In the future smart world, everything will be connected by the Internet of Things (IoT), and everything can be managed intelligently. Is this possible? Let experts from various fields that will be deeply transformed by connectivity, such as transportation, manufacturing, retail, energy, and healthcare, give you a glimpse. As Amy Webb, CEO of the Future Today Institute, stated: the technological IoT is a disruptive force that connects multiple fields. Unlike previous technologies, IoT links so many areas, leading to significant data processing and intelligent transformation.
According to Gartner, 5.5 million new things are connected every day; by 2020, there will be 21 billion components connected, sharing data. The key to this is IoT-related intelligent technologies, which are also considered by industry experts to be the driving technology behind Industry 4.0.
1) Transportation Industry
The three connectivity technologies for autonomous vehicles:
I. LiDAR
This sensor can rotate 360 degrees to sense and avoid obstacles, collecting appropriate data for autonomous vehicles.
II. V2X (Vehicle-to-Everything)
This technology connects vehicles to other components and devices, such as a pedestrian’s phone warning approaching vehicles or traffic signals to effectively control traffic.
III. Map Connectivity
Vehicles will transmit data via ‘crowd-sourced’ maps, continuously updating connectivity and traffic status.
The IoT vehicle market was approximately $225 billion in 2016 (up from $32 billion in 2015), and by 2020, around 250 million vehicles are expected to have autonomous driving capabilities!
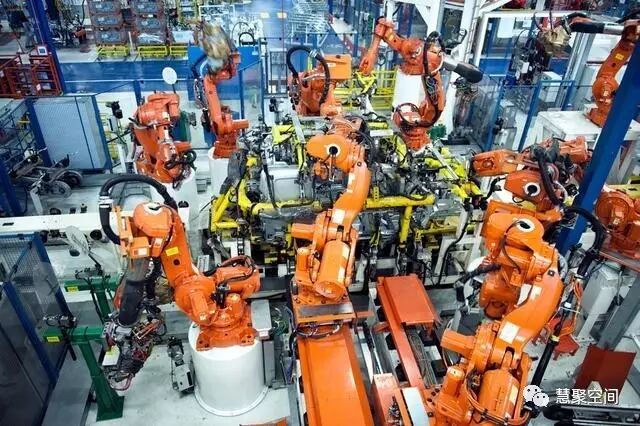

2) Manufacturing Industry
The future factory is driven by IoT. With the help of IoT and powered by artificial intelligence, the productivity, efficiency, and safety of Industry 4.0 factories and warehouses are significantly improved.
I. Digital Studio
Designers deliver product prototypes to engineers, who write development programs to connect, control, and operate the factory machines.
II. 3D Printers
These can control when to print, how to analyze and assemble from collected data, and can be remotely coded.
III. Exoskeletons
Lightweight wearable technology can help workers lift heavy objects and work in hard-to-reach spaces.
IV. Robots
Automated robots can work tirelessly on tasks requiring high precision.
V. Smart Production
All workers wear connected devices to collect production data, helping to facilitate a safer and more efficient production process.
3) Energy Industry
According to the World Wind Energy Association, the accumulated resources in wind energy have increased from 24 GW in 2001 to 340 GW in 2014, primarily due to the intelligent contributions of IoT.
Highlight I.
Real-time collection of big data that may indicate failures, such as turbine temperature, to initiate automatic maintenance mechanisms.
Highlight II.
Wind farm turbines are connected through IoT technology, collecting and communicating relevant information, analyzing data to automatically adjust without human intervention.
Highlight III.
Machine learning capabilities emphasize self-regulation, adjusting direction and angle to optimize the collection of natural resources and generate energy.
By 2020, energy companies will install over 1 billion smart meters.

4) Healthcare
According to a report by Market Research, the healthcare IoT market is expected to be worth $117 billion by 2020. This rapidly growing industry aims to focus on ‘prevention’ and ‘remote’ healthcare themes worldwide.
I. Digital Sleep Aids
Wearable devices will communicate with brain waves to help optimize REM (Rapid Eye Movement) sleep.
II. IoT-Embedded Pills
Pharmaceutical companies are developing smart ‘pills’ to monitor medication management conditions.
III. Wearable Devices
Beyond familiar pedometers and timers, wearable devices will eventually measure heart rate, blood pressure, blood sugar, and other parameters to remotely alert doctors about significant abnormalities.
IV. Remote Ultrasound
In developing countries, infant mortality rates remain very high; midwives can use connected devices to send pregnancy data to doctors, who can detect dangers before life-threatening situations arise and take necessary actions.
V. Glucose Monitoring
Developed arm sensors can automatically read 371 million glucose indices for diabetics every minute, allowing them to receive adequate care without needing to spend extra time in hospitals for related data.
Machina Research predicts that by 2025, around 1.3 billion healthcare IoT devices will be online, making it the fastest-growing industry in IoT over the next decade.
According to market forecasts, by 2020, there will be 21 billion IoT-enabled devices sharing data.
Although there is no shortage of theories in China, there is still a lack of a clear structure and explanation for practical intelligent applications of IoT. The purpose of this article is to provide a clear framework for the demand and application of core intelligent technologies. To truly achieve Industry 4.0, Made in China 2025, smart retail, smart healthcare, and other goals, it will require teams with years of cutting-edge technology product design and development experience in the fields of ABC (AI, Big Data, Cloud Computing) to help realize these great dreams.