If you don’t want to miss my updates, remember to check the public account in the upper right corner and set it as a star, giving me a star in return.
Based on the Cortex-M core, the mainstream download interfaces are JTAG and SWD.
Differences Between SWD and JTAG Pins:
-
TDI: Test Data In. Serial input pin
-
TDO: Test Data Out, serial output pin
-
TCK: Test Clock, clock pin
-
TMS: Test Mode Select, mode selection (control signal) pin
-
TRST: Test Reset, reset pin
-
SWDIO: Serial Wire Data Input Output, serial data input/output pin
-
SWCLK: Serial Wire Clock, serial wire clock pin
SWD only requires two lines (SWCLK and SWDIO), making it a good choice when PCB layout is limited and pin resources are tight.
SWD: Serial Wire Debug, represents serial wire debugging, is a protocol designed by ARM for programming and debugging its microcontrollers.
There are many downloaders on the market that support the SWD debugging interface, such as:ST-Link, J-Link, e-Link, GD-Link and most downloaders used for Cortex-M core processors support it.
For SWDIO, it is a bidirectional (input/output) data pin, and a pull-up must be applied to the circuit board (ARM recommends using 100 K).
Each time the direction of SWDIO changes in the protocol, a transition time is inserted, during which the line is not driven by either the host or the target. By default, this transition time is one bit time, but it can be adjusted by configuring the SWCLK frequency.
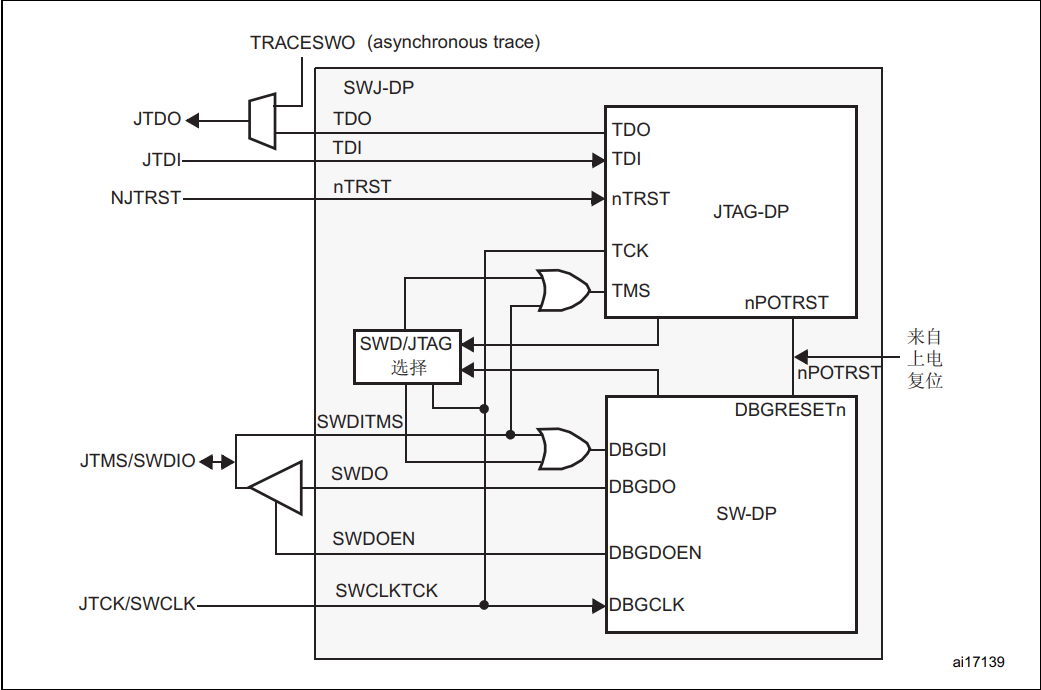
Common Cortex-M core processors integrateSWD and JTAG debug ports, where two JTAG pins of SW-DP are multiplexed with five JTAG pins of JTAG-DP.
Switching Mechanism Between JTAG and SWD:
The default debug interface is the JTAG interface. If the debugging tool wants to switch to SW-DP, it must provide a dedicated JTAG sequence on TMS/TCK (mapped to SWDIO and SWCLK) to disable JTAG-DP and enable SW-DP. This allows the activation of SWDP using only the SWCLK and SWDIO pins.
1. Output TMS (SWDIO) signal = 1 for more than 50 TCK cycles
2. Output 16 TMS (SWDIO) signals 0111100111100111 (MSB)
3. Output TMS (SWDIO) signal = 1 for more than 50 TCK cycles
Each sequence includes three stages:
-
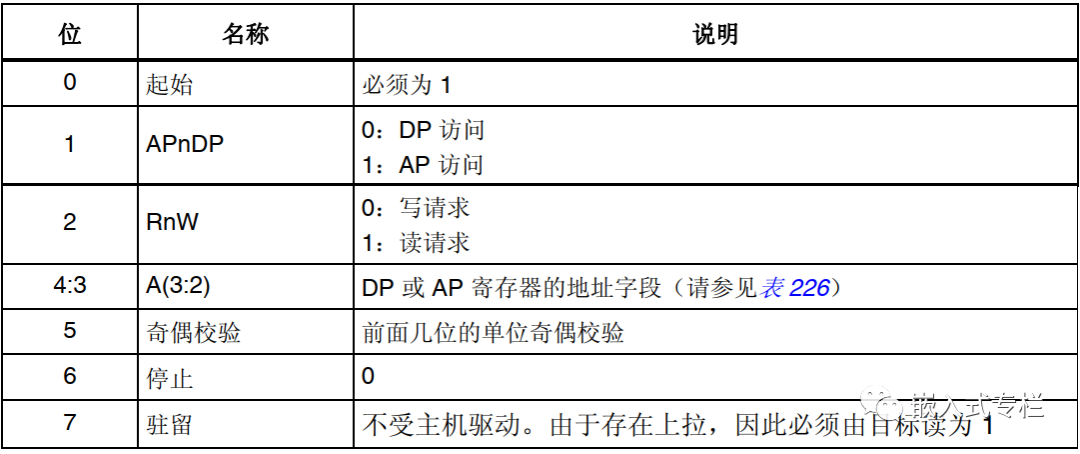
The host sends a data packet request (8 bits)
-
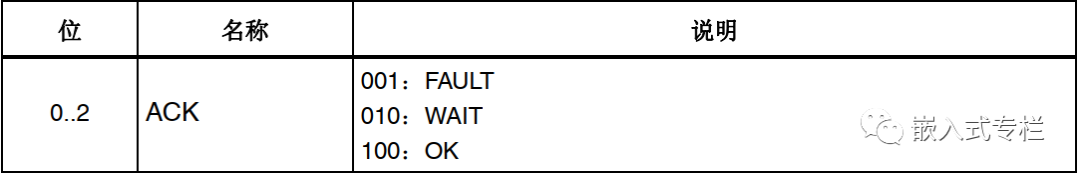
The target sends a confirmation response (3 bits)
-
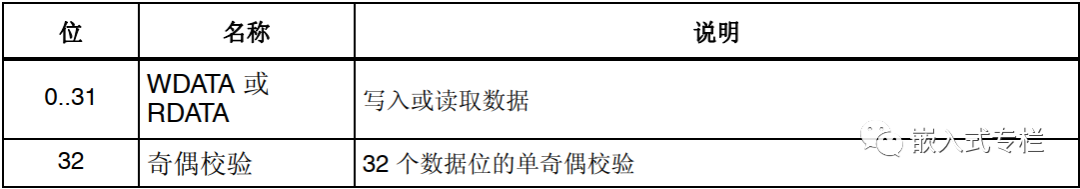
The host or target sends the data transfer stage (33 bits)
Data Packet Request (8 bits):
This is similar to some bit operations of registers, and some principles at the lower level are similar tocommon communication protocols.
The SW-DP state machine has an internal ID code to identify SW-DP, which mainly includes states: reset, idle state, ID code, etc.
-
After power-on reset, when DP switches from JTAG to SWD, or when the line stays high for more than 50 cycles, the SW-DP state machine is in the reset state.
-
If the line stays low for at least two cycles after the reset state, the SW-DP state machine is in the idle state.
-
After the reset state, the state machine must first enter the idle state and then perform a read access to the DP-SW ID CODE register. Otherwise, the target will issue a FAULT confirmation response on another transaction.
For more details on the SW-DP state machine, refer to some manuals related toCortex-M.
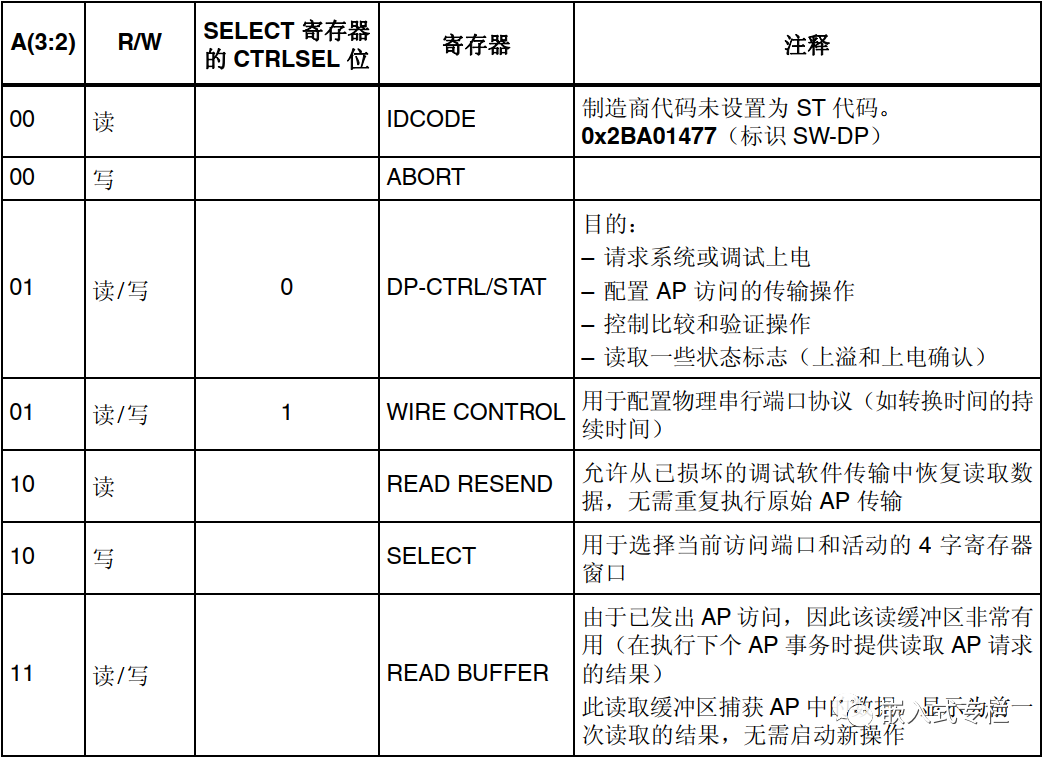
SWD is similar to ordinary peripherals and has a type of register. The programming operations (read/write) performed by developers are actually operations on the corresponding registers.
This concludes the introduction to the underlying aspects of SWD. For more details, please refer to theCortex-M core manual.
This article is reproduced from the public account: strongerHuang
Project Sharing | Electric Competition Series | Artificial Intelligence | Graduate School
Essential Knowledge Points | Graduation Project | Switching Power Supply | Job Hunting
We are Nimo, the founder of Darwin, and we only talk about technology without flirting. Darwin is an online education platform aimed at serving professionals in the electronics industry, providing skill training videos covering popular topics in various subfields, such as embedded systems, FPGA, artificial intelligence, etc. We tailor layered learning content for different groups, including commonly used knowledge points, disassembly assessments, electric competitions/intelligent vehicles/graduate school, etc. Welcome to follow.
Official website: www.darwinlearns.com
QQ Group: Group 1: 786258064 (full)
Group 2: 1057755357 (full)
Group 3: 871373286