To start with the conclusion: Simply put, the interrupt mechanism of the HX2000 is more flexible but complex, suitable for high-precision applications such as industrial motor control, whileCortex-M focuses more on ease of use and automated processing, making it suitable for general embedded control. First, let’s discuss the similarities: Firstly, the interrupt vector table mechanism: Both use an interrupt vector table to jump to the corresponding ISR (Interrupt Service Routine) based on the interrupt number. Secondly, nested support (optional): Both support a certain degree of interrupt priority and nested handling (though the methods differ).
First, let’s discuss the similarities: Firstly, the interrupt vector table mechanism: Both use an interrupt vector table to jump to the corresponding ISR (Interrupt Service Routine) based on the interrupt number. Secondly, nested support (optional): Both support a certain degree of interrupt priority and nested handling (though the methods differ).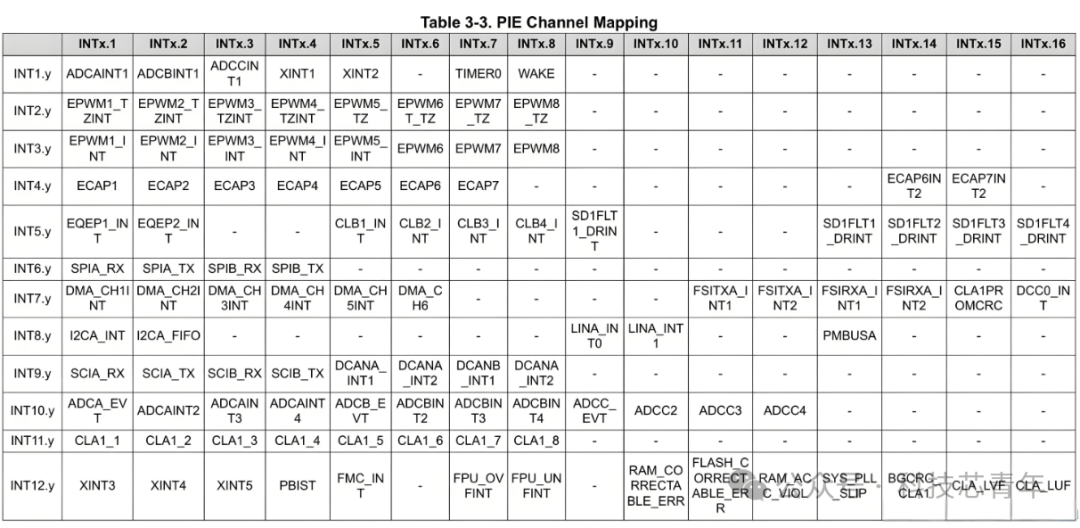 Next, let’s discuss the differences, with detailed descriptions available in the table below:
Next, let’s discuss the differences, with detailed descriptions available in the table below: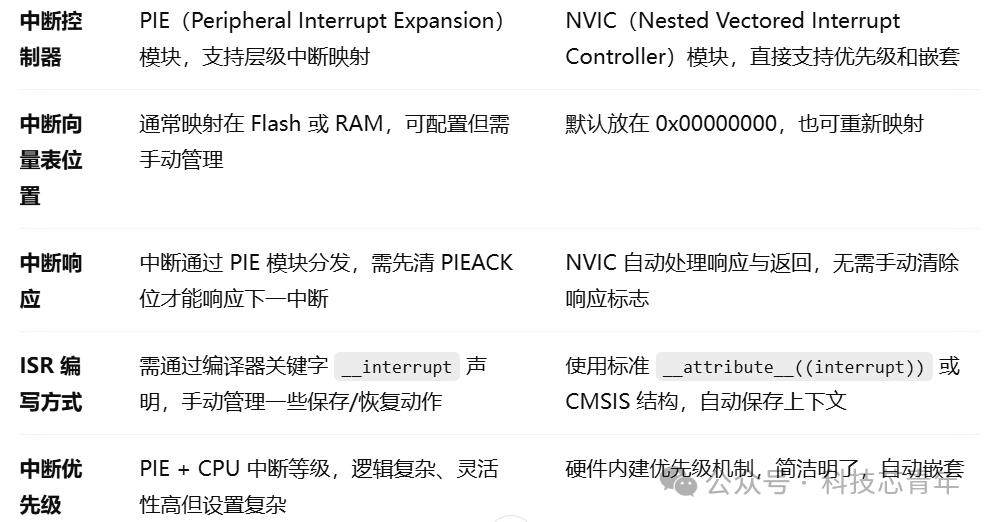 It can be seen that the PIE module of the HX2000 series DSP chips and the NVIC module of ARM Cortex-M have significant differences in structure and usage.The PIE adopts a two-level interrupt architecture, expandable to up to 96 peripheral interrupts, but requires manual management of interrupt enabling, flag clearing, and response priority, making it suitable for motor control scenarios that demand high flexibility and fine control over interrupts.The NVIC, on the other hand, is integrated into the Cortex-M core, supporting multi-level interrupt priorities, automatic nesting, and context saving, making it simple to use and fast in response, more suitable for general real-time control tasks in embedded systems.Core architectural differences
It can be seen that the PIE module of the HX2000 series DSP chips and the NVIC module of ARM Cortex-M have significant differences in structure and usage.The PIE adopts a two-level interrupt architecture, expandable to up to 96 peripheral interrupts, but requires manual management of interrupt enabling, flag clearing, and response priority, making it suitable for motor control scenarios that demand high flexibility and fine control over interrupts.The NVIC, on the other hand, is integrated into the Cortex-M core, supporting multi-level interrupt priorities, automatic nesting, and context saving, making it simple to use and fast in response, more suitable for general real-time control tasks in embedded systems.Core architectural differences Interrupt vector management
Interrupt vector management Interrupt control mechanism
Interrupt control mechanism Performance and user experience
Performance and user experience
In summary, the advantage of PIE is that it is more suitable for complex, high-density control scenarios (such as motor control and power electronics), with flexible interrupt mapping. Meanwhile, the advantage of NVIC is that it is more suitable for applications that require high real-time performance and response efficiency (such as IoT and consumer electronics), with more automated nested processing.
Taking motor control applications as an example, let’s compare the differences in response efficiency between the two. For current loop control, at an interrupt frequency of 10~20kHz, the HX2000 uses PIE+CLA to achieve fast current sampling and closed-loop control; Cortex-M (such as STM32G4 or M7) can also handle it, but may require manual optimization of ISR and DMA.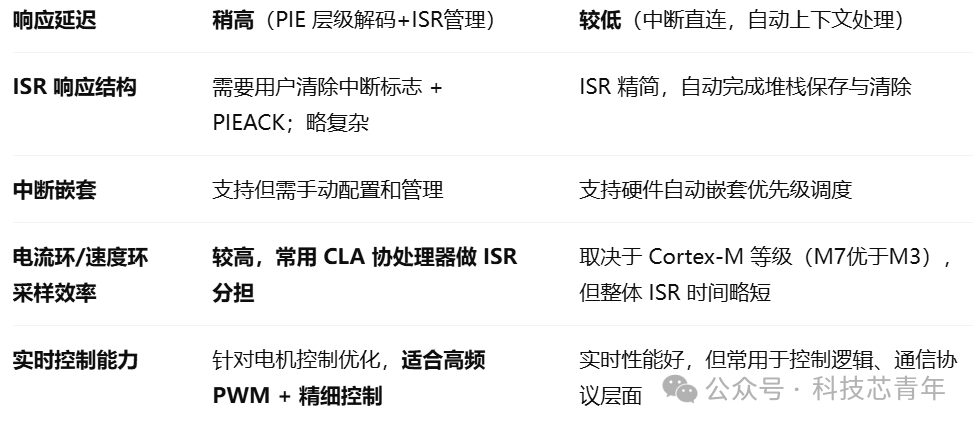 The PIE module is a unique interrupt extension system of the HX2000 RISC-V DSP, with a more complex structure that requires users to manually manage interrupt enabling, clearing, and response, making it suitable for high-precision scenarios such as motor control; while NVIC is the interrupt controller of ARM Cortex-M, which is fast in response, automatically nests, and is easy to use, making it suitable for general control and interrupt-intensive systems. The former is more flexible, while the latter is more efficient.
The PIE module is a unique interrupt extension system of the HX2000 RISC-V DSP, with a more complex structure that requires users to manually manage interrupt enabling, clearing, and response, making it suitable for high-precision scenarios such as motor control; while NVIC is the interrupt controller of ARM Cortex-M, which is fast in response, automatically nests, and is easy to use, making it suitable for general control and interrupt-intensive systems. The former is more flexible, while the latter is more efficient.
Summary and Recommendations:
-
If you need high-frequency ISR + fine control (such as FOC current/velocity dual closed-loop, compressors, servos), HX2000 + PIE is better;
-
If your application primarily involves logic, data processing, or multitasking systems, NVIC is easier to manage interrupts and responds quickly.