 There are messages from display manufacturers:“We hope to compile an article on common professional terms in TFT-LCD display modules.” In the display industry, there are many professional terms and abbreviations. These terms often appear in the specification documents of screen manufacturers, assembly plants, and customers. If these terms are understood literally, it is easy to misinterpret their meanings.
There are messages from display manufacturers:“We hope to compile an article on common professional terms in TFT-LCD display modules.” In the display industry, there are many professional terms and abbreviations. These terms often appear in the specification documents of screen manufacturers, assembly plants, and customers. If these terms are understood literally, it is easy to misinterpret their meanings.
During the development of new projects, screen manufacturers and assembly plants need to repeatedly communicate with customers to confirm requirement documents. If one cannot understand the professional terms in the documents or confuses their meanings, it not only creates an awkward situation but also gives an unprofessional impression.
To avoid such awkward situations, today we will review common professional terms and abbreviations in TFT-LCD displays to help everyone better understand this field.
Due to the sheer number of related terms, this article mainly introduces the most basic and commonly used terms as well as key performance parameters related to optical performance.
1. Basic Concepts of TFT-LCD

1. TFT LCD (Thin Film Transistor Liquid Crystal Display)
Definition: Combines microelectronics technology and liquid crystal display technology, using thin film transistors (TFT) to control the arrangement of liquid crystal molecules to achieve image display.
Features: High resolution, low power consumption, widely used in mobile phones, televisions, laptops, monitors, etc.
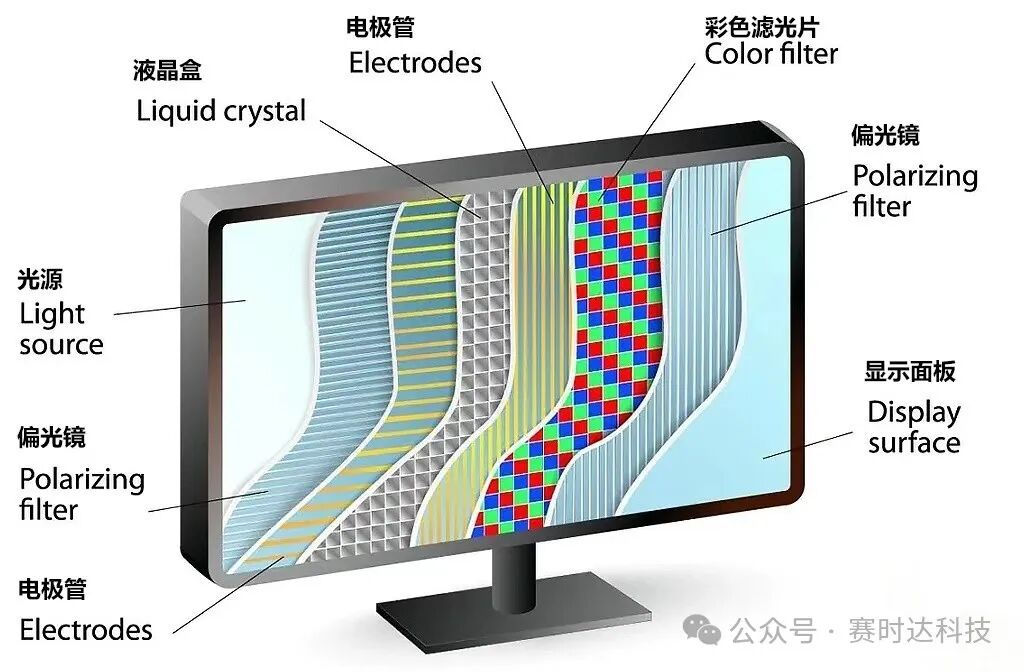
2. LCD (Liquid Crystal Display)
Definition: Utilizes the optical properties of liquid crystal molecules (changing arrangement when powered) to control whether light passes through, thus displaying images.
Features: Requires a backlight (such as LED), does not emit light by itself.
3. TFT (Thin Film Transistor)
Definition: Used to control the switching of liquid crystal molecules, with each pixel corresponding to a TFT, determining whether that pixel is transparent.
Function: Similar to a “faucet”, controlling the degree of deflection of liquid crystal molecules to adjust brightness.
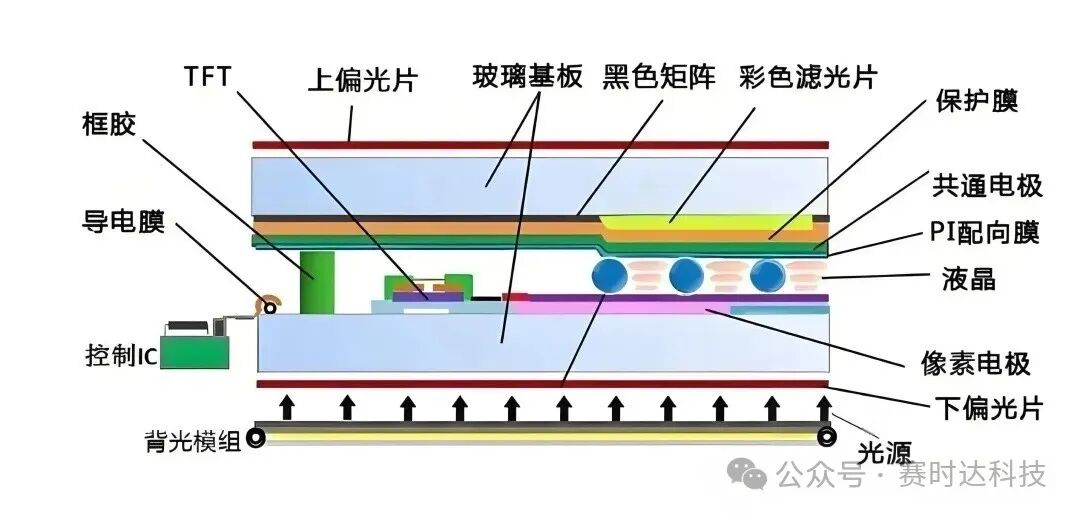
4. LCM (Liquid Crystal Module)
Definition: A complete display component consisting of an LCD panel, backlight, driver IC, FPC (Flexible Printed Circuit), polarizer, etc.
Features: Can be directly used in end products (such as laptops, monitors, mobile phones, televisions).
2. Screen Structure and Size

5. Substrate Size
-
Definition: The size of the large glass substrate used in the production of TFT-LCD, with different generation lines corresponding to different sizes.
-
Example:
-
G8.5 generation line → 2200×2500mm
-
G10.5 generation line → 2940×3370mm
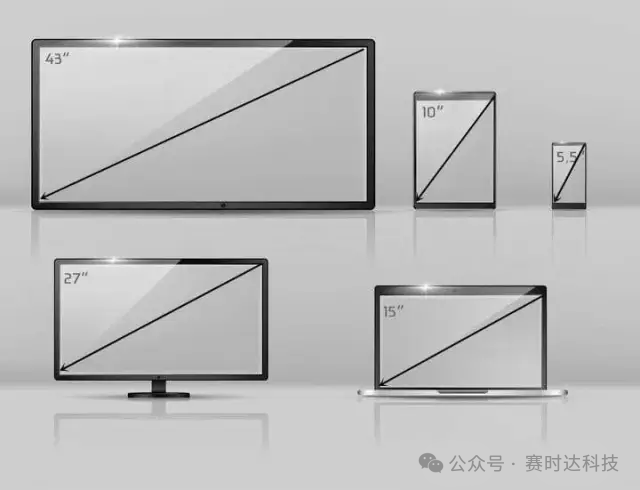
6. Screen Size
-
Definition: The length of the diagonal of the display screen, measured in inches (1 inch = 2.54 cm).
-
Example: 13.3-inch laptop screen, 27-inch monitor, 55-inch television screen.
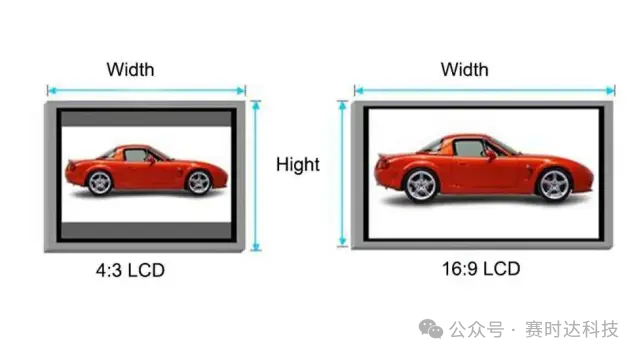
7. Aspect Ratio
-
Definition: The ratio of the width to the height of the screen, commonly seen as:
-
16:9 (TV, monitor)
-
18:9 (full-screen mobile phone)
-
4:3 (old monitors)
3. TFT Backplane Technology and Display Modes

8. TFT Backplane Technology
Definition: The material technology used in TFT transistors, affecting screen performance (such as resolution, power consumption).
Mainstream Technologies:
a-Si (Amorphous Silicon): Low cost, used in standard LCD screens.
IGZO (Indium Gallium Zinc Oxide): High resolution, used in high-end displays.
LTPS (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Silicon): High refresh rate, used in mobile OLED screens.
LTPO (Low-Temperature Polycrystalline Oxide): Adaptive refresh rate, used in high-end mobile phones (such as iPhone).
9. Display Mode
Normal Black Mode: The screen is black when not powered (e.g., IPS screens).
Normal White Mode: The screen is white when not powered (e.g., TN screens).
10. Display Type
TN (Twisted Nematic): Fast response, low cost, but narrow viewing angles (“soft screen”).
IPS (In-Plane Switching): Wide viewing angles, good color (“hard screen”).
VA (Vertical Alignment): High contrast, suitable for televisions.
FFS (Fringe Field Switching): An upgraded version of IPS, with better viewing angles and brightness.
4. Pixels and Interfaces

11. Pixel
Definition: The smallest display unit of the screen, composed of red (R), green (G), and blue (B) subpixels.
12. Pixel Pitch
Definition: The distance between the centers of adjacent pixels, determining screen clarity (the smaller, the finer).
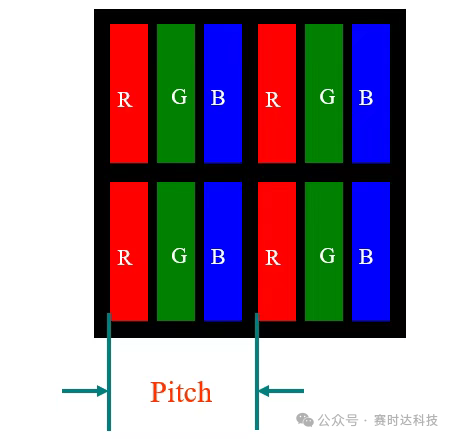
13. Pixel Arrangement
Standard RGB Arrangement: R, G, B subpixels arranged in order (e.g., computer monitors).
Other Arrangements: Pentile (common in OLED), Delta arrangement, etc.
14. Interface
MIPI: Commonly used in mobile phones, low power consumption, high transmission rate.
EDP: Used in laptops, tablets, and high-end displays, with lower power consumption and simpler circuit design.
LVDS: Commonly used in televisions and monitors, strong anti-interference, often used in industrial displays.
5. Core Indicators of Optical Performance

15. Display Clarity Dual Factors
PPI (Pixels Per Inch): The number of pixels per inch on the display screen, calculated as the number of pixels that pass through a straight line per inch along the diagonal of the display, used to measure the pixel density of the screen. Calculation formula: PPI=√(horizontal pixels² + vertical pixels²)/diagonal size.
(X: Number of pixels in length,Y: Number of pixels in width,Z: Size of the screen)
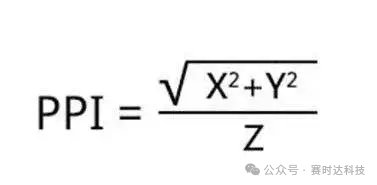
The higher the PPI value of a display, the more pixel points it can display at the same size, thus the finer and clearer the image.
Resolution: Refers to the number of pixel points that can be used for image display within the effective display area; the higher the resolution, the more pixel points on the display, resulting in clearer images and richer detail. For example, 1920×1080 (FHD). Higher resolution brings richer detail.
16. Brightness and Contrast
Brightness (Luminance): Maximum brightness of a white screen, measured in cd/m² (nits). Outdoor screens require ≥1000 nits.
Contrast Ratio (C/R): Contrast is essentially the ratio of brightness, more accurately, it measures the ratio of brightness at maximum gray level (L255) to brightness at minimum gray level (L0). A static contrast ratio ≥1000:1 is preferred, with VA screens reaching up to 3000:1.
Generally, the higher the brightness of a white screen and the lower the brightness of a black screen, the higher the corresponding contrast, meaning the display can show richer color levels.
17. Color Performance
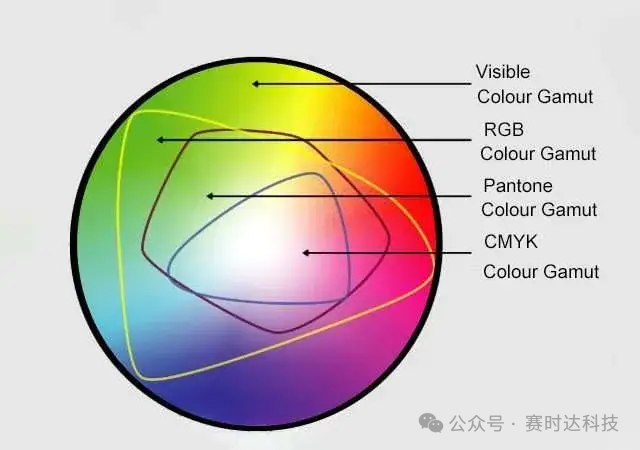
Color Gamut – Visible Spectrum and RGB Display
Color Gamut: Under the NTSC standard, 72% is a common value, while wide color gamut screens can reach 100% NTSC.
Color Depth: 6bit (262K colors), 8bit (16.7M colors), 10bit (1.07B colors). Professional displays require ≥8bit.
Color Accuracy: ΔE<3 is professional level, ΔE<1.5 is suitable for medical imaging.
18. Uniformity and Consistency
Brightness Uniformity: Full-screen brightness deviation ≤15% (ratio of center to corners)
Color Uniformity: Δu’v'<0.01, to avoid the “black and white screen” phenomenon.
Understanding the interrelationships of these parameters and testing methods (to be detailed in a subsequent article) is essential to accurately grasp the performance boundaries of displays and create high-quality LCD screen products that truly meet market demands.
TFT-LCD involves many technical terms, but once the core concepts are understood, one can quickly master industry knowledge.
This article covers core knowledge such as screen structure, display modes, driving technologies, and optical performance, serving as a handy reference guide.
If you have deeper questions, such as about technologies like Mini LED, feel free to leave a message for discussion!
Follow us
Sanstar Technology
Official website
www.san-star.com