
Author: Chen Zhi Yan
This article is approximately 5500 words long and is recommended to be read in 10 minutes.
This article introduces the concept and applications of intelligent agents.
1. The Concept of Intelligent Agents
1.1 What is an Intelligent Agent
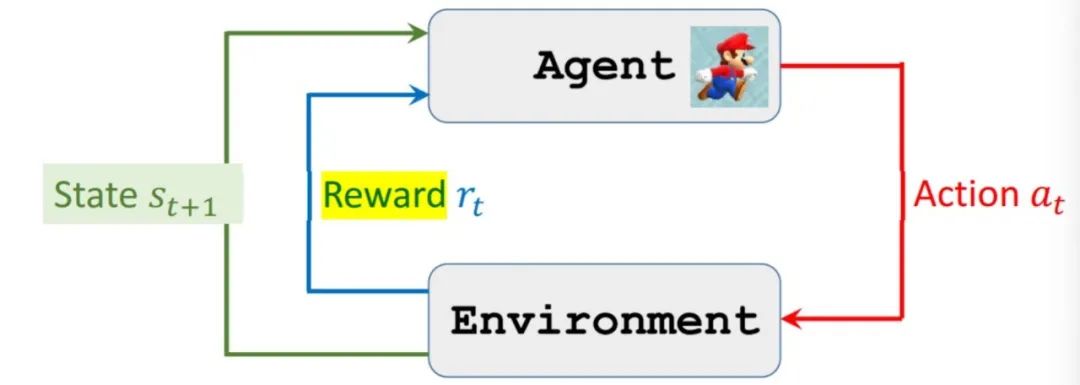
1.2 Basic Characteristics of Intelligent Agents
1.3 The Relationship between Intelligent Agents and Artificial Intelligence
2. Classification and Types of Intelligent Agents
2.1 Classification of Intelligent Agents
2.2 Different Types of Intelligent Agents and Their Characteristics
2.3 Applications of Intelligent Agents in Different Fields
3. Technical Principles and Implementation of Intelligent Agents
3.1 Technical Foundations of Intelligent Agents
3.2 Implementation Methods of Intelligent Agents
3.3 Algorithms and Models of Intelligent Agents
4. Application Scenarios and Cases of Intelligent Agents
4.1 Applications of Intelligent Agents in Smart Homes
4.2 Applications of Intelligent Agents in Healthcare
Introduction to the DataPi Research Department
The DataPi Research Department was established in early 2017, dividing into multiple groups based on interests, with each group adhering to the overall principles of knowledge sharing and project planning while having its unique characteristics:
Algorithm Model Group: Actively participates in competitions like Kaggle, producing original hands-on tutorial articles;
Research and Analysis Group: Explores the beauty of data products through interviews and research on big data applications;
System Platform Group: Tracks cutting-edge technologies in big data and AI system platforms, engaging with experts;
Natural Language Processing Group: Focuses on practice, actively participating in competitions and organizing various text analysis projects;
Manufacturing Big Data Group: Pursues the dream of an industrial powerhouse, integrating industry, academia, and government to uncover data value;
Data Visualization Group: Merges information and art, exploring the beauty of data, and learning to tell stories through visualization;
Web Crawling Group: Gathers information from the web to support creative projects in other groups.
Click at the end of the article to “Read the Original”, sign up for DataPi Research Department Volunteers, and find a group that suits you~
Reprint Notice
If you need to reprint, please prominently indicate the author and source at the beginning of the article (originally from: DataPi THU ID: DatapiTHU) and place a prominent QR code for DataPi at the end of the article. For articles with original markings, please send [Article Name – Pending Authorized Public Account Name and ID] to the contact email to apply for whitelist authorization and edit as required.
Unauthorized reprints and adaptations will be pursued legally.
 Click “Read the Original” to join the organization~
Click “Read the Original” to join the organization~