
The exact pathogenesis of Meige Syndrome is currently unclear; however, long-term use of psychiatric medications, facial nerve infections, and psychological factors may trigger MS.
Medication Treatment: Currently, the effectiveness of medication treatment is limited, and the duration of efficacy is often short. Commonly used medications include anticholinergic drugs, such as benztropine, which can reduce the frequency of eyelid spasms; sedative or antipsychotic medications, such as diazepam and haloperidol, can effectively alleviate symptoms but have significant side effects; muscle relaxants, such as baclofen.
-
Selective sectioning of the facial nerve to alleviate BSP involves primarily cutting the zygomatic or buccal branches of the facial nerve to reduce frequent involuntary blinking and closing while preserving the ability to close the eyelids voluntarily. -
Alleviating BSP by excising part of the eyelid muscles (part of the orbicularis oculi, pretarsal muscle, preseptal muscle, and corrugator muscle) is another method. -
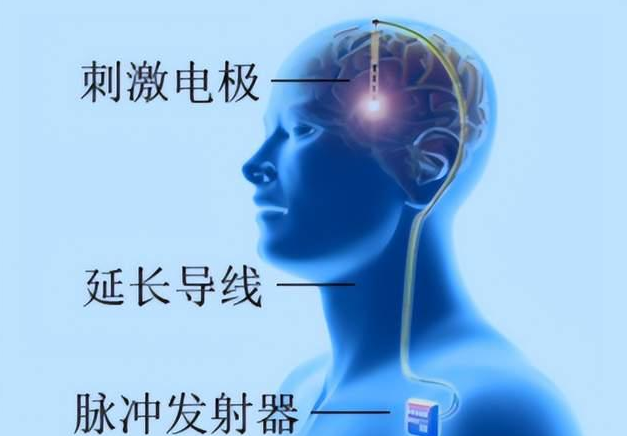
DBS is the most commonly used surgical method with the most clinical research. DBS surgery, also known as deep brain stimulation, is a new surgical method for treating Meige syndrome that has emerged with the development of stereotactic technology. It involves implanting fine electrodes in the brain to emit electrical pulses to stimulate specific nuclei in the brain, controlling the abnormal excitation of neurons, thereby improving motor symptoms, with characteristics of reversibility and controllability.
As one of the difficult-to-cure conditions, MS poses challenges for both patients and doctors, especially for patients who suffer not only physically but also psychologically.
Is there a better direction for treatment in the future? A complete reflex arc requires receptors – afferent nerves – central – efferent nerves – effectors. Some researchers have found that performing radiofrequency treatment on the trigeminal nerve for trigeminal neuralgia and on the facial nerve for facial spasms allows patients to open their eyes and reduces masticatory muscle strength post-surgery. Cutting the relevant responsible nerves controlling muscle movement in MS patients (such as selective facial nerve sectioning) can stop signal transmission.
So, would targeting different types of MS with radiofrequency treatment on the facial nerve and/or trigeminal nerve effectively alleviate MS symptoms? Perhaps this is a direction worth exploring.
Liu Xiaolan, Xu Shuangshuang, Zhao Wei, et al. Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment Progress of Meige Syndrome [J]. Chinese Journal of Pain, 2022, 18(3): 419-423.
『Voice of Pain』 is a learning team formed by young doctors in the field of pain medicine (anesthesiology) at the undergraduate, master’s, doctoral, and postdoctoral levels, if you are also eager to learn, join us! Professional content writing guides and excellent seniors are waiting for you to chat (scan the code below).
Do you have any experience in treating Meige Syndrome? Add the WeChat of the administrator below to join the group chat! Pain Doctors Group Chat // Anesthesia (Pain) Master’s and Doctoral Club // Anesthesia (Pain) Training Group // National Anesthesia (Pain) Graduate Circle, there’s bound to be a group chat that suits you

Author | Yao Weijie
Editor | Ma Xiaoxuan