 Easy Learning of TIA Portal SCL Programming Structured Variables
Easy Learning of TIA Portal SCL Programming Structured Variables
 Understand S7-1500 PLC Reading and Writing SQL Microsoft Database in Seconds
Understand S7-1500 PLC Reading and Writing SQL Microsoft Database in Seconds
 How to Design a Standardized Modular HMI Interface?
How to Design a Standardized Modular HMI Interface?
 Will Structured Programming with ST, SCL, etc. Become Mainstream?
Will Structured Programming with ST, SCL, etc. Become Mainstream?
PROFINET and PROFIBUS are two fieldbus technologies launched by the PNO organization. The two are not comparable; PROFINET is based on Industrial Ethernet, while PROFIBUS is based on RS485 serial bus. Due to the different media, the protocols are completely different and have no relation. Both have good real-time performance because they use a streamlined stack structure. Any development based on standard Ethernet can be directly applied in a PROFINET network, and there are far more developers for Ethernet-based solutions in the world than for PROFIBUS, thus providing more available resources for technological innovation.
01. For PROFIBUS, the maximum data transmission bandwidth is 12Mbps; for PROFINET, the bandwidth is 100Mbps.
02. For PROFIBUS, the data transmission method is half-duplex; for PROFINET, it is full-duplex.
03. For PROFIBUS, the maximum consistent data size is 32bytes; for PROFINET, it is 254bytes.
04. For PROFIBUS, the maximum user data size is 244bytes; for PROFINET, it is 1400bytes.
05. For PROFIBUS, the maximum bus length at 12Mbps is 100m; for PROFINET, the bus length between devices is 100m.
06. For PROFIBUS, the guiding axis must run in the DP master; for PROFINET, it can run in any SIMOTION.
07. For PROFIBUS, configuration and diagnostics require a special interface template, such as CP5512; for PROFINET, a standard Ethernet card can be used.
08. For PROFIBUS, if one PG connects, it may cause communication issues; for PROFINET RT, one PG connection may cause minimal response, while for PROFINET IRT, connections will not cause any issues.
09. For PROFIBUS, special tools are required for network diagnostics; for PROFINET, IT-related tools are sufficient.
10. For PROFIBUS, there is generally only one master on the bus. A multi-master system can lead to long DP cycle times; for PROFINET, any number of controllers can operate on the network without affecting IO response time.
11. For PROFIBUS, the main failure source on the bus is mismatched bus terminal resistances or poor grounding; for PROFINET, no bus terminal resistance is required.
12. For PROFIBUS, copper and fiber optics are used as communication media; for PROFINET, wireless (WLAN) can be used as an additional medium.
13. For PROFIBUS, an interface can only act as a master or slave; for PROFINET, all data types can be used in parallel, allowing an interface to act as both a controller and an IO device.
14. For PROFIBUS, it is impossible to determine the network location of devices; for PROFINET, the network location can be determined through topology information.
[Video] Direct Explanation of Why PROFINET is Superior to PROFIBUS?
 Click here to watch the video
Click here to watch the video
What are the Differences Between Ethernet, Industrial Ethernet, and PROFINET?
Ethernet (EtherNET) usually refers to the baseband local area network specification created by Xerox and jointly developed by Xerox, Intel, and DEC. It is the most widely used LAN technology today. It is not a specific network, but a technical specification. The standard mainly defines the cable types and signal processing methods used in local area networks (LAN).
Industrial Ethernet usually refers to Ethernet technology applied in the field of industrial control. It is technically compatible with ordinary Ethernet technology but has different requirements for specific products and applications. Since products must be used in industrial environments, they have higher requirements for materials, strength, applicability, interoperability, reliability, and anti-interference; moreover, Industrial Ethernet is aimed at industrial production control, with extremely high requirements for data real-time performance, determinism, and reliability.
PROFINET, launched by PROFIBUS International (PI), is an automation bus standard based on Industrial Ethernet technology. PROFINET provides a complete network solution for automation communication, encompassing real-time Ethernet, motion control, distributed automation, fault tolerance, and network security, among other current automation fields.
In simple terms, Ethernet is a LAN specification, Industrial Ethernet is Ethernet technology applied in the field of industrial control, and PROFINET is a real-time technical specification running on Industrial Ethernet.
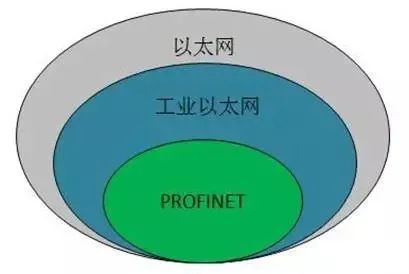
Figure 1 Relationship Diagram
PROFINET = PROFIBUS + Ethernet, transplanting the master-slave structure of PROFIBUS to Ethernet, so PROFINET will have Controllers and Devices, which can be simply mapped to the Master and Slave of PROFIBUS. Of course, there are differences, but this mapping can help understanding. Additionally, since PROFINET is based on Ethernet, it can have star, tree, and bus topologies, while PROFIBUS only has bus topology. Therefore, PROFINET is the product of combining the master-slave structure of PROFIBUS and the topology structure of Ethernet. Other features, such as timeliness, are also present in Ethernet; however, PROFINET can improve the accuracy of timeliness due to the presence of a control unit like a Controller.
PROFINET is a new Ethernet communication system developed by Siemens and the PROFIBUS user association. PROFINET has the communication capability between products from multiple manufacturers, automation and engineering modes, and is optimized for distributed intelligent automation systems. The application results can significantly save configuration and debugging costs. PROFINET integrates systems based on PROFIBUS, providing protection for existing system investments. It can also integrate other fieldbus systems.
PROFINET is an advanced communication system supporting distributed automation. In addition to communication functions, it also includes specifications for the concept of distributed automation, based on manufacturer-independent objects and connection editors, as well as XML device description language. Ethernet TCP/IP is used for communication between intelligent devices where timing requirements are not strict. All time-critical real-time data is transmitted via standard PROFIBUS DP technology, and data can be integrated into the PROFINET system from the PROFIBUS DP network through proxies. PROFINET is the only bus that uses existing IT standards without defining its dedicated industrial application protocol. Its object model is based on Microsoft’s Component Object Model (COM) technology. For interaction between all distributed objects on the network, Microsoft’s DCOM protocol and standard TCP and UDP protocols are used.
In the PROFINET concept, devices and factories are divided into technical modules, each module includes mechanical, electronic, and application software. The application software of these components can be developed using dedicated programming tools and downloaded to the relevant controllers. These dedicated software must implement the PROFINET component software interface and be able to export the PROFINET object definitions as XML language. XML files are used to input manufacturer-independent PROFINET connection editors to generate PROFINET elements. The connection editor defines the exchange operations between PROFINET elements on the network. Finally, the connection information is downloaded to PROFINET devices via Ethernet TCP-IP.
PROFINET (Real-Time Ethernet) is based on Industrial Ethernet, has excellent real-time performance, can directly connect field devices (using PROFINET IO), and supports distributed automation control methods (PROFINET CBA, equivalent to communication between master stations).
After Ethernet is applied in industrial control scenarios and improved for use in industrial environments, it becomes Industrial Ethernet. If you have ever used Siemens network cards CP343-1 or CP443-1 for communication, you may have used protocols like ISO or TCP connections. The TCP and ISO used here are protocols applied on Industrial Ethernet.
PROFINET is also a protocol in Siemens SIMATIC NET, specifically a collection of many protocols, including real-time protocols like PROFINET IO RT, CBA RT, IO IRT, etc. Therefore, PROFINET and Industrial Ethernet cannot be compared; it can only be said that PROFINET is a real-time protocol running on Industrial Ethernet. However, it is often said that some networks are PROFINET networks, simply because the PROFINET protocol is applied on that network.
 [Video] How Do German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets?
[Video] How Do German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets?
 [Video] What Is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like?
[Video] What Is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like?
 [Video] Why Is PROFINET Superior to PROFIBUS?
[Video] Why Is PROFINET Superior to PROFIBUS?

 Easy Learning of TIA Portal SCL Programming Structured Variables
Easy Learning of TIA Portal SCL Programming Structured Variables Understand S7-1500 PLC Reading and Writing SQL Microsoft Database in Seconds
Understand S7-1500 PLC Reading and Writing SQL Microsoft Database in Seconds How to Design a Standardized Modular HMI Interface?
How to Design a Standardized Modular HMI Interface? Will Structured Programming with ST, SCL, etc. Become Mainstream?
Will Structured Programming with ST, SCL, etc. Become Mainstream? Click here to watch the video
Click here to watch the video
 [Video] How Do German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets?
[Video] How Do German Engineers Make PLC Cabinets? [Video] What Is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like?
[Video] What Is the Office Environment of German Engineers Like? [Video] Why Is PROFINET Superior to PROFIBUS?
[Video] Why Is PROFINET Superior to PROFIBUS?