At the end of this article, there are 55 practical case materials.Introduction: In industrial automation, PLCs are one of the core devices that need to communicate with multiple external devices for real-time monitoring and response. In these applications, “heartbeat detection” is a very important function that can effectively mitigate significant production safety risks caused by communication interruptions or device failures.In this article, we will write a communication “heartbeat detection” function block for everyone’s reference.Approach: We can compare whether a certain status value changes within a time range; if it changes, communication is normal; if it does not change, communication is interrupted.1. SCL Language Programming Method(1) Create a new FB block in TIA Portal software.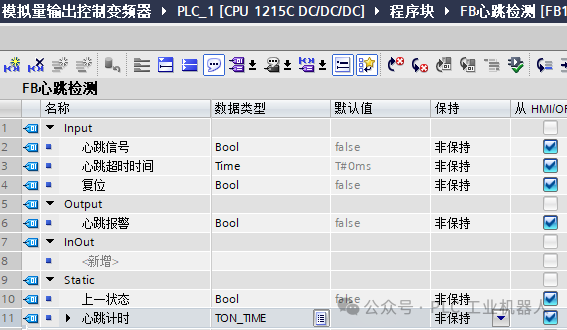 (2) Lines 1 to 4 of the program start the timer when the timer’s time has not been reached.Lines 7 to 13 of the program check whether the heartbeat signal is the same as the last status; if different, reset the timer and assign the status value of “#heartbeat signal” to “#previous status”.
(2) Lines 1 to 4 of the program start the timer when the timer’s time has not been reached.Lines 7 to 13 of the program check whether the heartbeat signal is the same as the last status; if different, reset the timer and assign the status value of “#heartbeat signal” to “#previous status”. Lines 15 to 22 of the program check the timer’s time; when the time is reached, the alarm output value is 1, otherwise it is 0. Pressing the reset button can reset the timer and the alarm.
Lines 15 to 22 of the program check the timer’s time; when the time is reached, the alarm output value is 1, otherwise it is 0. Pressing the reset button can reset the timer and the alarm. (3) The main program calls the FB program block.
(3) The main program calls the FB program block.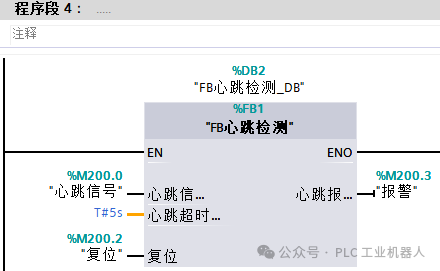 2. Ladder Diagram Language Programming Method(1) Create a new FB block in TIA Portal software.
2. Ladder Diagram Language Programming Method(1) Create a new FB block in TIA Portal software.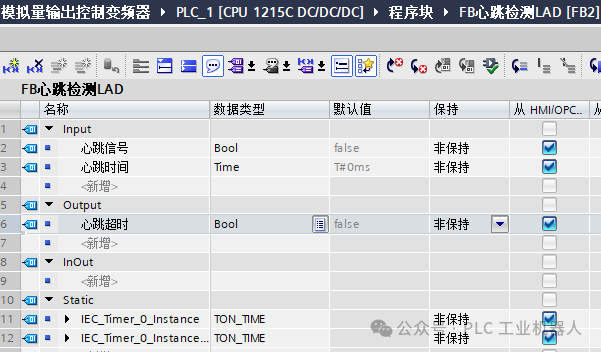 (2) Program writingAs long as the heartbeat signal continuously changes between 0 and 1, the timer will count, but if the signal does not change, one of the timers will be activated, and when the time is reached, an alarm signal will be output.
(2) Program writingAs long as the heartbeat signal continuously changes between 0 and 1, the timer will count, but if the signal does not change, one of the timers will be activated, and when the time is reached, an alarm signal will be output.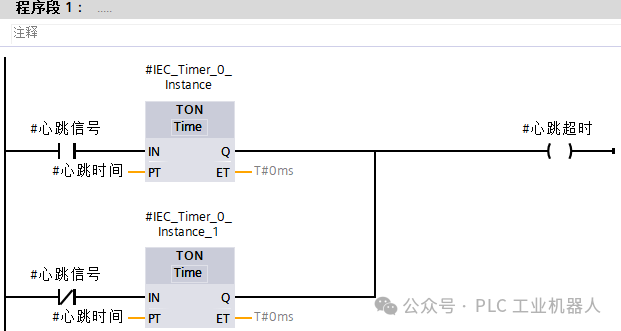 (3) The main program calls the FB program block.
(3) The main program calls the FB program block.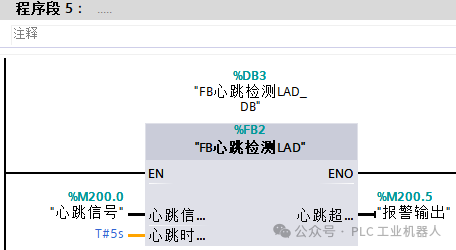 Conclusion: In this case, whether using ladder diagrams or SCL language programming, it essentially requires the signal sent by the other device to continuously change between 0 and 1, which means that M200.0 in the program is the signal sent by the other device. If communication is interrupted at any moment, the value will not change.Recently, many friends have asked for case books, saying that reading articles on mobile phones is not very convenient. I took some time to organize all 55 practical cases, which are quite typical, including cylinder control programs, alarm programs, program frameworks, motion control program encapsulation, analog control of frequency converters, communication, and other practical cases.If you need them, you can add me on WeChat: biao467524527. If you can’t add me, you can send me a private message.
Conclusion: In this case, whether using ladder diagrams or SCL language programming, it essentially requires the signal sent by the other device to continuously change between 0 and 1, which means that M200.0 in the program is the signal sent by the other device. If communication is interrupted at any moment, the value will not change.Recently, many friends have asked for case books, saying that reading articles on mobile phones is not very convenient. I took some time to organize all 55 practical cases, which are quite typical, including cylinder control programs, alarm programs, program frameworks, motion control program encapsulation, analog control of frequency converters, communication, and other practical cases.If you need them, you can add me on WeChat: biao467524527. If you can’t add me, you can send me a private message.


Previous Recommendations
Learn mode switching and automatic control program with one case.
Having trouble adjusting the PID of the 1200 PLC? This issue might be the cause!
PLC automatic control programming “three axes”.
PLC addressing that confuses 80% of beginners is actually very simple!
POKE programming method for IO mapping of the 1200 PLC.
How to change PLC input and output point functions on a touch screen.
Four underlying logics for learning PLC programming.
Automatic rotation of 8 water pumps (fault auto-skip).
How to automatically select the shortest and longest running time and corresponding number from 5 water pumps.
It’s not that you can’t program PLCs; you might just be missing an idea!
Interpreting standard program encapsulation ideas and methods with cases.
Mastering three practical programming methods for device mode switching control.
Programming idea: Random start and stop case for 7 motors.
Methods to reduce 3 days of programming workload to 1 day—complex data types.
How many of the 12 classic questions about TIA Portal software do you know?