Today, I will share some common underlying data transmission principles of communication; UART, SPI, and I2C are very common communication methods in embedded development, and the fundamental communication principles of these methods are not difficult to understand.
1. UART Serial Communication
UART: Universal Asynchronous Receiver/Transmitter.
The UART serial port is the most common type of serial communication. Below is an animation showing the connection of the serial port to a PC, as well as the application of RS232.
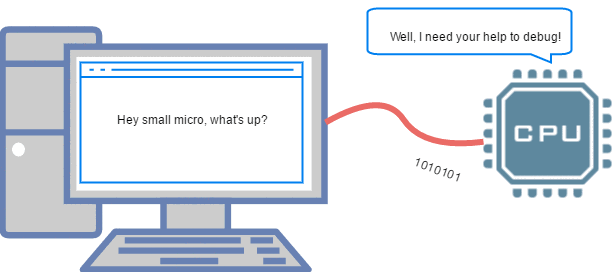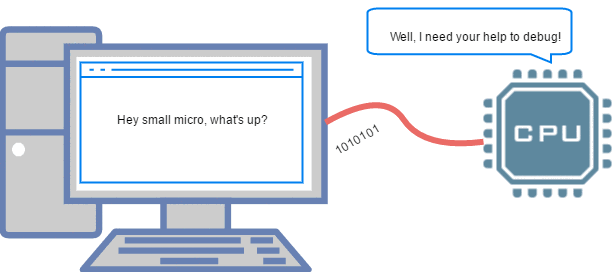
▲ Debugging MCU through UART on PC
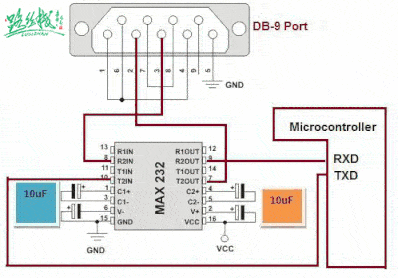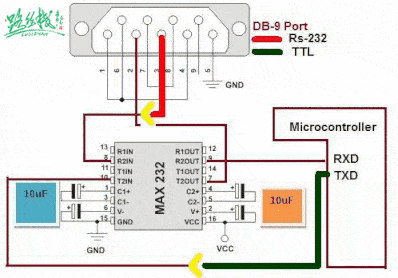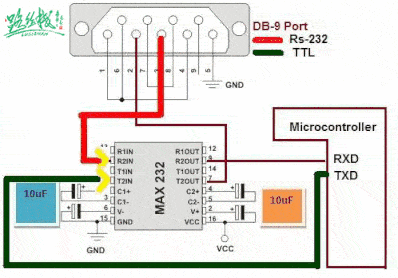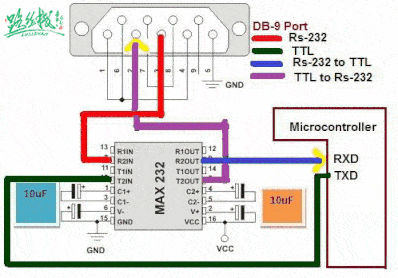
▲ RS-232 communication with MCU through level conversion chip
2. SPI Serial Communication
SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface.
SPI is a common serial synchronous communication protocol with very wide applications.
Below is the timing diagram of SPI data transmission:
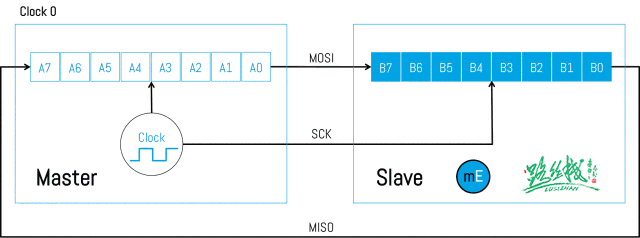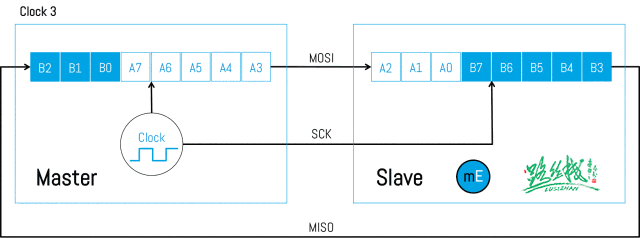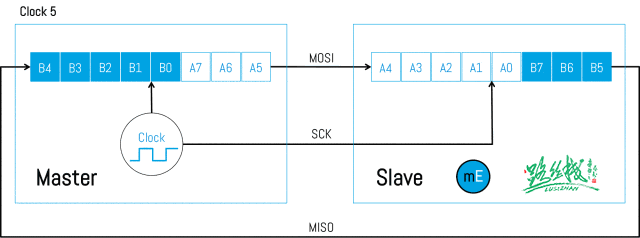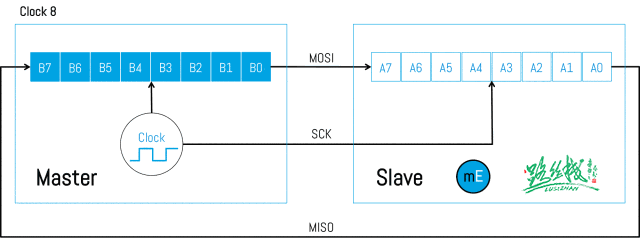
▲ SPI Data Transmission (1)
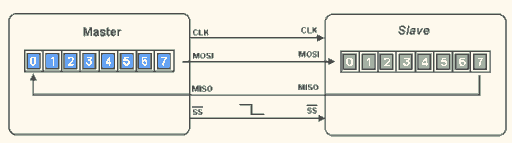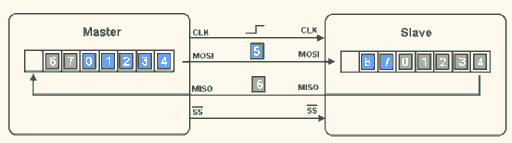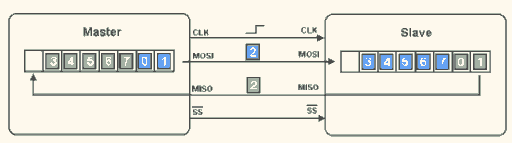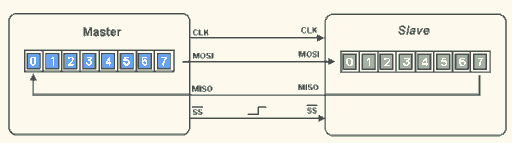
▲ SPI Data Transmission (2)

▲ SPI Timing Signals
3. I2C Communication
I2C: Inter-Integrated Circuit, literally meaning communication between integrated circuits, is short for I2C Bus.
I2C mainly distinguishes slave devices through addresses, and its communication principle is relatively simple.
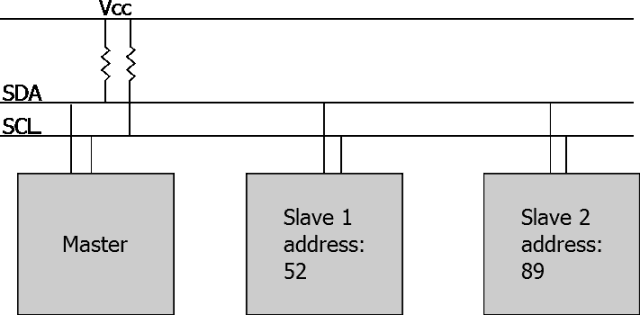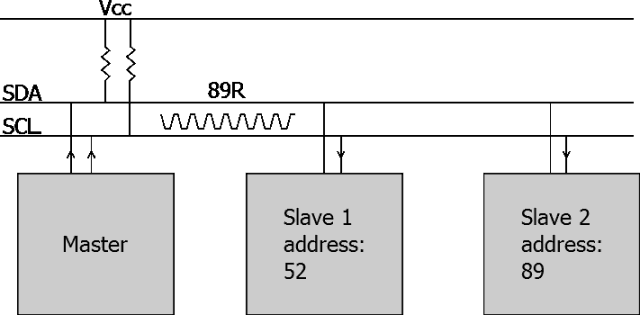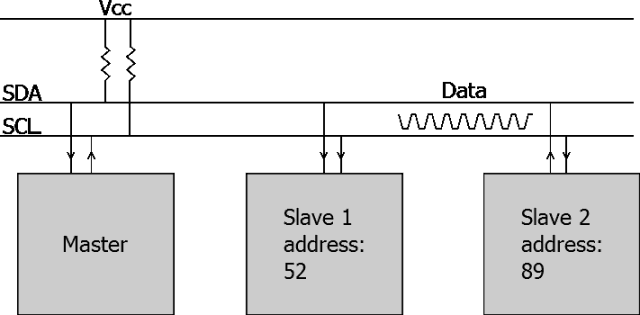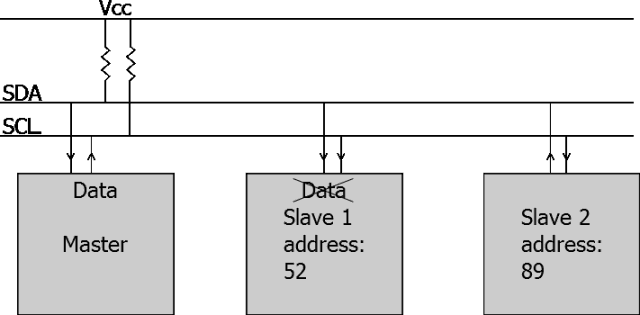
▲ I2C Bus and Addressing Method
4. Infrared Remote Control
Infrared remote control is quite common in our daily lives, as most household remote controls are infrared.
Infrared remote control communicates by controlling pulse width (the duration of high and low levels). It establishes a communication link using infrared wireless signals (obstruction of infrared signals will not work, but they can be reflected).
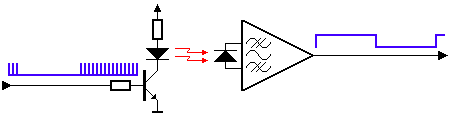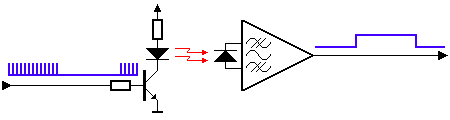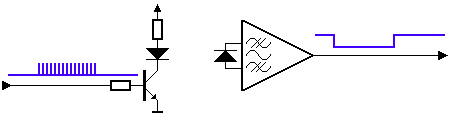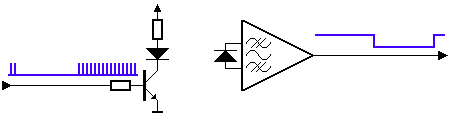
▲ Infrared control signal is also a serial communication signal
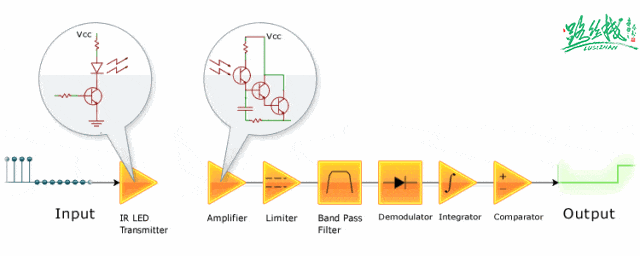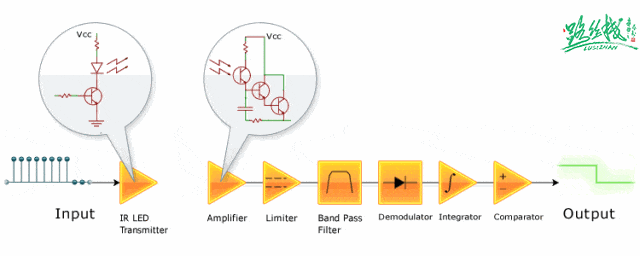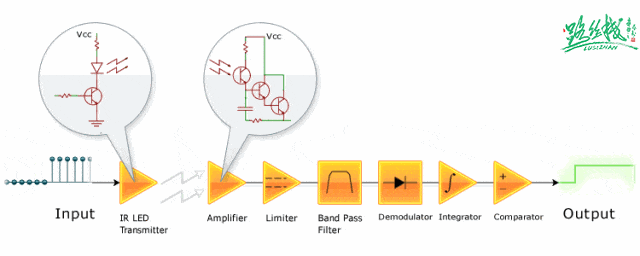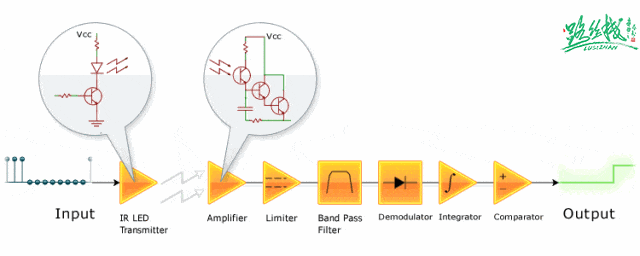
▲ Infrared signal reception and amplification shaping circuit
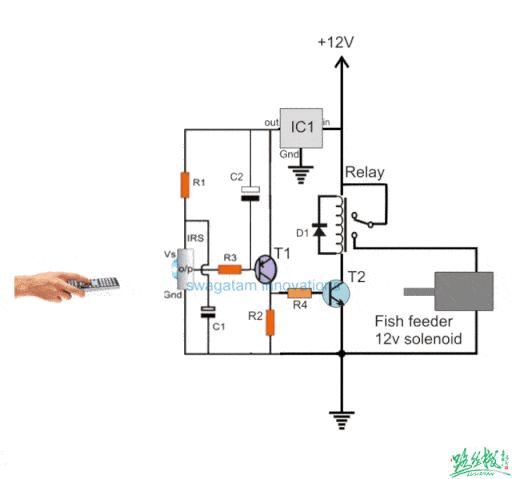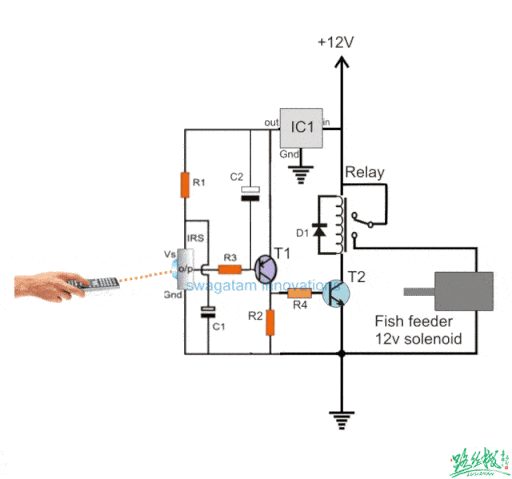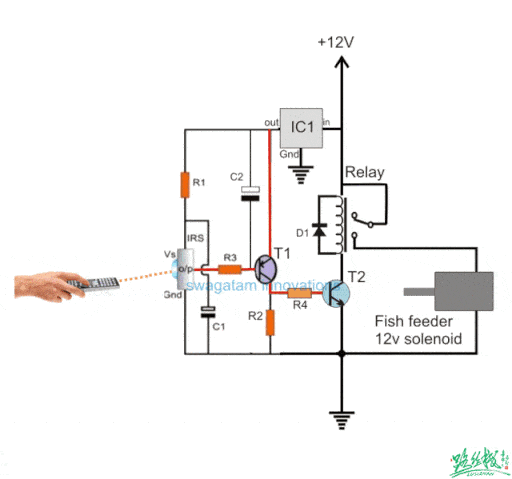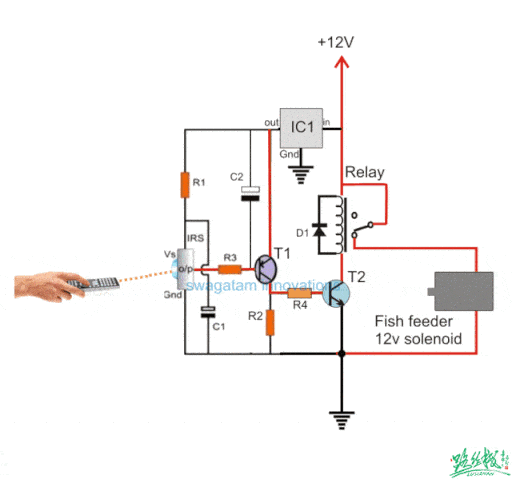
▲ A circuit that uses an infrared receiver tube to control a relay for fish feeding
5. Serial to Parallel Conversion Circuit
Serial to parallel conversion means converting serial data into parallel data. The clock controls the serial data to be transmitted bit by bit, and when they are gathered into a byte (8 bits), it becomes parallel data.
There are many ready-made chips for this type of converter, and the principle is quite simple.
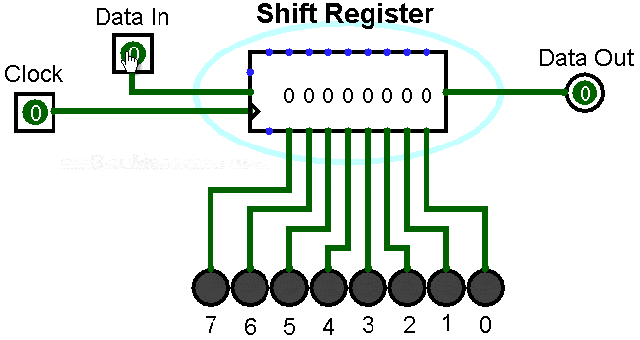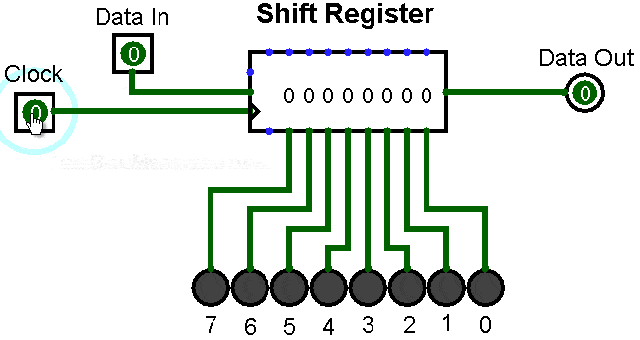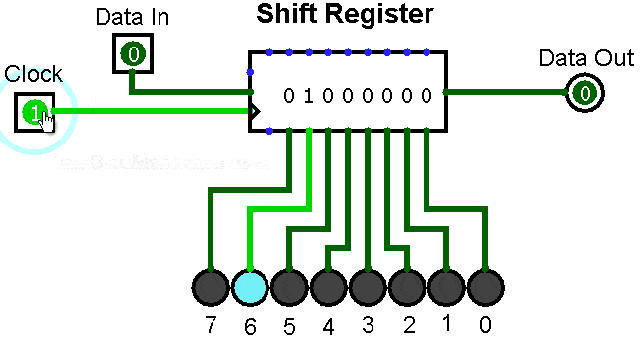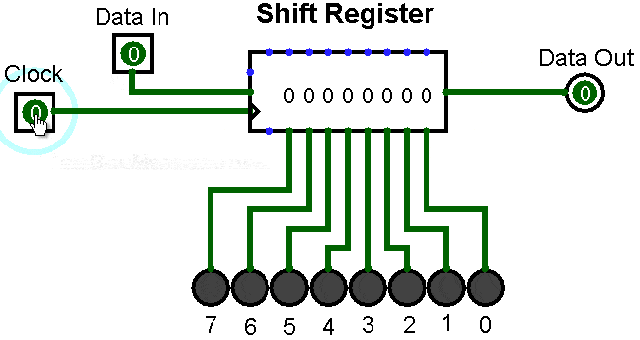
▲ Shift register with serial input and parallel output
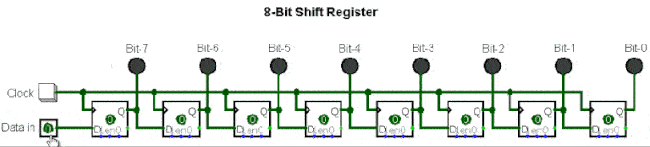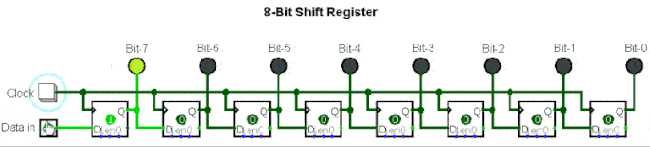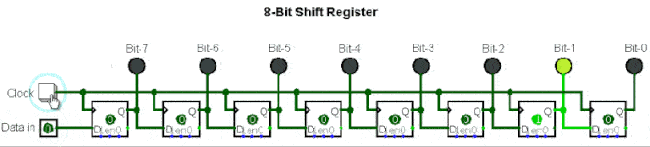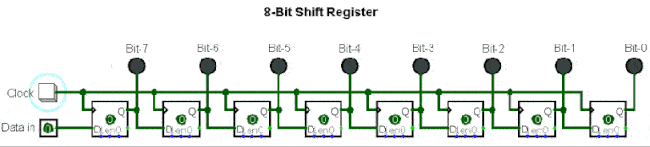
▲ Shift register composed of eight D flip-flops

▲ Serial transmission schematic
6. Others
Here are some additional principles of serial transmission (waveforms):
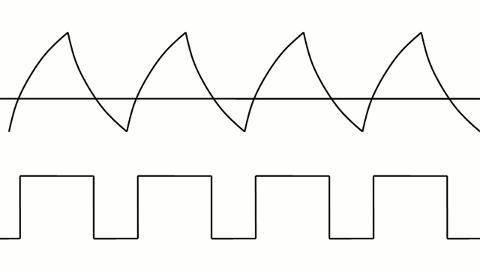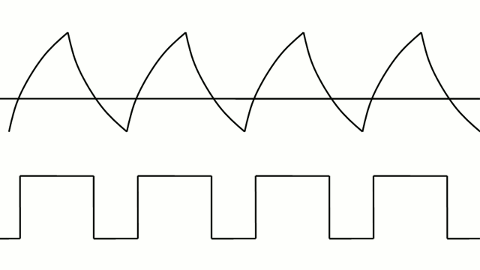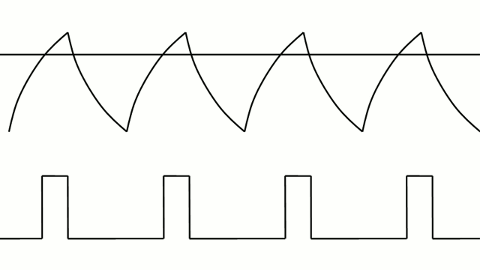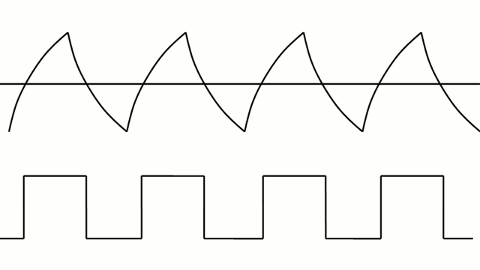
▲ PWM control of LED brightness

▲ PWM control of LED brightness
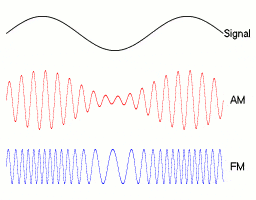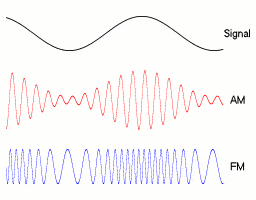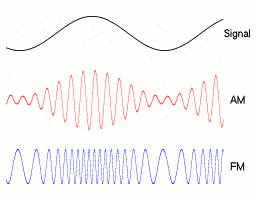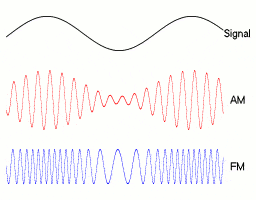
▲ Amplitude and Frequency Modulation Signals
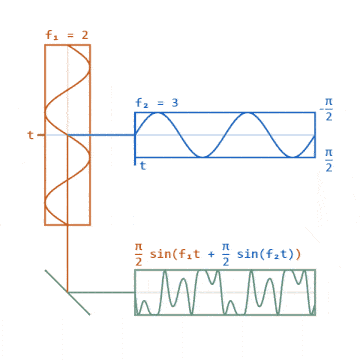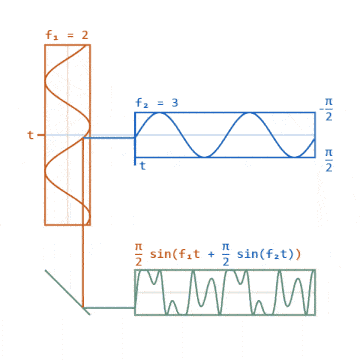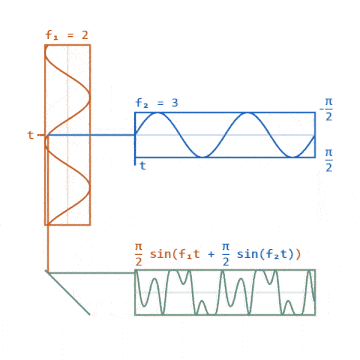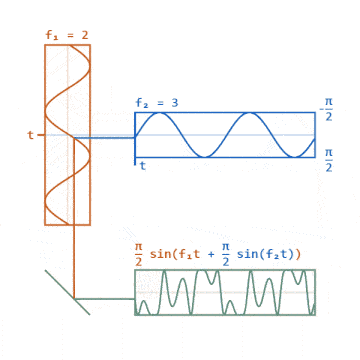
▲ Phase Modulation Signal
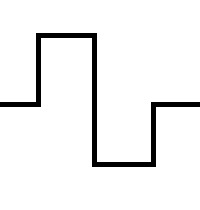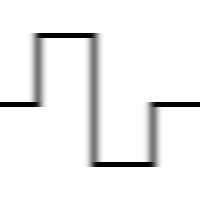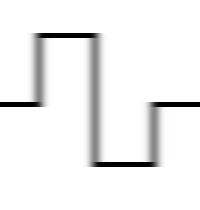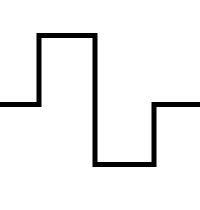
▲ Square Wave Edge Jitter Waveform
Disclaimer: The materials in this article are sourced from the internet, and the copyright belongs to the original author.