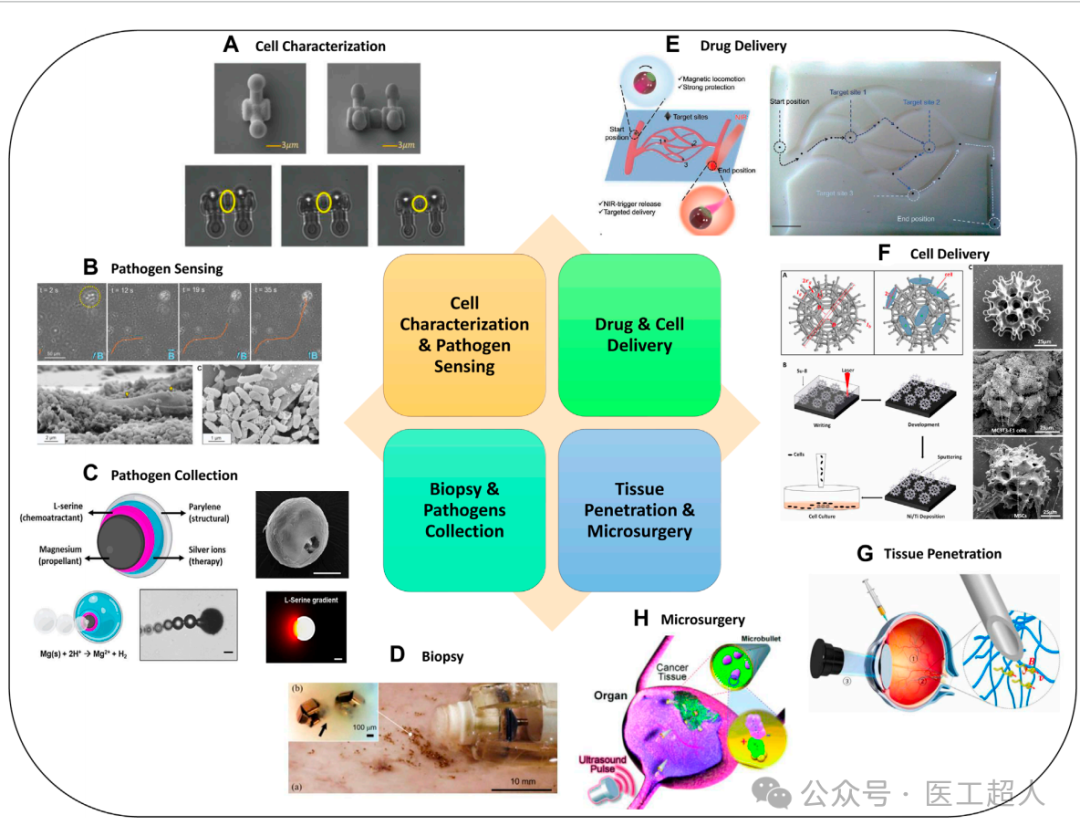
Advanced microrobots for biomedical applications
Application of Ultrasound Technology in Microrobots:
The application of ultrasound technology in the article focuses on supporting the positioning and navigation of microrobots through ultrasound imaging. Specifically, ultrasound imaging is used for precise control and guidance of microrobots, enabling them to effectively move and perform tasks in complex internal environments of the human body, such as within blood vessels and tissue interstices.Ultrasound imaging provides a non-invasive way to observe and track the position of microrobots, which is crucial for ensuring their correct movement path and reaching designated targets. Additionally, through ultrasound signals, researchers can obtain real-time positional information of the robots within the body, allowing for real-time adjustments to optimize their performance in drug delivery and therapeutic operations.

Cornell University scientists invented swimming robots that manipulate cell size using ultrasound
Future Development Trends:
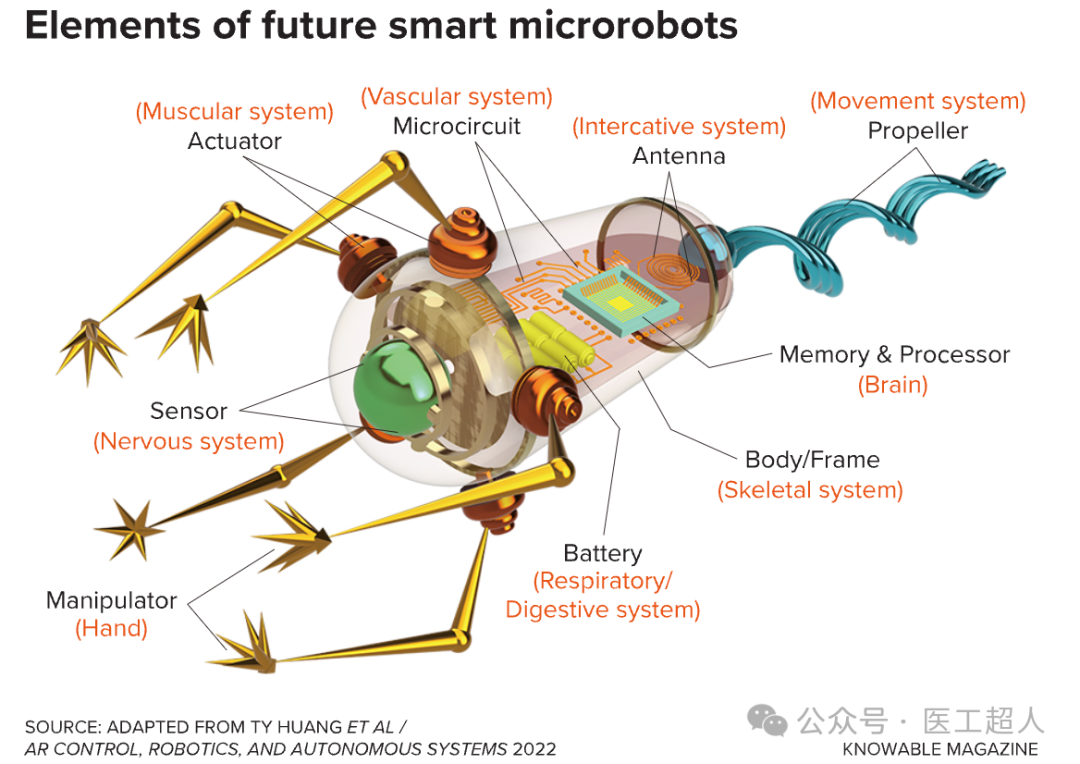
With advancements in materials science, machine learning, and artificial intelligence technologies, microrobots are expected to achieve greater breakthroughs in autonomous navigation, multitasking parallel processing, and real-time data processing. At the same time, discussions on their biosafety and ethical issues will become key to promoting their clinical applications.
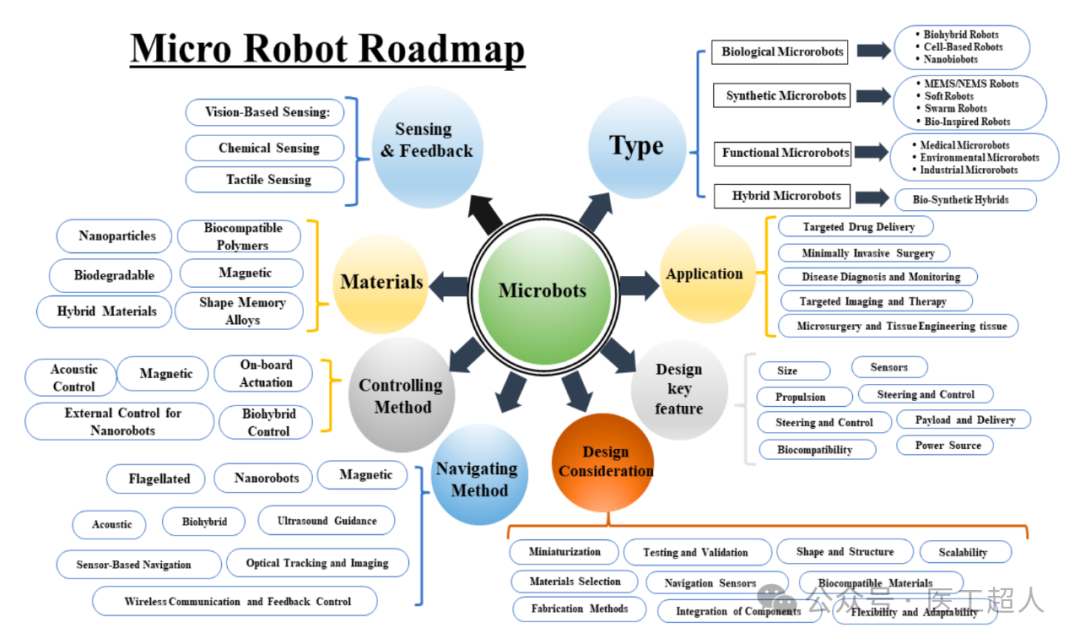 Future development trends of microrobots
Future development trends of microrobots
Microrobot technology has shown great application potential and broad development prospects in the medical field. Through continuous technological innovation and interdisciplinary collaboration, microrobots are expected to address more current challenges in medicine, providing patients with safer and more effective diagnostic and therapeutic solutions.
References:
Moshayedi, A. J., Khan, A. S., Davari, M., Mokhtari, T., & Andani, M. E. (2024). Micro robot as the feature of robotic in healthcare approach from design to application: the State of art and challenges. EAI Endorsed Transactions on AI and Robotics, 3.
Last AI routine image:

Welcome to join the cutting-edge information exchange group for R&D, cooperation, and other informationGroup joining method:Follow the “Medical Engineering Superman” official accountAdd the editor’s WeChat ID:YiGongSupermanNote (Name – Interested Direction)(You can scan the QR code below to add)
