The concept of the “metaverse” keeps the heat of VR headset products high. As VR technology continues to develop, the underlying display technologies, LCD and OLED, are also evolving. Currently, both are doing their utmost to compete in the metaverse.

The Dominance of LCD Remains Unshaken
From the current application situation in the VR market, most VR headsets use LCD screens.
According to IDC data, the global shipment of VR headsets reached 10.95 million units in 2021, with Oculus alone accounting for 80% of the market share. Currently, among the top 5 global brands by shipment volume, only Sony’s PlayStation VR uses OLED screens. Mainstream terminal manufacturers like Oculus, Pico, HTC, and Valve all use LCD screens in their VR products, including Oculus Quest 2, HTC Vive and Focus 3, DPPI Ultra all-in-one machine, and Pico Neo 3 and Valve Index models. It is worth mentioning that both the popular Oculus Quest 2 and HTC Vive have abandoned the OLED screens used in the first generation and switched to LCD.
In fact, early VR headsets mostly used ordinary LCD screens, which were gradually replaced by OLED.
“LCD technology is already very mature and can achieve very high resolutions,” said Liu Tan, deputy general manager of the IoT Industry Research Center at CCID Consulting, in an interview with China Electronics News. However, due to its slower response speed and other reasons, it leads to a poor user experience, which is why VR products have not been truly accepted by consumers.
According to Liu, the response speed of ordinary LCDs is only 1/100 to 1/1000 of AMOLED, and when users turn their heads significantly while wearing the headset, there will be uncorrectable motion blur.
In practical applications, compared to ordinary LCDs, OLEDs have a faster response speed and can effectively avoid screen motion blur. Thus, around 2016, OLED technology was attempted for use in VR devices and briefly became the first choice for VR device manufacturers.
However, at that time, VR products using OLED technology also had fatal flaws: noticeable screen door effect.
Yang Tingting, general manager of the VR/AR BU at BOE Technology Group, told China Electronics News that glass-based OLEDs are constrained by the FMM (Fine Metal Mask) process, making it extremely difficult to achieve ultra-small pixels. The PPI (Pixels Per Inch) is not high, leading to a noticeable grainy effect and screen door effect, which affects the immersion and visual clarity of VR.
It is reported that the current pixel density of OLEDs has not yet surpassed 1000 PPI, hovering around 600. Samsung Display showcased VR OLED panels with 806 PPI and 1200 PPI in 2018, but due to a lack of large orders, they could not achieve mass production. In contrast, LCD pixel density has exceeded 1000 PPI. According to TCL Huaxing, the screen of Skyworth VR’s PANCAKE 1 is a 2.1-inch 1512 PPI LCD-VR screen from TCL Huaxing.
“For VR to quickly reach consumers, technology must keep up, and costs must be low enough,” said Gu Wei, founding partner of the metaverse industry consulting service provider Weishi Consulting, in an interview with China Electronics News. LCDs, while maintaining cost advantages, are also beginning to effectively solve the slow response speed issue.
After 2018, the emergence of Fast-LCD technology began to tilt the balance towards LCD for manufacturers. The improved Fast-LCD technology uses new liquid crystal materials (ferroelectric liquid crystal materials) and ultra-fast driving technology to effectively increase the refresh rate to 75-90Hz, significantly improving response speed and greatly narrowing the gap with OLED, while also having high mass production stability and yield.
IDC’s senior analyst Zhao Siquan pointed out in an interview with China Electronics News that with technological advancements, Fast-LCD display technology, backed by cost advantages, is outperforming OLED in the VR field. Currently, Fast-LCD, which combines performance and cost-effectiveness, is widely used in mainstream VR headsets.

Technological Progress Continues Unabated
Today, consumer demand for near-eye displays continues to upgrade, and both LCD and OLED technologies have not stopped their progress. Mini LED backlight Fast-LCD and silicon-based OLED (OLEDoS) have emerged.
“While Fast-LCD has advantages, it also has some drawbacks. For example, due to the presence of a backlight layer, it is prone to issues like backlight leakage,” said Geng Yi, director of the Optoelectronics Research Laboratory at CCID Consulting’s Integrated Circuit Research Institute, in an interview with China Electronics News. Fast-LCD combined with Mini LED not only effectively solves the backlight leakage problem but also further enhances Fast-LCD’s performance in terms of high contrast, high refresh rate, and high brightness, complemented by HDR functionality, to better meet the ultra-clear and delicate picture quality requirements of VR products for near-eye displays.
Industry insiders expect that in the VR field, Fast-LCD, supported by Mini LED backlight technology, will occupy a large portion of the application market, potentially reaching over 85% market share in the future.
Meanwhile, in order to improve the screen door effect, OLED is also shifting towards silicon-based OLED. Silicon-based OLED innovatively combines semiconductors and OLED, with display devices using single crystal silicon chip substrates. Since silicon-based OLEDs are small-area evaporated on 6-inch and 8-inch wafers, it significantly reduces the challenges of achieving uniform evaporation when producing OLEDs. Both brightness and pixel density of silicon-based OLEDs show significant improvements. It is reported that the pixel density of silicon-based OLEDs can reach 3000-4000 PPI.
Currently, silicon-based OLEDs are quickly becoming the new favorite for near-eye display devices like VR. According to South Korean media The Elec, Samsung Display and LG Display are both developing silicon-based OLED and silicon-based LED technologies. The Apple AR/MR headset, expected to be released next year, may use LG’s silicon-based OLED display technology. Consulting firm DSCC predicts that by 2027, silicon-based OLED will account for 48% of all AR/VR display shipments.
“However, the cost of silicon-based OLED is relatively high,” said Liu Yushi, a senior analyst at CINNO Research, in an interview with China Electronics News. On one hand, large-area silicon substrates are expensive; on the other hand, using smaller silicon chips requires more complex optical designs, keeping costs high, hence it will mainly be used for high-end VR products.
Liu pointed out that with the development of technology and the market, silicon-based OLED will inevitably usher in an explosion as it meets cost competitiveness.
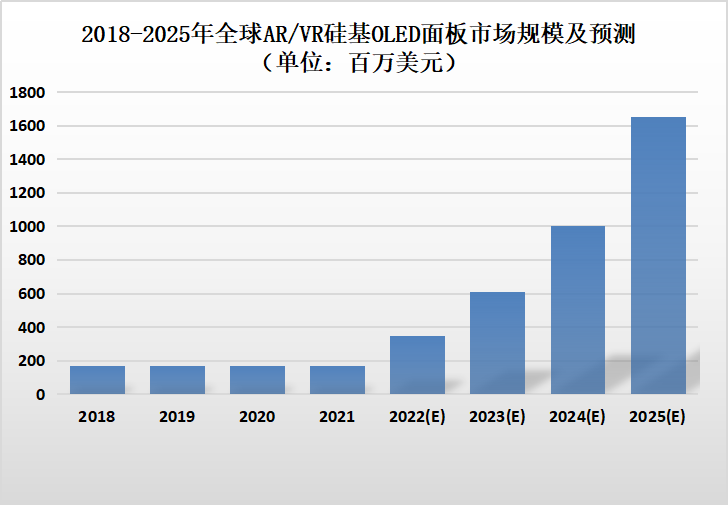
CINNO Research statistics show that the global market size for silicon-based OLED display panels in AR/VR reached $170 million in 2021. With the development of the AR/VR industry and further penetration of silicon-based OLED technology, it is expected to reach $1.67 billion by 2025, with a compound annual growth rate of 77.1% from 2021 to 2025.
Metaverse Display Technology Will Not Be Limited to One Type
Industry insiders believe that Fast-LCD and silicon-based OLED will become two important tracks in the AR/VR headset field.
Recently, BOE responded to investors regarding its products and plans in the AR/VR and sensing fields, stating that the display solutions it provides for VR/AR/MR smart terminals include representative display technologies such as high PPI, high refresh rate Fast-LCD and ultra-high resolution, ultra-high contrast silicon-based OLED.
Companies like OLED, Visionox’s Kunshan Dream Vision, Xitai Technology, and Hefei Shiya have all entered the silicon-based OLED market, with production line investments exceeding 10 billion yuan.
Liu Honghui, a technology mentor at Microsoft’s Innovation Base, stated in an interview with China Electronics News: “In the future, with cost-performance advantages and guaranteed production capacity, Fast-LCD will become the main driver of rapid development in the VR industry. However, when products advance to higher-end markets, silicon-based OLED may still be chosen as the leading technology.”
During the interview, it was learned that from LCD, OLED, to Fast-LCD, and then to silicon-based OLED, AR/VR has raised higher demands for display technology, and the display technology route is progressing step by step. Metaverse display technology is not limited to VR forms, but also includes AR, MR, and various different formats such as horizontal screens, vertical screens, curved screens, and even holographic projections.
Gu Wei pointed out that in the future, more cutting-edge display technologies will be developed, so metaverse display technology will not be limited to one type, but should be a multi-technology parallel structure.
(Source: China Electronics News)