
The former world’s richest person wrote on his personal blog:
AI Agent (AI Intelligent Agent/Assistant) “will completely change the way we use computers and disrupt the software industry.”
He also predicted that “Android, iOS, and Windows are platforms; AI Agents will become the next platform.”
A leading figure in the internet industry emphasized at the 2024 World Artificial Intelligence Conference: “AI Agents played a significant role in filling out college entrance examination applications, attracting 2 million users on peak days.”
So what exactly is an AI Agent? What does it have to do with me? Let’s fill in the information gap and clarify what AI Agents are all about.
At the end of the article, there will be a question about AI Agents; can you answer it?
1
What is an AI Agent
Academia and industry have proposed various definitions for the term “AI Agent.” Among them, OpenAI defines an AI Agent as “a system driven by a large language model as its brain, capable of understanding, perceiving, planning, remembering, and using tools autonomously, and able to automate the execution of complex tasks.”
In simpler terms, most of the time, you give it a final goal you want to achieve, and it can deliver results directly without you having to manage the process.
2
What is the relationship between AI Agents and LLMs?
So what is the relationship between AI Agents and LLMs (Large Language Models)? It can be simply understood that large models are the premise and foundation for AI Agents.
We can visually compare AI Agents to living organisms and their brains; AI Agents have hands and feet and can work and execute tasks themselves, while LLMs are their brains.
For example, imagine you have an AI chef in your kitchen—an AI Agent.
-
If you only use a large AI model, it might only output a recipe, telling you what ingredients and steps are needed to make a dish.
-
However, using an AI Agent, it can not only provide the recipe but also help you choose the most suitable ingredients based on your taste preferences and nutritional needs, even automatically placing orders, monitoring the cooking process, and ensuring the quality and taste of the food, ultimately serving you a dish that is visually appealing and delicious.
Currently, LLMs may have some issues, such as generating hallucinations, not always producing true and reliable results, or having limited knowledge of the latest events, which can make them seem inadequate when handling complex tasks.
However, AI Agents can compensate for these shortcomings by integrating autonomous verification and decision-making processes, ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of actions.
This makes the entire system more reliable and efficient when facing complex tasks, like an experienced chef who not only knows how to make delicious food but can also flexibly adjust based on actual situations to ensure the final result is satisfactory.
3
How Do AI Agents Work
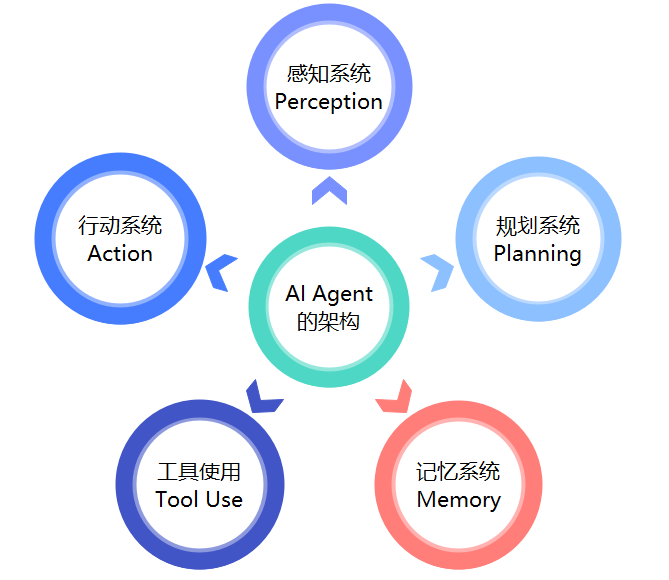
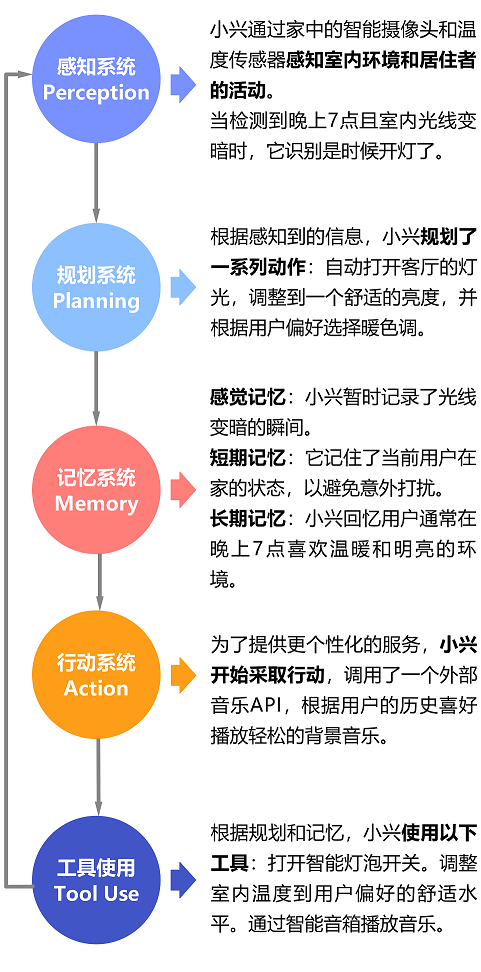
The architecture of AI Agents is the foundation of their intelligent behavior, typically including key components such as perception, planning, memory, tool usage, and action, which work together to achieve efficient intelligent behavior.
| ArchitectureComponents | Function Description |
|---|---|
| PerceptionSystem | The perception system is the first step for AI Agents to interact with the external world. It captures environmental information through diverse input methods, such as text analysis, image recognition, sound processing, etc. |
| PlanningSystem | The planning system is the decision-making center of AI Agents. It determines how to achieve established goals based on perceived information. This process requires AI Agents to make decisions, break down complex tasks into executable subtasks, and devise corresponding strategies to achieve complex tasks. |
| MemorySystem |
The memory system is a core component of AI Agents, allowing AI to store and retrieve information, supporting learning and long-term knowledge accumulation. This system enables AI to remember past experiences and apply them to future decisions and actions.
|
| ToolUsage |
Tool usage is the process by which AI Agents utilize external resources or tools to enhance their perception, decision-making, and action capabilities. In this way, AI Agents can extend their capabilities to more effectively complete tasks. For example, on an e-commerce platform, AI Agents use machine learning algorithms to analyze users’ purchase history and browsing habits, intelligently recommending products, enhancing the shopping experience, and improving conversion rates. |
| ActionSystem | The action system is the specific implementer of AI Agents’ task execution and interaction with the environment. Based on the results of planning, the Agent executes specific actions. |
Let’s take a relatable example:
Combining the above content, let’s summarize:
The workflow of AI Agents is essentially a continuous loop process.
It starts with perceiving the environment, followed by information processing, planning, and decision-making, then executing actions. Finally, it adjusts based on execution results and environmental feedback to optimize future actions and decisions.
4
What Are the Practical Applications of AI Agents
Next, let’s share two excellent cases of innovative exploration: ChatDev and Stanford’s AI Western Town.
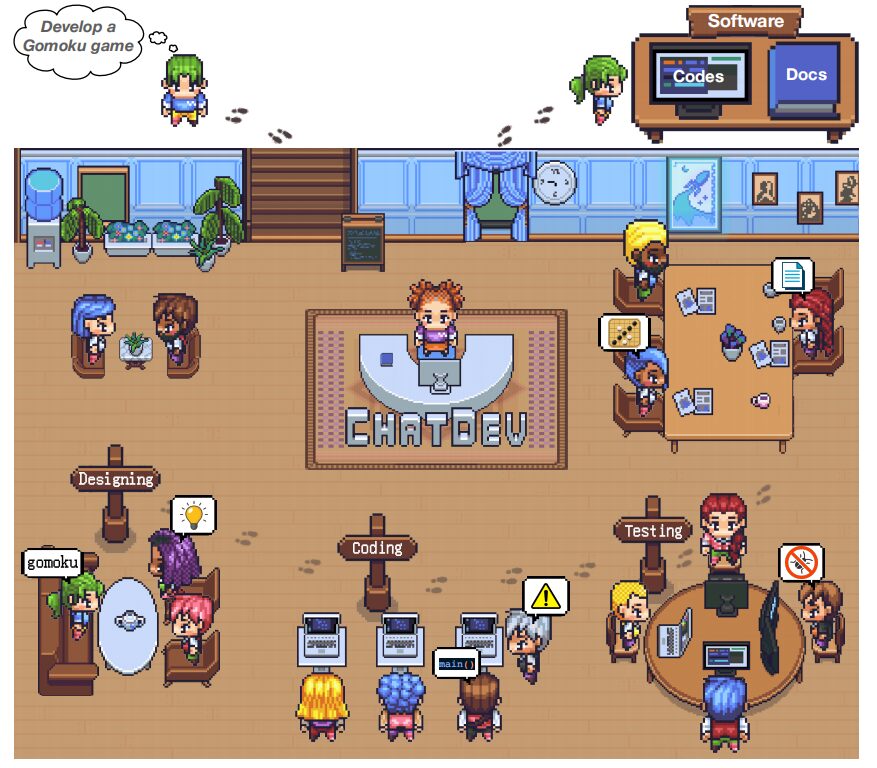

Image from the paper “ChatDev: Communicative Agents for Software Development”
ChatDev is an innovative project jointly developed by Tsinghua University, Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, and Brown University. It is a software development company with only AI Agent employees, achieving full-process automated software development driven by large models.
On this platform, AI employees autonomously start from user needs, through an intelligent dialogue window, led by the CEO Agent, breaking down tasks and assigning them to various AI Agent roles such as CTO, CPO, Designer, Programmer, Tester, Reviewer, etc.
Although there are still challenges such as content randomness, insufficient logical correlation, and potential security risks, ChatDev undoubtedly points the way for AI in the software development field.
The future chain for software products will be greatly shortened. What humans need to do is supervise and make decisions, which is exciting to think about~
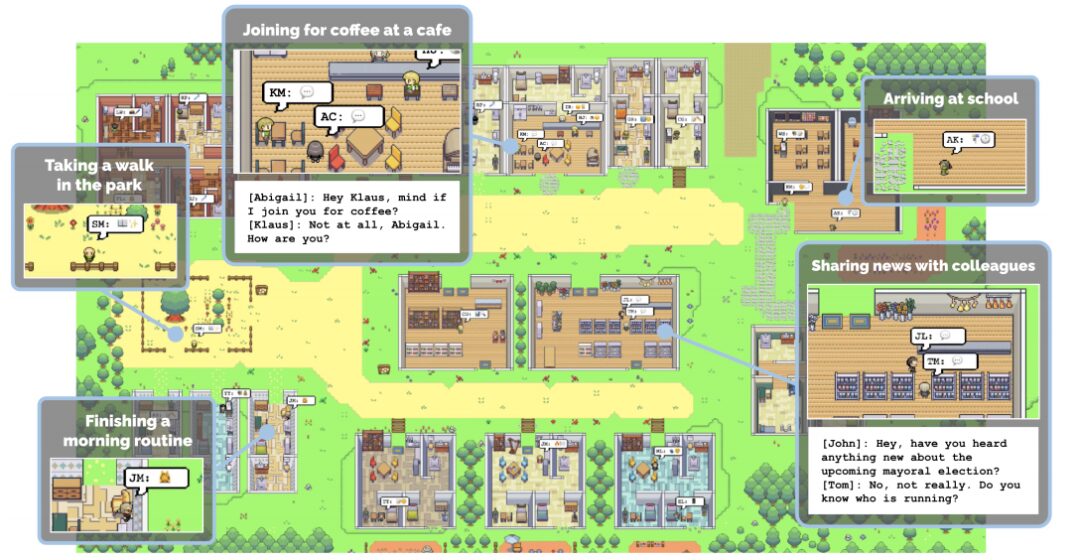
Image from the paper “ChatDev: Communicative Agents for Software Development”
The virtual Western Town, also known as Smallville, is a research project developed by researchers at Stanford University. This virtual town is an interactive sandbox environment. In this sandbox-like interactive environment, 25 AI Agent residents exhibit remarkable social abilities with their human-like behavior patterns.
Source: ZTE Document
Editor: Apo
Reproduced content only represents the author’s views
It does not represent the position of the Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences
For reprints, please contact the original public account
↓ Click on the title to view ↓
1.If a gun has a range of 1500m, can I catch the bullet with my hand at 1501m?
2.Clearly green beans, how did they boil red soup, is this healthy? | No.416
4.Heard that only oily ears can have body odor? Our ancestors really left us many talents
