Serial Communication
My Diary 2024
Is the most basic communication method faced by electrical engineers, with RS-232 being the simplest among them. Many beginners often struggle to understand the relationship and differences between UART and RS-232, RS-422, RS-485. This article will discuss these concepts to help clarify their relationships.
If we compare serial communication to traffic, UART can be likened to a bus station, while a frame of data is akin to a car. Cars on the road must adhere to traffic rules. In urban areas, speed limits are generally 30 or 40, while on highways, they can reach 120. The protocol dictates what kind of road a car can take and the speed limit. Common serial protocols include RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485. What are the subtle differences between them? Let’s explore.
1. What is UART
My Diary 2024
UART, or Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter, is a key module for asynchronous communication between devices. UART handles the serial/parallel conversion between the data bus and the serial port and specifies the frame format; as long as both communication parties use the same frame format and baud rate, they can communicate using just two signal lines (Rx and Tx) without sharing a clock signal, hence it is also referred to as asynchronous serial communication.
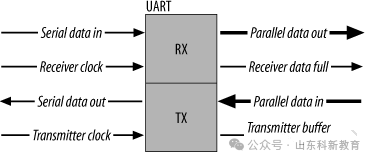
If a suitable level converter, such as SP3232E or SP3485, is added, UART can also be used for RS-232 and RS-485 communication or to connect to a computer’s port. UART is widely used in applications such as mobile phones, industrial control, and PCs.

UART uses asynchronous, serial communication.
Serial communication refers to the transmission of data bit by bit over a single transmission line. Its characteristics include simple communication lines, which can be implemented with simple cables, reducing costs and making it suitable for long-distance communication, although it is slower.
Asynchronous communication uses a character as the transmission unit, and the time interval between two characters is variable; however, the time interval between two adjacent bits in the same character is fixed.
The data transmission rate is expressed in baud rate, which indicates the number of binary bits transmitted per second. For example, if the data transmission rate is 120 characters per second, and each character consists of 10 bits (1 start bit, 7 data bits, 1 parity bit, 1 stop bit), then the baud rate would be 10×120 = 1200 characters per second = 1200 baud.
The data communication format is as shown in the figure below:
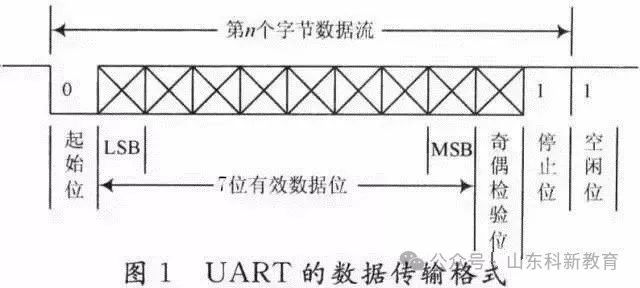
The meanings of each bit are as follows:
Start Bit: A logical “0” signal is sent first, indicating the beginning of the transmission character.
Data Bit: Can be 5 to 8 bits of logical “0” or “1”. For example, ASCII code (7 bits), extended BCD code (8 bits). Little-endian transmission.
Parity Bit: This bit, when added to the data bits, ensures that the number of “1” bits is even (even parity) or odd (odd parity).
Stop Bit: This indicates the end of a character data. It can be 1 bit, 1.5 bits, or 2 bits of high level.
Idle Bit: Remains in a logical “1” state, indicating that there is no data transmission on the current line.
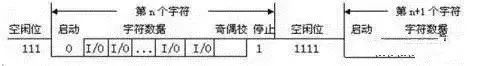
Note: Asynchronous communication is character-based. The receiving device can correctly receive the data as long as it can synchronize with the sending device within the transmission time of one character after receiving the start signal. The arrival of the start bit of the next character recalibrates the synchronization (achieved by detecting the start bit for self-synchronization of the clocks of the sender and receiver).
2. RS-232 Standard
My Diary 2024
RS-232 is a serial physical interface standard established by the Electronic Industry Association (EIA) in the United States. RS is an abbreviation for “Recommended Standard,” and 232 is the identification number. RS-232 specifies electrical and physical characteristics that apply only to the data transmission path; it does not include data processing methods. It should be noted that many people often mistakenly refer to RS-232, RS-422, and RS-485 as communication protocols; this is incorrect as they are merely mechanical and electrical interface standards for UART communication (at most, they pertain to the physical layer of network protocols).
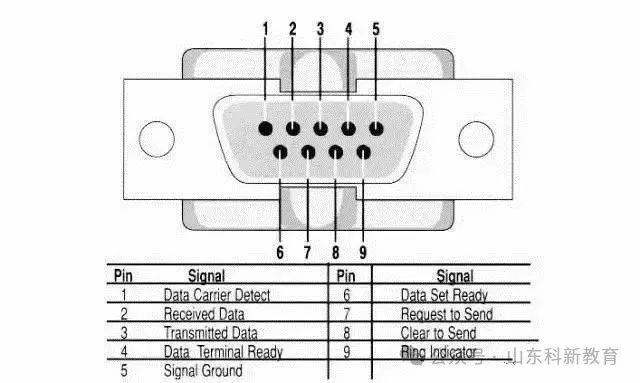
The standard specifies the use of a 25-pin DB-25 connector, detailing the signal content for each pin, and also specifying the voltage levels for various signals. Later, IBM simplified RS-232 to a DB-9 connector, which has become the de facto standard today. The RS-232 port in industrial control generally only uses three lines: RXD (2), TXD (3), and GND (5).
In the early days, as PCs were equipped with RS-232 interfaces, RS-232 was the choice for UART usage. However, personal computers today, including laptops and desktops, no longer come with RS-232 interfaces; you may notice that there are no DB9 connectors on computer motherboards. Therefore, development boards now prefer TTL UART or directly implement UART to USB on the boards.
In embedded systems, the term “serial port” generally refers to the UART port, but we often confuse it with the COM port, as well as the relationship between RS-232, TTL, etc. In fact, UART and COM refer to the physical interface form (hardware), while TTL and RS-232 refer to the voltage standards (electrical signals).
UART has 4 pins (VCC, GND, RX, TX), using TTL levels, with low level as 0 (0V) and high level as 1 (3.3V or above).

3. RS-485/ RS-422 Standard
My Diary 2024
RS-232 Interface can achieve point-to-point communication, but this method cannot realize network functions. To solve this problem, a new standard, RS-485, was developed. RS-485 uses differential transmission for data signals, also known as balanced transmission, employing a pair of twisted wires designated as A and B.
Typically, the positive voltage between the sending driver A and B is +2 to +6V, representing one logical state, while the negative voltage is -2 to 6V, representing another logical state. There is also a signal ground C, and in RS-485, there is an