 MLNLPThe MLNLP community is a well-known machine learning and natural language processing community both domestically and internationally, covering NLP graduate students, university professors, and corporate researchers.The vision of the communityis to promote communication and progress between the academic and industrial sectors of natural language processing and machine learning, especially for beginners.Source | Deep Learning Natural Language Processing
MLNLPThe MLNLP community is a well-known machine learning and natural language processing community both domestically and internationally, covering NLP graduate students, university professors, and corporate researchers.The vision of the communityis to promote communication and progress between the academic and industrial sectors of natural language processing and machine learning, especially for beginners.Source | Deep Learning Natural Language Processing
Paper: Why Do Multi-Agent LLM Systems Fail? Link: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2503.13657
Why Do Multi-Agent Systems Fail?
Imagine you have assembled a team: programmers, testers, and project managers each performing their roles. The result is a product riddled with bugs, team members blaming each other, and some even altering requirements without permission—this is not a workplace drama, but a true reflection of current multi-agent LLM systems!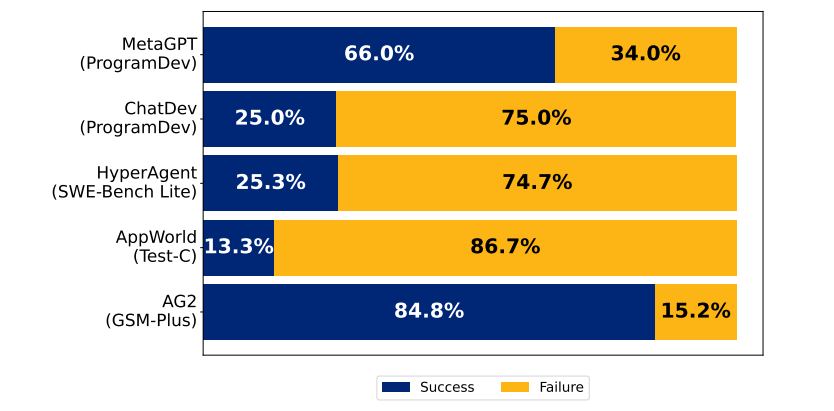 The paper’s tests on five major frameworks, including ChatDev, show that in the worst cases, the system’s accuracy is only 25%, worse than AI operating alone (e.g., Best-of-N sampling). It’s like a group of top students working on a project, but their grades are worse than if they had taken the exam individually.
The paper’s tests on five major frameworks, including ChatDev, show that in the worst cases, the system’s accuracy is only 25%, worse than AI operating alone (e.g., Best-of-N sampling). It’s like a group of top students working on a project, but their grades are worse than if they had taken the exam individually.
14 Failure Modes and 3 Major Fatal Traps
The researchers analyzed over 150 task dialogue records (totaling more than 150,000 lines of text) and found that the root causes of failure can be categorized into three main types:
① Specification Failures (Specification Failures)
- AI employees altering requirements without permission (e.g., changing chess input from “Kc8” to coordinates)
- Testers forgetting to check core rules
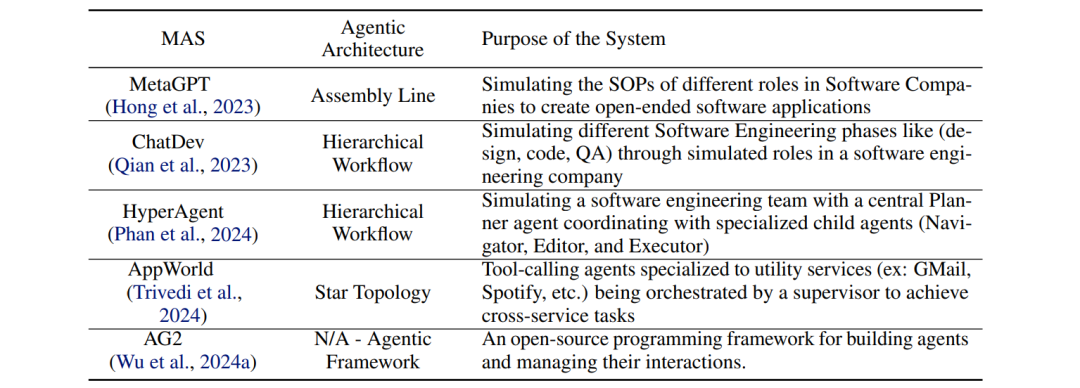
② Inter-Agent Misalignment (Inter-Agent Misalignment)
- Programmers and architects having seven rounds of dialogue with no progress
- Knowing the API documentation is incorrect but concealing it
③ Verification Failures (Verification Failures)
- As long as the code runs, testing relies entirely on “intuitive acceptance”
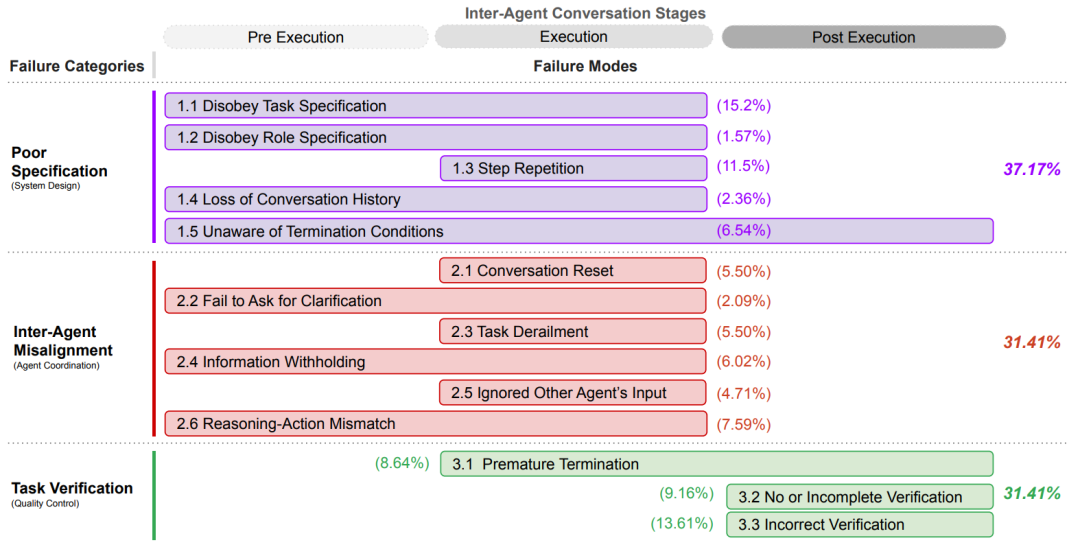
Real Case: Why Did the Chess Game Turn into a Coordinate Inputter?
The paper reveals a classic failure scene: the user requested a game that supports standard chess notation (e.g., Qd4), but the version delivered by the Agent team could only accept (x1,y1) coordinate input.
Even more absurd, the testing phase only checked if the code could compile, completely ignoring rule validation. This is akin to a new house inspection where the supervisor only counts the doors and windows but doesn’t check if the bathroom has a drainage system.
Do Agents Also Pass the Buck? The Verification Phase Turns Out to Be the Biggest Scapegoat
Data shows that 47% of failures can be traced back to the verification phase. However, the paper emphasizes:“We cannot blame the quality inspectors entirely”. Just as a building collapse cannot solely be blamed on the inspection, issues like substandard steel reinforcement and design errors are the root causes.
Researchers found that even if the verification AI is given a boost (using GPT-4o for review), 23% of failures remain unavoidable. This indicates that the collapse of multi-agent systems is often a concentrated outbreak of systemic design flaws.
Insights from Human Organizational Studies
Shockingly, the failure modes of these Agent teams closely align with classic collapse cases in human organizations:
- Bypassing Authority (CTO usurping the decision-making power of the CEO)
- Expert Silence (Knowing the process is wrong but not daring to question it)
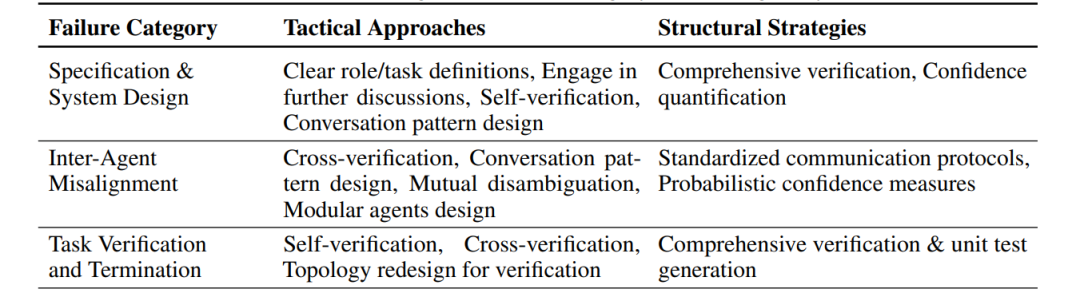
The paper suggests drawing on the experiences ofHigh-Reliability Organizations (HRO) such as nuclear power plants and air traffic control, for example:
- Strict hierarchical authorization (prohibiting AI roles from overstepping authority)
- Building psychological safety (encouraging AI to question upper management decisions)
What to Do?
The current mainstream solutions are like “patching”:
- Tactical Fixes: Making prompts more detailed (+14% success rate)
- Seat Change Experiments: Adjusting AI dialogue processes (results vary)
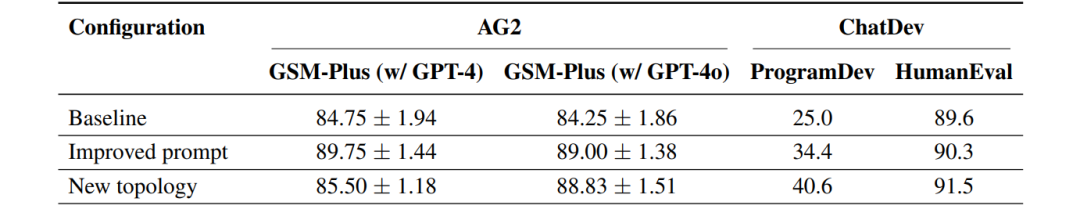
However, fundamental solutions requirereconstructing the system’s DNA:
- Installing a “risk radar” for AI (quantifying decision confidence)
- Developing an organizational memory database (to avoid repeating mistakes)
- Establishing standardized communication protocols (eliminating “dialect-style dialogue”)
What is the Ultimate Form of Agent Team Collaboration?
The researchers predict that future multi-agent systems will resemblespecial forces:
- Assaulters (rapid response)
- Scouts (real-time verification)
- Commanders (dynamic coordination) through reinforcement learning to train team synergy, ultimately achieving “1+1>10” in intelligent emergence.
Technical Community Invitation

△ Long press to add the assistant
Scan the QR code to add the assistant on WeChat
Please note:Name – School/Company – Research Direction (e.g., Xiao Zhang – Harbin Institute of Technology – Dialogue Systems) to apply for joiningNatural Language Processing/Pytorch and other technical communities
About Us
MLNLP Community is a grassroots academic community jointly established by scholars in machine learning and natural language processing from both domestic and international backgrounds. It has developed into a well-known community for machine learning and natural language processing, aiming to promote progress between the academic and industrial sectors of machine learning and natural language processing.The community provides an open communication platform for practitioners’ further education, employment, and research. Everyone is welcome to follow and join us.
