Since the second half of 2024, the concept of AI Agents has suddenly emerged, with a dramatic increase in the number of AI Agents in the market. Industry leaders like Jensen Huang and Sam Altman believe that AI Agents are the future of artificial intelligence applications, predicting that in five years, everyone will have at least one, if not more, AI Agents serving them. This indicates a paradigm shift in the field of artificial intelligence, moving from traditional, single-function AI applications to more autonomous and interactive AI Agents. This shift represents not only a technological advancement but also a fundamental change in human-computer interaction.

In simple terms, artificial intelligence is transitioning from being a tool for humans to becoming a partner for humans.
Traditional AI Applications: Efficient Tools
Traditional AI applications, such as image recognition software, voice assistants, and recommendation systems, are essentially tools. They are designed to perform specific tasks and operate under predefined rules and parameters. The advantages of these applications include:
Efficiency and Accuracy: Traditional AI applications can complete tasks faster and more accurately than humans. Cost-Effectiveness: Once developed, traditional AI applications can be deployed on a large scale, reducing labor costs. User-Friendly: Most traditional AI applications are designed with user-friendly interfaces for easy operation.
However, traditional AI applications also have limitations, the most significant being their lack of flexibility; they can only perform predefined tasks and cannot adapt to new scenarios or needs: Passive Response: They require users to initiate commands and cannot make decisions or take actions independently. Limited Interactivity: Interactions with users are usually confined to simple commands and feedback, lacking deep understanding and emotional resonance.
AI Agents: Intelligent Partners
AI Agents represent the next generation of artificial intelligence technology, functioning more like intelligent partners rather than mere tools. AI Agents possess the following characteristics:
Autonomy: AI Agents can perceive their environment, analyze information, formulate plans, and execute actions without human intervention.
Interactivity: AI Agents can engage in natural language interactions with humans, understanding user intentions and emotions, and providing personalized services.
Learning Ability: AI Agents can continuously learn and evolve from interactions with their environment and users, enhancing their capabilities. (Remember JARVIS from Iron Man? This could be the ultimate form of AI Agents.)
These characteristics enable AI Agents to be applied in a wider range of scenarios, such as:
Personal Assistants: Managing schedules, arranging itineraries, and providing personalized recommendations.
Intelligent Customer Service: Providing 24/7 online answers to user inquiries and delivering efficient and convenient services.
Autonomous Driving: Perceiving the surrounding environment, making driving decisions, and achieving safe and reliable autonomous driving.
Medical Diagnosis: Analyzing medical data to assist doctors in diagnosing diseases and formulating treatment plans.
From Tools to Partners: A New Era of Human-Machine Collaboration
The emergence of AI Agents marks the beginning of a new era in human-machine collaboration. Traditional AI applications, as tools, inherently impose certain barriers to users, which has objectively hindered the promotion of AI applications. AI Agents, however, are no longer cold tools; they are intelligent partners that can understand, learn, and evolve. Humans can engage in more natural and in-depth interactions with them through everyday conversations, allowing them to provide more personalized and efficient services, ultimately completing the evolution of AI in providing consultation, advice, and decision-making for humans.
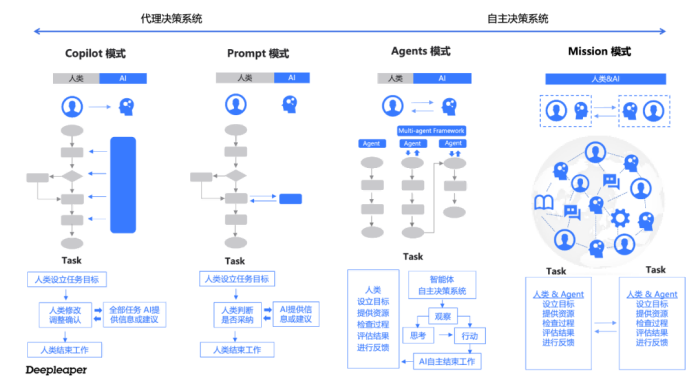
Despite facing challenges such as data security and legal regulations, AI Agents are showing an unstoppable trend of development. With continuous technological advancements and deeper applications, AI Agents will play an increasingly important role in more fields, bringing significant changes to human society.
In summary, the difference between AI Agents and traditional AI applications lies in the former evolving from tools to partners, from passively executing tasks to actively providing services, from single-function to multifunctional integration, and even being able to replace human decision-making. This transformation will profoundly impact our ways of life and work, opening a new chapter in human-machine collaboration.