Source | Pistachio Need CarKnowledge Circle | In the camera lens/module/CMOS chip group, add micro yijijuechen2023This article focuses on the wake-up, sleep, and reset of the ECU, and examines whether your understanding differs from this explanation.
1. ECU Wake-up
To clarify the wake-up of the ECU, we must study the corresponding hardware schematic. The essence of ECU wake-up is to supply power to the ECU. To facilitate understanding, this article simplifies a circuit schematic composed of Battery (KL30), KL15, SBC (System Basic Chip), uC, and CAN Transceiver, as shown below: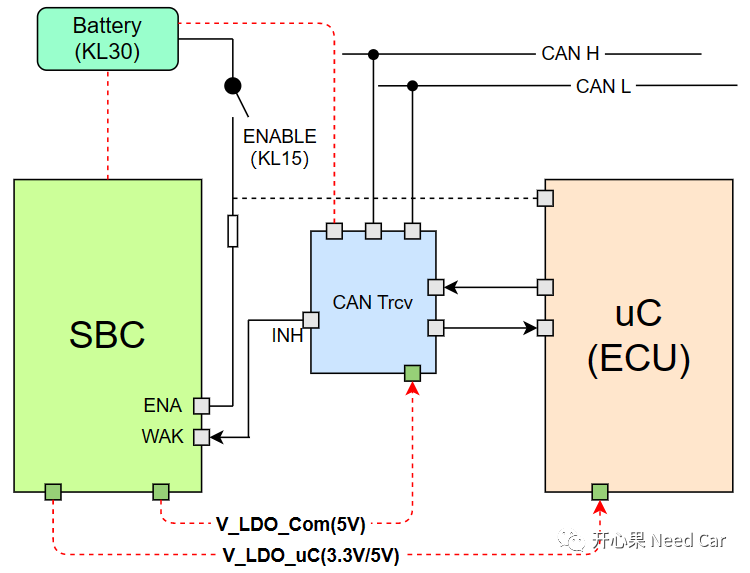 (1) KL15 Wake-up ECUAs shown in the figure, SBC and CAN Trcv are always connected to the Battery (12V). When the KL15 hard wire is enabled, the ENA Pin of the SBC enables the V_LDO_Com and V_LDO_uC voltage outputs. At this point, the CAN Trcv can obtain the communication operating voltage, which is generally 5V (Vcc). Meanwhile, the ECU receives 3.3V or 5V voltage, and the program begins to run from the reset vector location, thus waking up the ECU.The process of KL15 waking up the ECU (power supply) is illustrated as follows:
(1) KL15 Wake-up ECUAs shown in the figure, SBC and CAN Trcv are always connected to the Battery (12V). When the KL15 hard wire is enabled, the ENA Pin of the SBC enables the V_LDO_Com and V_LDO_uC voltage outputs. At this point, the CAN Trcv can obtain the communication operating voltage, which is generally 5V (Vcc). Meanwhile, the ECU receives 3.3V or 5V voltage, and the program begins to run from the reset vector location, thus waking up the ECU.The process of KL15 waking up the ECU (power supply) is illustrated as follows: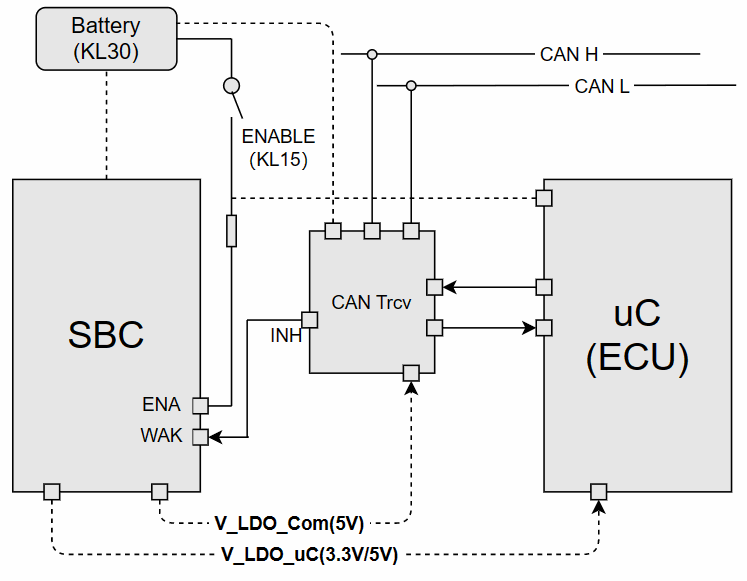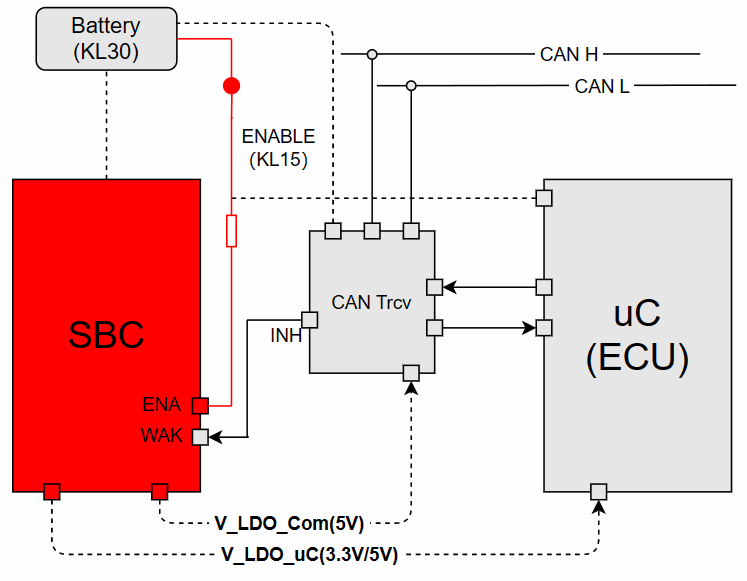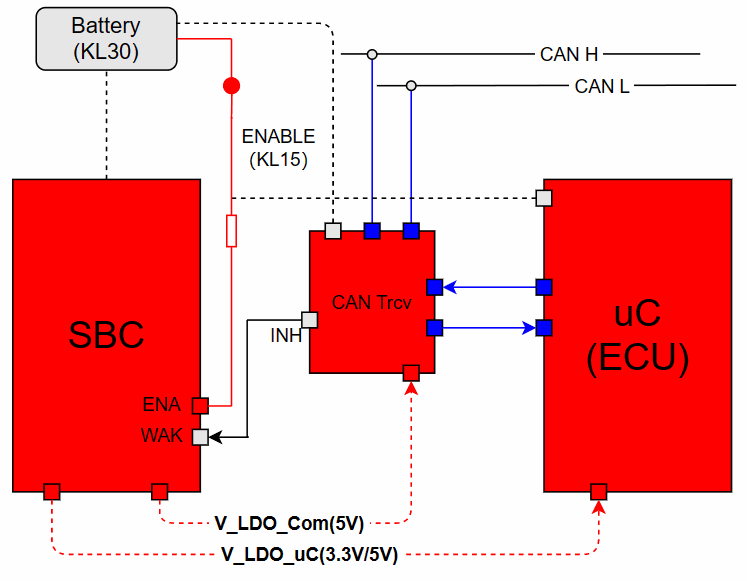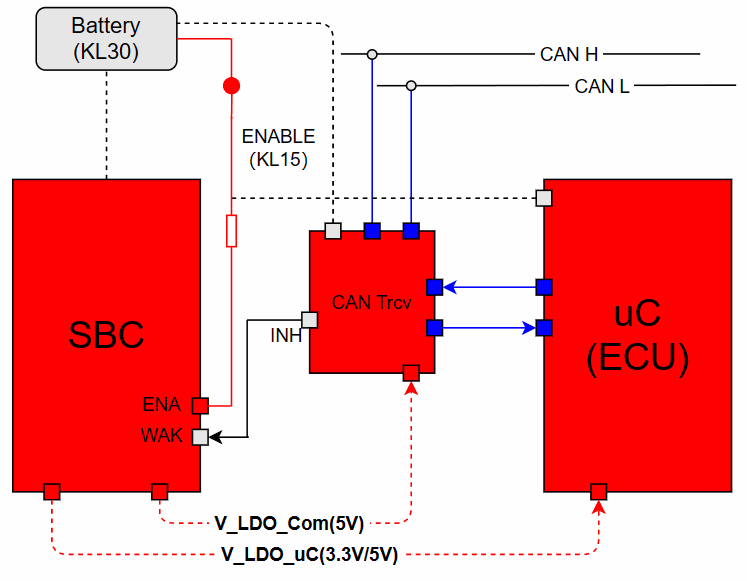 Note: Trcv is always connected to KL30, listening to the bus. SBC outputs 5V communication voltage to Trcv.(2) BUS Wake-up ECUIn the CAN BUS, when a valid network management message frame is received or the bus presents a Wakeup Pattern that meets the wake-up criteria for the CAN Trcv, the CAN Trcv enables the INH Pin, which is generally connected to the WAK Pin of the SBC, thereby enabling the V_LDO_Com and V_LDO_uC voltage outputs. At this point, the CAN Trcv can obtain the operating voltage, which is generally 5V (Vcc). Meanwhile, the ECU receives 3.3V or 5V operating voltage, and the program begins to run from the reset vector location, thus waking up the ECU.The process of the ECU being awakened by the bus message is illustrated as follows:
Note: Trcv is always connected to KL30, listening to the bus. SBC outputs 5V communication voltage to Trcv.(2) BUS Wake-up ECUIn the CAN BUS, when a valid network management message frame is received or the bus presents a Wakeup Pattern that meets the wake-up criteria for the CAN Trcv, the CAN Trcv enables the INH Pin, which is generally connected to the WAK Pin of the SBC, thereby enabling the V_LDO_Com and V_LDO_uC voltage outputs. At this point, the CAN Trcv can obtain the operating voltage, which is generally 5V (Vcc). Meanwhile, the ECU receives 3.3V or 5V operating voltage, and the program begins to run from the reset vector location, thus waking up the ECU.The process of the ECU being awakened by the bus message is illustrated as follows:
2. ECU Sleep
For different functions of the ECU, the number and method of wake-up sources may vary. For example, ECU1 can only be awakened by the bus (e.g., network management message), while ECU2 can be awakened by both the bus and KL15 hard wire. Although different ECUs may have different wake-up sources and counts, if the ECU wants to enter sleep mode, all corresponding wake-up events must be absent.As previously mentioned, the EcuM phase includes two timing states: SLEEP and OFF. If the ECU enters the SLEEP phase, it is still powered, consuming a certain amount of energy to monitor wake-up events (e.g., bus NM Msg); if the ECU enters the OFF phase, it is completely powered off and consumes no energy. Regardless of whether the ECU enters the SLEEP phase or the OFF phase, we commonly refer to this as “ECU sleep”. During ECU sleep, the ECU no longer performs its main functions and waits to be awakened.
3. ECU Reset
ECU Reset primarily refers to the behavior of the software program. There are many types of resets; here we discuss the commonly referred to “ECU Reset” in engineering. When a reset occurs, unlike ECU sleep, the ECU remains powered. The reset action causes the program to “start over” as shown below: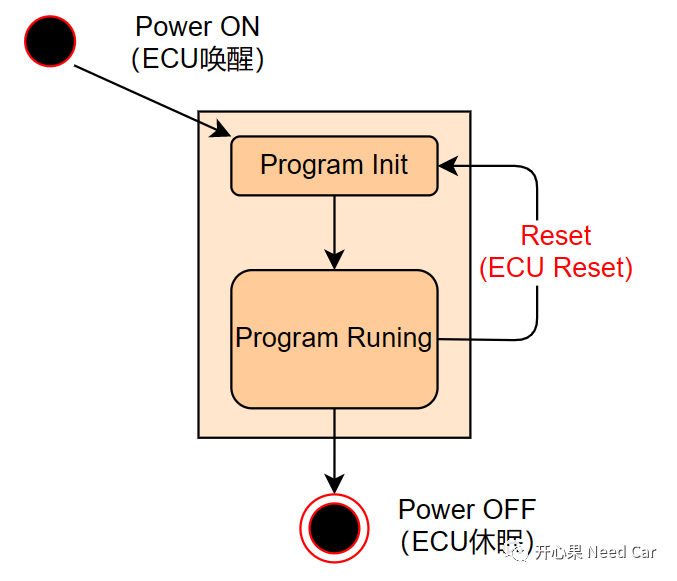 For resets, some are expected, e.g., diagnostic service $10 02/82, $11 xx. Some are unexpected, e.g., program runaway, not “feeding the watchdog” in the specified time, etc. However, whether the reset is expected or unexpected, the goal is to return the program to its initial state and start again.[Disclaimer] The article represents the author’s personal views and does not reflect the position of Yanzhi Automotive. If there are issues regarding the content, copyright, etc., please contact Yanzhi Automotive within 30 days of publication for deletion or copyright negotiation.
For resets, some are expected, e.g., diagnostic service $10 02/82, $11 xx. Some are unexpected, e.g., program runaway, not “feeding the watchdog” in the specified time, etc. However, whether the reset is expected or unexpected, the goal is to return the program to its initial state and start again.[Disclaimer] The article represents the author’s personal views and does not reflect the position of Yanzhi Automotive. If there are issues regarding the content, copyright, etc., please contact Yanzhi Automotive within 30 days of publication for deletion or copyright negotiation.