
Welcome to Follow
Share the Wonderful


Go 2022
Click the Above Blue Words to Follow This Official Account.
Long-term Updates on DCS, DEH, TSI, ETS, CCS, FSSS, PLC, Relay Protection, Digitalization and other core technologies in power.
Add WeChatepengcser, Face to Face with the Blogger.
Follow the Blogger on Today’s Headlines, Xigua Video, and Bilibili Energy Studies, More Exciting Content Preview!
Ethernet is a well-known network created by Xerox and jointly developed by Xerox, Intel, and DEC as a baseband local area network standard. It is the most commonly used communication protocol standard in existing local area networks, including standard Ethernet (10 Mbit/s), Fast Ethernet (100 Mbit/s), and 10G Ethernet (10 Gbit/s).

PROFIBUS is an international, open, fieldbus standard that does not depend on device manufacturers. The transmission speed of PROFIBUS can be selected within the range of 9.6 kbaud to 12 Mbaud, and when the bus system starts, all devices connected to the bus should be set to the same speed. It is widely used in manufacturing automation, process industry automation, building, transportation, and other fields. PROFIBUS is a fieldbus technology used for workshop-level monitoring and data communication and control at the field device layer. It enables decentralized digital control and field communication networks from the field device layer to workshop-level monitoring, providing feasible solutions for integrated factory automation and intelligent field devices.

PROFINET = PROFIBUS + Ethernet, transplanting the master-slave structure of Profibus to Ethernet, so Profinet has Controllers and Devices, which can be simply associated with the Master and Slave of Profibus. Of course, there are differences, but this correspondence can help with understanding. Additionally, since Profinet is based on Ethernet, it can have star, tree, and bus topologies, while Profibus only has a bus topology. Therefore, Profinet is a product that combines the master-slave structure of Profibus with the topology structure of Ethernet. Other features like real-time characteristics, which Siemens promotes, are also present in Ethernet; however, Profinet can enhance the accuracy of real-time characteristics due to the presence of a Controller.

PROFINET is a new Ethernet communication system developed by Siemens and the Profibus User Association. PROFINET has communication capabilities between multi-manufacturer products, automation and engineering modes, and is optimized for distributed intelligent automation systems. Its application results can significantly save configuration and debugging costs. The PROFINET system integrates Profibus-based systems, providing protection for existing system investments. It can also integrate other fieldbus systems.
PROFINET is an advanced communication system that supports distributed automation. In addition to communication functions, PROFINET also includes specifications for the distributed automation concept, which is based on manufacturer-independent objects and connection editors and XML device description languages. Ethernet TCP/IP is used for communication between intelligent devices where timing requirements are not strict. All time-critical real-time data is transmitted through standard PROFIBUS DP technology, and data can be integrated into the PROFINET system from the PROFIBUS DP network through proxies. PROFINET is unique in using existing IT standards without defining its own dedicated industrial application protocol bus. Its object model is based on Microsoft’s Component Object Model (COM) technology. For interaction between all distributed objects on the network, Microsoft’s DCOM protocol and standard TCP and UDP protocols are used.

In the PROFINET concept, devices and factories are divided into technical modules, each module includes mechanical, electronic, and application software. The application software of these components can be developed using dedicated programming tools and downloaded to the relevant controllers. These dedicated software must implement the PROFINET component software interface and be able to export the PROFINET object definitions in XML language. The XML file is used to input manufacturer-independent PROFINET connection editors to generate PROFINET components. The connection editor defines the exchange operations between PROFINET components on the network. Finally, the connection information is downloaded to the PROFINET devices via Ethernet TCP-IP.
PROFINET (Real-time Ethernet) is based on Industrial Ethernet, has good real-time performance, can directly connect field devices (using PROFINET IO), and supports distributed automation control methods (PROFINET CBA, equivalent to communication between master stations).
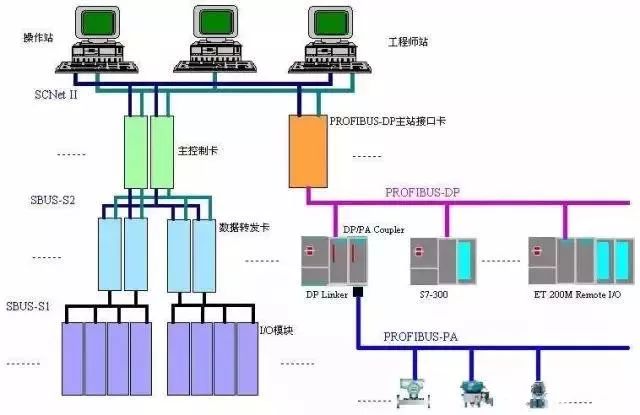
When Ethernet is applied to industrial control scenarios, it is improved for use in industrial sites, becoming Industrial Ethernet. If you have ever used Siemens network cards CP343-1 or CP443-1 for communication, you may have used protocols like ISO or TCP connections. The TCP and ISO used here are protocols applied to Industrial Ethernet.
PROFINET is also a protocol in Siemens SIMATIC NET, specifically a collection of many protocols, including PROFINET IO RT, CBA RT, IO IRT, etc. Therefore, PROFINET and Industrial Ethernet cannot be compared; it can only be said that PROFINET is a real-time protocol running on Industrial Ethernet. However, it is often said that some networks are PROFINET networks, as it simply means that the PROFINET protocol is applied on that network.
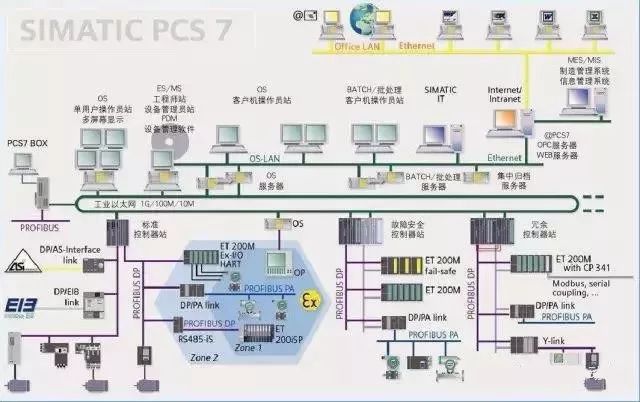
PROFINET is based on Industrial Ethernet, while PROFIBUS is based on RS485 serial bus. The two protocols are completely different due to the different media and have no correlation. They both have good real-time performance because they utilize a streamlined stack structure. Any development based on standard Ethernet can be directly applied in the PROFINET network, and there are far more developers of Ethernet-based solutions in the world than those of PROFIBUS, leading to more available resources for technological innovation.
For PROFIBUS, the maximum data transmission bandwidth is 12 Mbps, while for PROFINET, it is 100 Mbps.
For PROFIBUS, the data transmission method is half-duplex, while for PROFINET, it is full-duplex.
For PROFIBUS, the maximum consistent data size is 32 bytes, while for PROFINET, it is 254 bytes.
For PROFIBUS, the maximum user data size is 244 bytes, while for PROFINET, it is 1400 bytes.
For PROFIBUS, the maximum bus length at 12 Mbps is 100m, while for PROFINET, the bus length between devices is also 100m.
For PROFIBUS, configuration and diagnostics require specialized interface templates, such as CP5512, while for PROFINET, standard Ethernet network cards can be used.
For PROFIBUS, special tools are required for network diagnostics, whereas for PROFINET, IT-related tools are sufficient.
For PROFIBUS, the main source of faults on the bus comes from mismatched bus terminal resistors or poor grounding, while for PROFINET, bus terminal resistors are not required.
This article is copyrighted by the original author. If there is any copyright issue, please contact for deletion!
◆◆
1. Discussing the Openness, Compatibility, and Barriers of Enterprise Digitalization!
2. Things About the DEH System in Thermal Power Plants!
3. Discussing OPC Action Signals in the DEH System!
4. Discussing the Turbine DEH Speed Signal in Thermal Power Plants!
5. Collection | Notes on the DEH System in Thermal Power Plants
6. Understanding the TSI System of Turbines from Scratch! Attached: Complete Explanation of Bentley 3500 Configuration
7. Classic Physics That Cannot Be Avoided in Thermal Power Generation – Rankine Cycle
8. Four Videos, Two Thousand Six Hundred Words, Let’s Talk About PID Parameter Tuning Again!
9. Comparison of Several Mainstream DCS Systems’ PID Regulation!
10. In a Lifetime, When Paths Cross, How to Integrate and Master Multiple DCS Systems
