1Module Source>>>
Product Physical Display:

Data Download Link:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1FNGHM0u5MQ2li3QOrTkTuA
Data Extraction Code:8888
2Specifications>>>
The following information can be found in the manufacturer’s screen specification document.
Operating Voltage:3.3V ~ 5V
Operating Current:20mA
Module Size:33.5 x 35.4 MM
Pixel Pitch:0.23(H) x 0.23(V)
Pixel Size:0.21(H) x 0.21(V)
Driver Chip:SH1106
Communication Protocol:SPI (Adjustable IIC)
3Porting Process>>>
Our goal is to port the example routine to the Lichuang CW32F030C8T6 development board. Follow the steps below to complete the porting.
- Import the source code into the project;
- Make rough modifications based on compilation errors;
- Modify pin configurations;
- Modify timing configurations;
- Porting verification.
3.1View Data
Open the manufacturer’s example routine (example download can be found in the Baidu Cloud link). The specific path can be found in the example path.
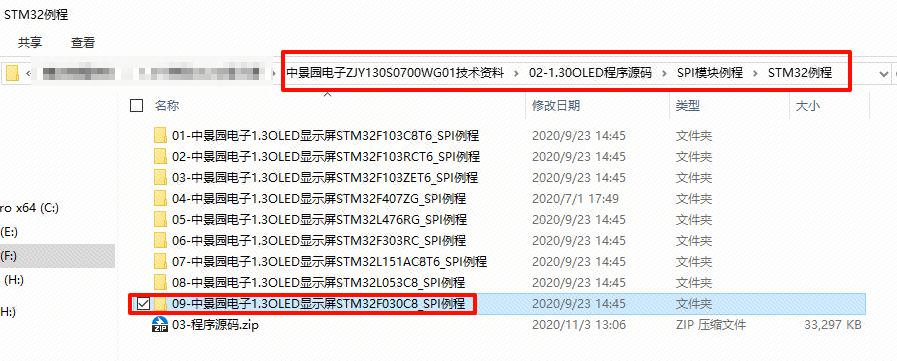
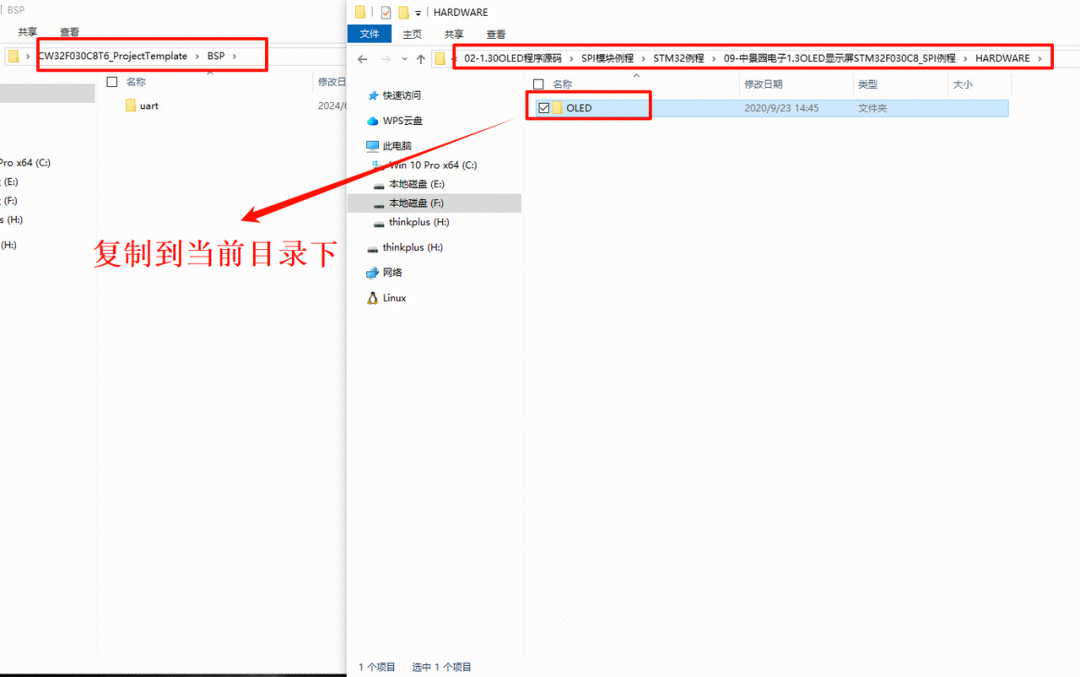
Open your project and import the .c and .h files that we just copied.
Change sys.h in the oled.h file to board.h.

Comment out delay.h in the oled.c file.


The module is a slave of the SPI communication protocol, SCL is the SPI signal line (SCK), SDA is the SPI output line (MOSI), and CS is the SPI chip select line (NSS).
If the MCU’s GPIO pins are insufficient, you can leave two pin interfaces of the screen unconnected to the MCU’s GPIO.
- Connect RES to the MCU’s reset pin, so that when the MCU resets, the screen also resets;
Next, we will explain the software SPI porting and hardware SPI porting.
3.4Software SPI Porting
The current manufacturer’s source code uses a software SPI interface, and the SPI timing part has been completed by the manufacturer, so we only need to configure the pins and delays. Therefore, please connect the screen pins according to your needs. The selected pins are shown in the table below.

Add the OLED pin porting definitions in oled.h
//-----------------OLED Port Porting Definitions----------------#define OLED_RCC_GPIO_ENABLE() __RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE()#define OLED_GPIO_PORT CW_GPIOA#define OLED_SCL_PIN GPIO_PIN_5#define OLED_MOSI_PIN GPIO_PIN_7#define OLED_RES_PIN GPIO_PIN_3#define OLED_DC_PIN GPIO_PIN_2#define OLED_CS_PIN GPIO_PIN_4After selecting the pins, enter the project and start writing the screen pin initialization code. Changeoled.c source code’s **void OLED_Init(void)** to the following code.
//OLED Initializationvoid OLED_Init(void){ GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct; // GPIO initialization structure OLED_RCC_GPIO_ENABLE(); // Enable GPIO clock GPIO_InitStruct.Pins = OLED_SCL_PIN| // GPIO pins OLED_MOSI_PIN| OLED_RES_PIN| OLED_DC_PIN| OLED_CS_PIN; GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP; // Push-pull output GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_HIGH; // High output speed GPIO_Init(OLED_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct); // Initialize OLED_RES_Clr(); delay_ms(200); OLED_RES_Set(); OLED_WR_Byte(0xAE,OLED_CMD); /*display off*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x02,OLED_CMD); /*set lower column address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x10,OLED_CMD); /*set higher column address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD); /*set display start line*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xB0,OLED_CMD); /*set page address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x81,OLED_CMD); /*contract control*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xcf,OLED_CMD); /*128*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA1,OLED_CMD); /*set segment remap*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA6,OLED_CMD); /*normal / reverse*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA8,OLED_CMD); /*multiplex ratio*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x3F,OLED_CMD); /*duty = 1/64*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xad,OLED_CMD); /*set charge pump enable*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x8b,OLED_CMD); /* 0x8B internal supply VCC */ OLED_WR_Byte(0x33,OLED_CMD); /*0X30---0X33 set VPP 9V */ OLED_WR_Byte(0xC8,OLED_CMD); /*Com scan direction*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD3,OLED_CMD); /*set display offset*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x00,OLED_CMD); /* 0x20 */ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD5,OLED_CMD); /*set osc division*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x80,OLED_CMD); OLED_WR_Byte(0xD9,OLED_CMD); /*set pre-charge period*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x1f,OLED_CMD); /*0x22*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xDA,OLED_CMD); /*set COM pins*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x12,OLED_CMD); OLED_WR_Byte(0xdb,OLED_CMD); /*set vcomh*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD); OLED_Clear(); OLED_WR_Byte(0xAF,OLED_CMD); /*display ON*/}Change the LCD port definition macros in lcd_init.h to the style shown on the right.
//-----------------OLED Port Definitions----------------#define OLED_SCL_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_SCL_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//SCL#define OLED_SCL_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_SCL_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_SDA_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_MOSI_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//SDA#define OLED_SDA_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_MOSI_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_RES_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_RES_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//RES#define OLED_RES_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_RES_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_DC_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_DC_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//DC#define OLED_DC_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_DC_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_CS_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_CS_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//CS#define OLED_CS_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_CS_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)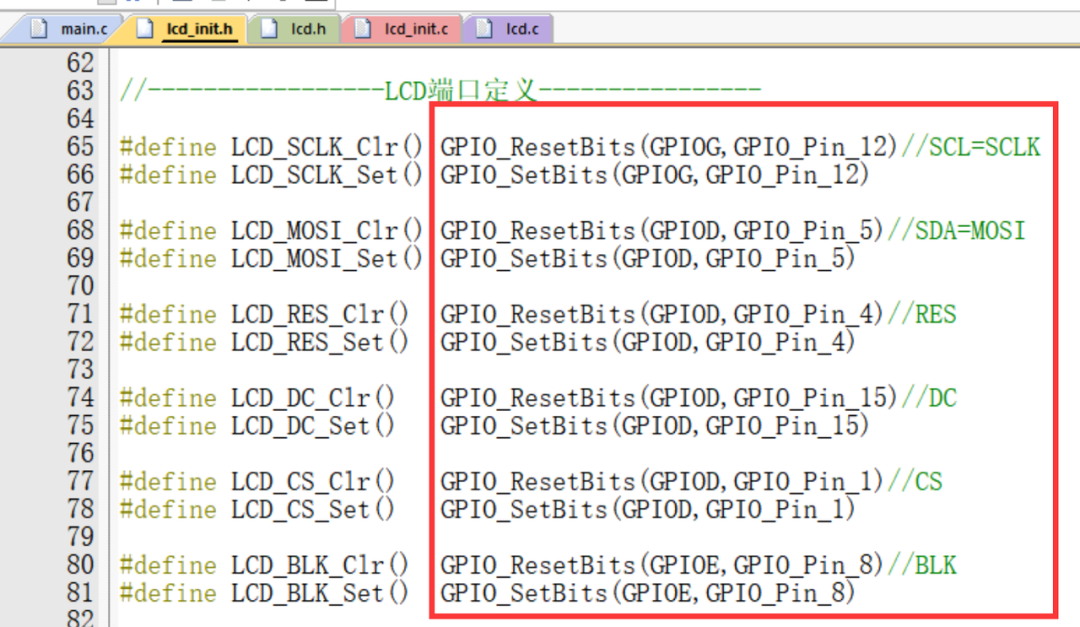 Source Port Definitions
Source Port Definitions
 Modified Port Definitions
Modified Port Definitions
At this point, the software SPI porting is complete. Please proceed to section 4 for porting verification.
Compared to software SPI, hardware SPI relies on the hardware SPI controller, where all clock edge sampling, clock generation, and timing control are handled by hardware. This reduces CPU usage and increases operating speed. Software SPI controls IO output high and low levels through code, simulating SPI timing, which is slower and less reliable.
To use hardware SPI to drive the screen, you need to ensure that the pins used have SPI peripheral functionality. This can be checked in the data sheet.
The data sheet and user manual are available in the Baidu Cloud data, see the introductory manual for the link.
The current implementation uses a hardware SPI interface, and we only need to control the screen without reading data from it, so we use a 3-wire SPI, utilizing the clock line SCK, master output slave input line MOSI, and software-controlled chip select line NSS. The NSS is controlled by software, so aside from the SCL(SCK)/SDA(MOSI) pins that need to use hardware SPI function pins, other pins can use other GPIOs on the development board.Here, we choose to use the PA5/PA7 SPI multiplexing function for the corresponding screen pins according to your needs. The selected pins are shown in the hardware SPI wiring table.

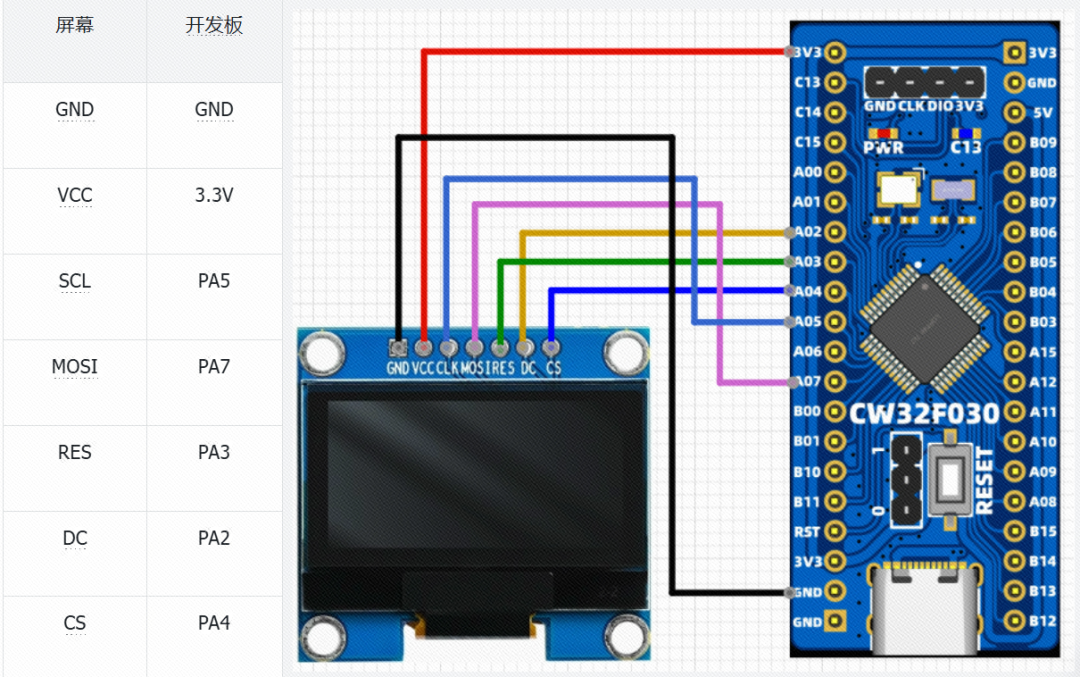
Add the OLED pin porting definitions in oled.h
//-----------------OLED Port Porting Definitions----------------#define OLED_RCC_GPIO_ENABLE() __RCC_GPIOA_CLK_ENABLE()#define OLED_RCC_SPI1_ENABLE() __RCC_SPI1_CLK_ENABLE()//GPIO AF#define SPI1_AF_SCK() PA05_AFx_SPI1SCK()#define SPI1_AF_MOSI() PA07_AFx_SPI1MOSI()#define BSP_SPI1 CW_SPI1#define OLED_GPIO_PORT CW_GPIOA#define OLED_SCL_PIN GPIO_PIN_5#define OLED_MOSI_PIN GPIO_PIN_7#define OLED_RES_PIN GPIO_PIN_3#define OLED_DC_PIN GPIO_PIN_2#define OLED_CS_PIN GPIO_PIN_4After selecting the pins, enter the project and start writing the screen pin initialization code.
The pin initialization configuration is shown in the following code.
//OLED Initializationvoid OLED_Init(void){ GPIO_InitTypeDef GPIO_InitStruct; // GPIO initialization structure OLED_RCC_GPIO_ENABLE(); // Enable GPIO clock OLED_RCC_SPI1_ENABLE(); // Enable SPI1 clock SPI1_AF_SCK(); SPI1_AF_MOSI(); GPIO_InitStruct.Pins = OLED_SCL_PIN| // GPIO pins OLED_MOSI_PIN| OLED_RES_PIN| OLED_DC_PIN| OLED_CS_PIN; GPIO_InitStruct.Mode = GPIO_MODE_OUTPUT_PP; // Push-pull output GPIO_InitStruct.Speed = GPIO_SPEED_HIGH; // High output speed GPIO_Init(OLED_GPIO_PORT, &GPIO_InitStruct); // Initialize SPI_InitTypeDef SPI_InitStructure; // SPI Initialization structure SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Direction = SPI_Direction_2Lines_FullDuplex; // Full duplex SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Mode = SPI_Mode_Master; // Master mode SPI_InitStructure.SPI_DataSize = SPI_DataSize_8b; // Frame data length is 8 bits SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPOL = SPI_CPOL_High; // Clock idle level is high SPI_InitStructure.SPI_CPHA = SPI_CPHA_2Edge; // Sample on the second edge SPI_InitStructure.SPI_NSS = SPI_NSS_Soft; // Chip select signal controlled by SSI register SPI_InitStructure.SPI_BaudRatePrescaler = SPI_BaudRatePrescaler_8; // Baud rate is PCLK divided by 8 SPI_InitStructure.SPI_FirstBit = SPI_FirstBit_MSB; // Most significant bit MSB sent first SPI_InitStructure.SPI_Speed = SPI_Speed_Low; // Low-speed SPI SPI_Init(BSP_SPI1, &SPI_InitStructure); // Initialize SPI_Cmd(BSP_SPI1, ENABLE); // Enable SPI1 OLED_RES_Clr(); delay_ms(200); OLED_RES_Set(); OLED_WR_Byte(0xAE,OLED_CMD); /*display off*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x02,OLED_CMD); /*set lower column address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x10,OLED_CMD); /*set higher column address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD); /*set display start line*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xB0,OLED_CMD); /*set page address*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x81,OLED_CMD); /*contract control*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xcf,OLED_CMD); /*128*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA1,OLED_CMD); /*set segment remap*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA6,OLED_CMD); /*normal / reverse*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xA8,OLED_CMD); /*multiplex ratio*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x3F,OLED_CMD); /*duty = 1/64*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xad,OLED_CMD); /*set charge pump enable*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x8b,OLED_CMD); /* 0x8B internal supply VCC */ OLED_WR_Byte(0x33,OLED_CMD); /*0X30---0X33 set VPP 9V */ OLED_WR_Byte(0xC8,OLED_CMD); /*Com scan direction*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD3,OLED_CMD); /*set display offset*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x00,OLED_CMD); /* 0x20 */ OLED_WR_Byte(0xD5,OLED_CMD); /*set osc division*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x80,OLED_CMD); OLED_WR_Byte(0xD9,OLED_CMD); /*set pre-charge period*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x1f,OLED_CMD); /*0x22*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0xDA,OLED_CMD); /*set COM pins*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x12,OLED_CMD); OLED_WR_Byte(0xdb,OLED_CMD); /*set vcomh*/ OLED_WR_Byte(0x40,OLED_CMD); OLED_Clear(); OLED_WR_Byte(0xAF,OLED_CMD); /*display ON*/}Change the LCD port definition macros in oled.h to the style shown on the right.
//-----------------OLED Port Definitions----------------#define OLED_SCL_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_SCL_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//SCL#define OLED_SCL_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_SCL_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_SDA_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_MOSI_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//SDA#define OLED_SDA_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_MOSI_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_RES_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_RES_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//RES#define OLED_RES_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_RES_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_DC_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_DC_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//DC#define OLED_DC_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_DC_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)#define OLED_CS_Clr() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_CS_PIN,GPIO_Pin_RESET)//CS#define OLED_CS_Set() GPIO_WritePin(OLED_GPIO_PORT,OLED_CS_PIN,GPIO_Pin_SET)The initialization part is complete, and we also need to modify the data sending part. The source code uses software SPI, and the timing is completed by the manufacturer. We need to modify it for hardware SPI. In theoled.c file, change the source code’s **void OLED_WR_Byte(u8 dat,u8 cmd)** function to the style shown on the right.
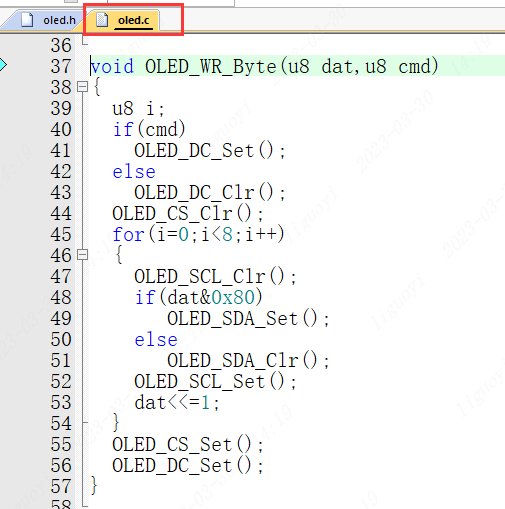 Source Code Format
Source Code Format
 Modified Code
Modified Code
void OLED_WR_Byte(u8 dat,u8 cmd){ if(cmd) OLED_DC_Set(); else OLED_DC_Clr(); OLED_CS_Clr(); while (SPI_GetFlagStatus(BSP_SPI1, SPI_FLAG_TXE) == RESET); SPI_SendData(BSP_SPI1, dat); // Send data while (SPI_GetFlagStatus(BSP_SPI1, SPI_FLAG_RXNE) == RESET); uint16_t temp = SPI_ReceiveData(BSP_SPI1); // Return data OLED_CS_Set(); OLED_DC_Set();}At this point, the hardware SPI porting is complete. Please proceed to section 4 for porting verification.
* Change Logs: * Date Author Notes * 2024-06-19 LCKFB-LP first version */#include "board.h"#include "stdio.h"#include "bsp_uart.h"#include "oled.h"int32_t main(void){ board_init(); // Development board initialization uart1_init(115200); // Serial port 1 baud rate 115200 OLED_Init(); // Initialize OLED OLED_Clear(); uint32_t t = 0; while(1) { OLED_ShowString(0,0,(uint8_t *)"ABC",8,1);//6*8 "ABC" OLED_ShowString(0,8,(uint8_t *)"ABC",12,1);//6*12 "ABC" OLED_ShowString(0,20,(uint8_t *)"ABC",16,1);//8*16 "ABC" OLED_ShowString(0,36,(uint8_t *)"ABC",24,1);//12*24 "ABC" OLED_ShowString(50,8,(uint8_t *)"Num:",16,1);//12*24 "ABC" OLED_ShowNum(90,8,t,3,16,1); t += 1; OLED_Refresh(); delay_ms(1000); }}Power-on effect:

Successful Porting Example Code:
Link:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1t08db9FJIMY00ys3gNvPag?pwd=LCKF
Extraction Code: LCKF
ENDPrevious ReviewsREVIEW
[Product Application] CW32 Electric Tool Product Open Source
[Product Solution] Low-Cost Electric Tool Solution Based on CW32L010
[Product Application] Smart Power Bank Based on CW32 (Open Source Solution)
[Product Application] CW-W88 Water Pump General Control Board Design Scheme (Open Source)
[Product Application] Controller Product Scheme for Angle Grinder Based on CW32
[Product Solution] Low-Voltage Brushless Fan Sensorless Controller Based on CW32F030C8
[Product Solution] Brushless DC Hollow Cup Motor Sensor Control Drive Scheme Based on CW32
[Product Solution] Brushless DC Hollow Cup Motor Sensorless Square Wave Control Drive Scheme Based on CW32
[Product Solution] Digital Voltage and Current Meter Product Scheme Based on CW32F003E4P7
[Product Solution] Low-Cost Industrial Instrument Based on CW32L010
CW32 Ecological Community (WX) Group
 Scan to Join QQ Group4 Group| 478586307
Scan to Join QQ Group4 Group| 478586307
Get materials and“Developer Support Program”First-hand information
