
Introduction
The Internet of Things (IoT), as a cutting-edge technology in recent years, has been widely applied in new smart hospitals due to its characteristics of efficiency, accuracy, flexibility, and intelligence. It has become a key indicator in the evaluation system of smart hospitals. On April 20, 2020, the National Development and Reform Commission explicitly listed IoT technology as one of the key areas of “new infrastructure”, highlighting its importance in information infrastructure construction. Therefore, how to reasonably design and apply IoT systems in smart hospitals, respond to national policies, and build a comprehensive smart service information system has become a core issue in the current construction of smart hospitals. Specifically, how to fully leverage the advantages of IoT technology in smart healthcare, smart nursing, smart patient services, smart management, and smart logistics support to enhance patient experience and achieve comprehensive health management throughout the lifecycle is the focus of current research.

1. IoT in Hospitals
Technology Overview
1.1 Origins and Development of IoT
The concept of the Internet of Things (IoT) was first proposed by British scientist Professor Ashton, describing a network composed of numerous smart devices and facilities that can interconnect through various wired or wireless communication technologies. These devices include, but are not limited to, sensors, mobile terminals, industrial control systems, smart facilities, and video surveillance systems. IoT technology allows these devices and facilities to monitor, locate, alert, and command in real-time, providing efficient, energy-saving, safe, and environmentally friendly comprehensive solutions.
1.2 Applications of IoT Technology in Hospitals
As IoT technology continues to mature, its applications in the hospital sector are becoming increasingly widespread. Hospital IoT primarily refers to the use of technology to facilitate the interaction, transmission, analysis, and sharing of information among various personnel and devices related to medical services.
| Main Application Scenarios of IoT Technology in Smart Hospitals | ||
| Usage Dimension | Main Application Scenarios | Business Segment |
| Smart Healthcare | Mobile ward rounds, mobile ECG collection, etc. | Medical Services |
| Smart Nursing | Mobile nursing, wireless monitoring of patient vital signs, patient temperature monitoring, mobile ECG telemetry, wireless infusion pumps, wireless analgesic pumps, etc. | Medical Services |
| Smart Patient | Wireless infusion monitoring, perioperative management, wireless nurse call, prevention of psychiatric patient wandering, prevention of elderly patient wandering, infant theft prevention, remote video monitoring, in-hospital navigation, etc. | Medical Services |
| Smart Management | Medical asset management, hand hygiene compliance, medical waste management, wireless cold chain management, surgical gown management, surgical instrument tracking, endoscope disinfection management, etc. | Medical Management |
| Smart Logistics | Intelligent lighting, equipment energy efficiency management, operational analysis, cost analysis, etc. | Logistics Management |
| Smart Security | Security intercom, visual patrol, emergency intelligence, etc. | Security Management |
The application of this technology allows hospitals to perceive the status of medical service objects in real time, collect and analyze various medical data, thereby achieving dynamic monitoring, continuous tracking management, and precise medical health decision-making for medical service activities. In the hospital environment, the application scenarios of IoT are rich and diverse, covering patient monitoring, medical equipment management, drug management, logistics support, and more. These applications not only improve the efficiency of hospital operations but also greatly enhance the patient experience.

2. Spectrum of IoT System Applications in Hospitals
In the construction of smart hospitals, IoT technology achieves extensive applications through various communication technologies such as RFID, ZigBee, Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, LoRa, and WMTS. These different communication technologies have their unique application spectrums, which directly affect the architecture of IoT systems and the access methods of application terminals. Therefore, understanding the application spectrum of IoT systems is crucial for comprehending the overall architecture and design solutions of hospital IoT systems.
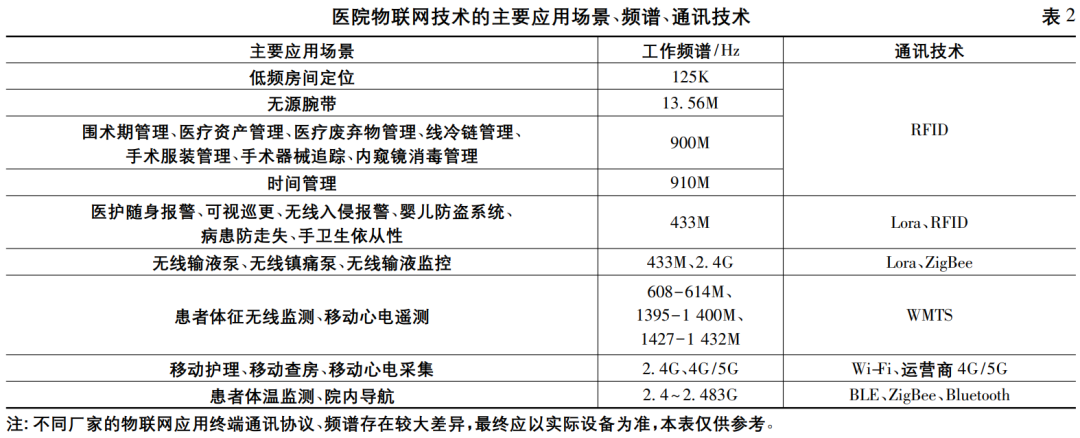 Image Source: Intelligent Building Electrical Magazine
Image Source: Intelligent Building Electrical Magazine
Through a detailed analysis of Table 2, we can clearly see the communication technologies and their corresponding working spectrums chosen for different application scenarios. These technology choices not only ensure the stability and efficiency of the hospital IoT system but also fully consider the uniqueness and complexity of the medical environment. For instance, in scenarios requiring high-precision positioning and fast data transmission, RFID and ZigBee technologies may be selected; while in scenarios needing wide coverage and high-speed data transmission, Wi-Fi and WMTS technologies may be more suitable.
With this information in mind, hospitals can choose the most appropriate communication technologies and application spectrums based on their actual needs and scenario characteristics when planning and constructing IoT systems, thereby building a smart hospital IoT system that meets medical business needs while maintaining high flexibility and scalability.

3. System Architecture of Hospital IoT
The core goal of constructing the hospital IoT system architecture is to achieve interconnectivity between devices and facilities with different communication standards and working spectrums, thereby building a unified IoT operation platform that promotes comprehensive interconnectivity and intelligence of “people and things” in smart hospitals. When choosing the system architecture, multiple factors need to be weighed, including cost, security, and maintainability.
3.1 Solutions Based on Dedicated IoT Networks
This solution constructs an ultra-wideband indoor signal distribution system that can simultaneously support the working spectrums and communication protocols of various smart hospital IoT applications, achieving multi-network integration. Its greatest advantage lies in simplifying the network architecture, avoiding the repeated construction of different application systems, thereby reducing overall operating and maintenance costs. At the same time, dedicated IoT networks can ensure data security. However, the initial investment of this solution is relatively high, and the wiring workload is substantial.
3.2 Solutions Based on Internet Wireless AP + IoT Base Stations
This solution utilizes the existing wireless internal and external networks and IoT base stations of the hospital to construct a smart medical IoT system based on wireless networks. Its advantages include simple wiring, flexible system access, and low construction costs. However, since the logistics management areas involved in IoT applications may not be fully covered by the hospital’s internal and external Wi-Fi, it is necessary to add independent IoT base stations in areas without Wi-Fi. Additionally, wireless APs need to have multiple IoT expansion slots to support various IoT applications. Although this solution reduces wiring costs, it may compromise the data security of the IoT, and numerous IoT base stations may increase the system failure rate and management maintenance costs.
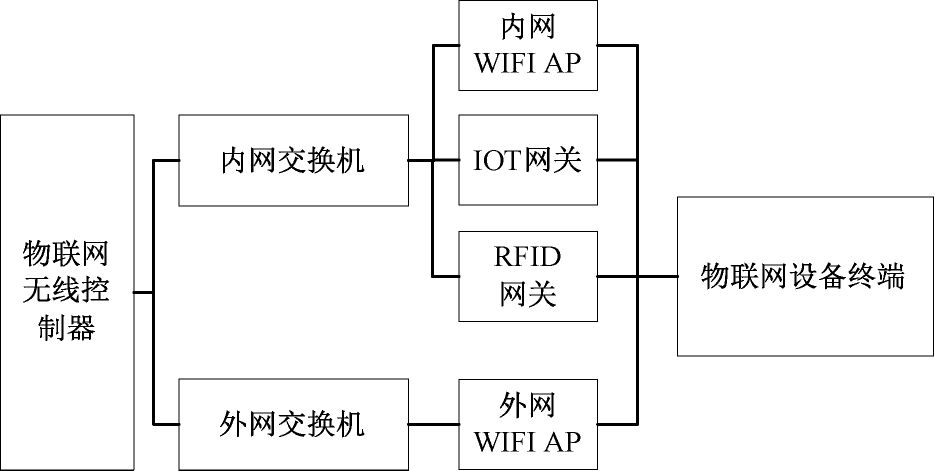 Image Source: Intelligent Building Electrical Magazine
Image Source: Intelligent Building Electrical Magazine
With technological advancements, IoT cameras, as devices that integrate video surveillance and IoT functions, are becoming a new choice for smart hospital construction. This solution upgrades traditional video surveillance systems by replacing some cameras with IoT cameras and combining them with micro base stations, locators, etc., to achieve comprehensive IoT coverage without blind spots in the entire hospital.
The core advantage of this solution is that it achieves full visualizability of the IoT system, which not only enhances management intuitiveness and efficiency but also helps in promptly identifying and resolving issues. Moreover, since the IoT system is relatively independent, its data security is effectively guaranteed. However, this solution imposes certain constraints on camera selection, requiring the use of specialized IoT cameras. Additionally, in areas not covered by IoT cameras, such as patient rooms, micro base stations need to be added.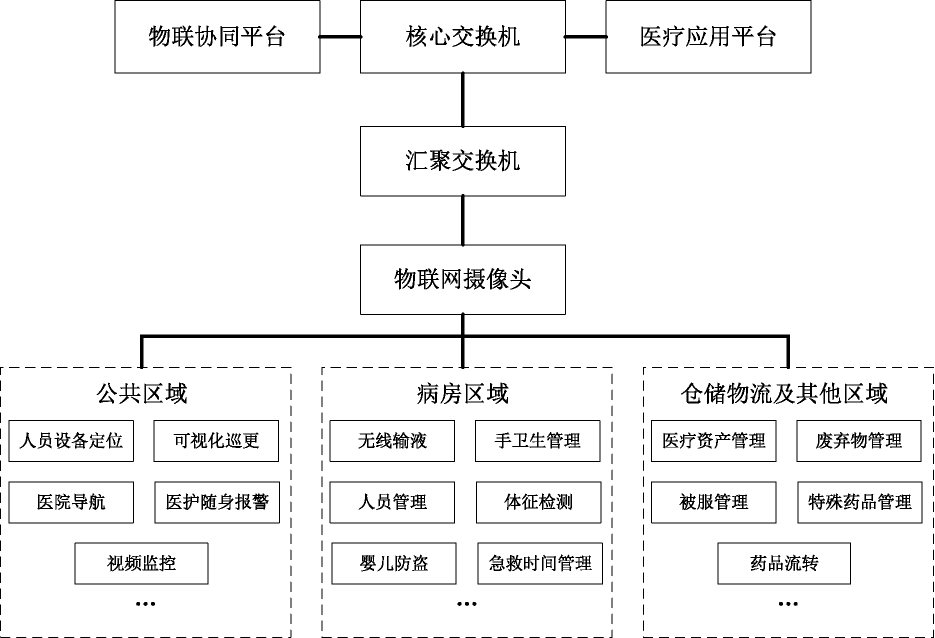
Image Source: Intelligent Building Electrical Magazine
When selecting the architecture for the hospital IoT system, multiple factors need to be comprehensively considered. Although the dedicated IoT network solution requires a higher initial investment, it guarantees security and stability; the internet wireless AP + IoT base station solution has lower costs and flexible deployment but may sacrifice some data security; while the visual IoT solution based on IoT cameras achieves full visualizability, high management efficiency, but has certain requirements for device selection and deployment locations.

4. Application Scenarios of IoT in Smart Hospitals
In the construction of smart hospitals, the intelligence of in-hospital application scenarios is a core element in enhancing the quality and efficiency of medical services. Below is a detailed explanation of different application scenarios in smart hospitals:
Scenario 1: Smart Pre-hospital Emergency
Smart pre-hospital emergency significantly enhances the efficiency and accuracy of emergency management through the “5G + Medical IoT Perception Network” model. Advanced IoT devices deployed in emergency vehicles can monitor patients’ vital signs in real-time and transmit data to the hospital emergency center, enabling doctors to obtain detailed patient conditions before arriving at the hospital and prepare for treatment in advance. This model not only improves the success rate of emergencies but also greatly shortens treatment time.
Scenario 2: Smart Outpatient Services
Smart outpatient services optimize the allocation of medical resources and facilitate patient access through the integration of the hospital’s smart brain and internet technology. In pre-consultation services, patients can make appointments for medical resources through various channels such as Alipay, WeChat, and apps, reducing on-site waiting times. During consultation, IoT technology enables functions such as patient temperature detection and health code recognition, ensuring a safe and orderly medical process. Post-consultation services offer doctor-patient interaction, satisfaction surveys, follow-up management, and other services to meet diverse patient needs.
Scenario 3: Smart Wards
Smart wards, as an upgraded version of ordinary wards, utilize IoT technologies such as wearable devices to achieve real-time monitoring and intelligent analysis of patients’ vital signs. This continuous monitoring can promptly detect significant risks that may arise for patients, providing valuable rescue time for doctors. Additionally, smart wards include functions such as fall detection, infusion monitoring, and medical waste management, providing a safer and more comfortable hospital environment for patients.
Scenario 4: Smart Equipment Management
Smart equipment management utilizes IoT technology to achieve structured and standardized acquisition of data such as medical equipment operation logs and records. This data can be used for cost-benefit analysis, refined management, preventive maintenance, and more. Through big data mining and analysis, equipment failure warning models can be established, effectively reducing the failure rate and maintenance costs of medical equipment, saving hospitals substantial expenses.
In summary, the construction of smart hospitals not only enhances the quality and efficiency of medical services but also greatly improves patient experience. The application of IoT technology allows for more refined and intelligent hospital management, providing patients with higher-quality and more convenient medical services.

5. Considerations for Designing Hospital IoT Systems
Key Issues to Address
With the continuous advancement of medical technology and the deepening of information construction, hospital IoT systems have gradually become key to enhancing the quality of medical services, management efficiency, and patient experience. When designing hospital IoT systems, in addition to ensuring the basic functions of the system such as security, reliability, and stability, special attention should be paid to the following issues:
5.1 Integration with Hospital Information Systems
Hospital IoT systems do not exist in isolation but are part of the overall information architecture of the hospital. Therefore, IoT systems must be able to seamlessly interface with the hospital’s existing information systems such as HIS (Hospital Information System), LIS (Laboratory Information System), PACS (Picture Archiving and Communication System), etc. This requires that the IoT system considers issues such as data exchange standardization, interface compatibility, and information security from the design stage.
5.2 Considerations for Phased Construction
The construction of hospital IoT systems often cannot be completed in one go and needs to be implemented in phases based on the actual situation of the hospital. This involves considerations of funding, technology, and business needs. Therefore, when designing the system, sufficient expansion space should be reserved to ensure that the system can transition smoothly during subsequent upgrades or expansions without affecting the normal use of existing functions.
5.3 Openness and Scalability of the System
As medical technology continues to advance, the application scenarios and functional requirements of hospital IoT systems are also constantly changing. This requires that the system be designed with a high degree of openness and scalability, capable of flexibly adapting to new technologies and application demands. This includes hardware compatibility, software system upgradability, and system architecture scalability.
5.4 Selection of Application Terminal Devices
There is a wide variety of terminal devices for hospital IoT systems, including various sensors, actuators, mobile devices, etc. When selecting these devices, factors such as performance, stability, security, and cost need to be considered. At the same time, it is necessary to ensure that these devices can work well with the system software to achieve overall optimization and efficient operation of the system.

6. IoT Technology
Driving Innovation in Smart Healthcare
As IoT technology delves deeper into the smart hospital system, it injects unprecedented vitality and possibilities into the field of smart healthcare. The real-time monitoring, telemedicine, interconnectivity of medical devices, big data analysis, and innovative applications of smart medical devices brought about by IoT technology present new development opportunities for the medical field, indicating that medical services are moving towards a more intelligent, efficient, and human-centered direction.
The popularity of IoT technology enables precise management of patients and medical resources in the healthcare sector. By building an integrated platform for IoT systems, hospitals can achieve transparency in medical processes, scientific medical workflows, and digitalization of medical information. This not only greatly enhances the efficiency of medical staff but also significantly improves the service experience for patients. For example, by monitoring patients’ vital signs in real-time, doctors can diagnose and take corresponding treatment measures more quickly; and through telemedicine technology, patients can receive expert medical advice without having to come to the hospital, saving time and costs.
Moreover, IoT technology also helps hospitals achieve intelligent management of “things”. In traditional hospital management models, maintenance of medical equipment, inventory management of drugs, personnel scheduling, etc., rely on a large amount of manual operation, which is not only inefficient but also prone to errors. Now, through IoT technology, hospitals can achieve digital collection, storage, transmission, processing, and sharing of these resources, making management more efficient and precise. This not only reduces management costs for hospitals but also improves the quality of services provided.
Looking ahead, with the continuous advancement and innovation of IoT technology, we have reason to believe that it will bring more unprecedented breakthroughs and developments to smart healthcare. From achieving more efficient medical services to enhancing patient experience, and optimizing hospital management mechanisms, IoT technology will play an irreplaceable role. The medical field, driven by IoT technology, is ushering in a new era of development.
References:
Source: Medical Health Architecture
