
Introduction
On January 4, 2025, the National Standardization Administration officially released the mandatory national standard “Energy Efficiency Limits and Energy Efficiency Grades for Microcomputers” (GB 28380-2025). This standard, as an upgraded version of GB 28380-2012, aims to further promote the optimization of energy efficiency in computer products by comprehensively enhancing technical indicators and testing requirements, accelerating the green and low-carbon development of the computer industry.Looking back at the industry development, the GB 28380-2012 standard served as the early mandatory certification specification for microcomputer energy efficiency in China, systematically establishing an energy efficiency limit value system covering home desktop computers, all-in-one desktop computers, and laptops, along with a complete set of testing methods and evaluation systems, effectively guiding the industry to complete the first round of energy efficiency upgrades. With advancements in chip manufacturing processes and changes in market demand, the new standard makes stricter revisions to energy efficiency indicators while optimizing experimental verification plans, resulting in a more rigorous and scientific evaluation standard.This standard is scheduled to be fully implemented on February 1, 2026, during which relevant industry enterprises need to actively optimize product design layouts to comply with the new national standard requirements.
Drafting Units of GB 28380-2025
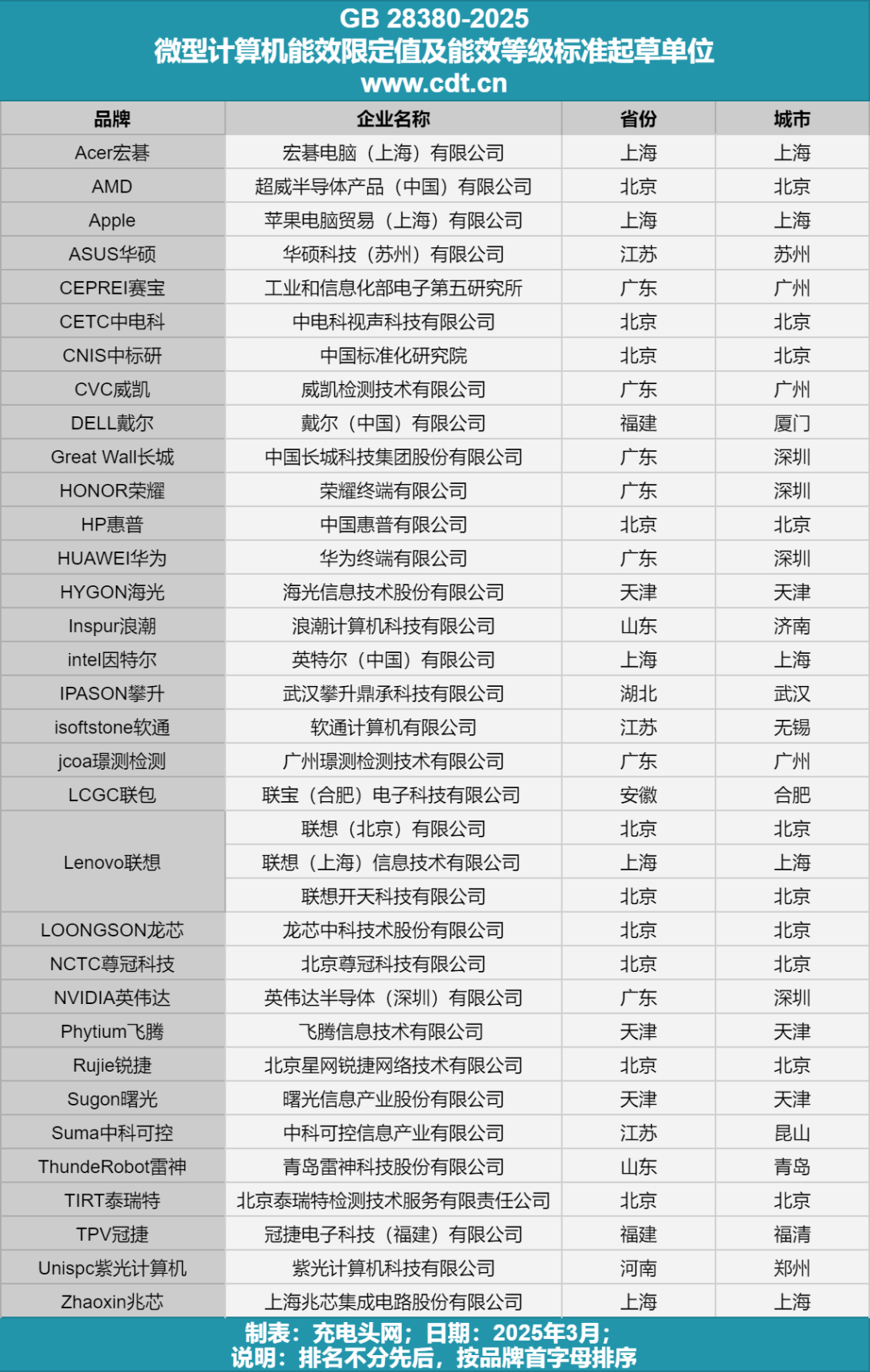 The drafting units for the GB 28380-2025 standard include leading domestic and international enterprises and authoritative institutions, including testing organizations, chip companies, and domestic and foreign smart terminal companies that participated in the formulation of this national standard.
The drafting units for the GB 28380-2025 standard include leading domestic and international enterprises and authoritative institutions, including testing organizations, chip companies, and domestic and foreign smart terminal companies that participated in the formulation of this national standard. The following list is not in any particular order and is sorted by the first letter of the brand:Acer Computer (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.Advanced Micro Devices (China) Co., Ltd.Apple Computer Trading (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.ASUS Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.Fifth Research Institute of the Ministry of Industry and Information TechnologyChina Electronics Technology Group CorporationChina National Institute of StandardizationVikay Testing Technology Co., Ltd.Dell (China) Co., Ltd.China Great Wall Technology Group Co., Ltd.Honor Terminal Co., Ltd.HP (China) Co., Ltd.Huawei Terminal Co., Ltd.Haiguang Information Technology Co., Ltd.Inspur Computer Technology Co., Ltd.Intel (China) Co., Ltd.Wuhan Pansheng Dingcheng Technology Co., Ltd.Softcom Computer Co., Ltd.Guangzhou Jingce Testing Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Hefei) Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Beijing) Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Shanghai) Information Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo Kaitian Technology Co., Ltd.Loongson Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing Zunguan Technology Co., Ltd.NVIDIA Semiconductor (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.Phytium Information Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing StarNet Ruijie Network Technology Co., Ltd.Shuguang Information Industry Co., Ltd.China Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.Qingdao Thunder God Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing Tairuite Testing Technology Service Co., Ltd.AOC Electronics Technology (Fujian) Co., Ltd.Unisoc Computer Technology Co., Ltd.
The following list is not in any particular order and is sorted by the first letter of the brand:Acer Computer (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.Advanced Micro Devices (China) Co., Ltd.Apple Computer Trading (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.ASUS Technology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd.Fifth Research Institute of the Ministry of Industry and Information TechnologyChina Electronics Technology Group CorporationChina National Institute of StandardizationVikay Testing Technology Co., Ltd.Dell (China) Co., Ltd.China Great Wall Technology Group Co., Ltd.Honor Terminal Co., Ltd.HP (China) Co., Ltd.Huawei Terminal Co., Ltd.Haiguang Information Technology Co., Ltd.Inspur Computer Technology Co., Ltd.Intel (China) Co., Ltd.Wuhan Pansheng Dingcheng Technology Co., Ltd.Softcom Computer Co., Ltd.Guangzhou Jingce Testing Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Hefei) Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Beijing) Co., Ltd.Lenovo (Shanghai) Information Technology Co., Ltd.Lenovo Kaitian Technology Co., Ltd.Loongson Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing Zunguan Technology Co., Ltd.NVIDIA Semiconductor (Shenzhen) Co., Ltd.Phytium Information Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing StarNet Ruijie Network Technology Co., Ltd.Shuguang Information Industry Co., Ltd.China Electronics Technology Co., Ltd.Qingdao Thunder God Technology Co., Ltd.Beijing Tairuite Testing Technology Service Co., Ltd.AOC Electronics Technology (Fujian) Co., Ltd.Unisoc Computer Technology Co., Ltd.
Provinces and Cities of Drafting Units for GB 28380-2025
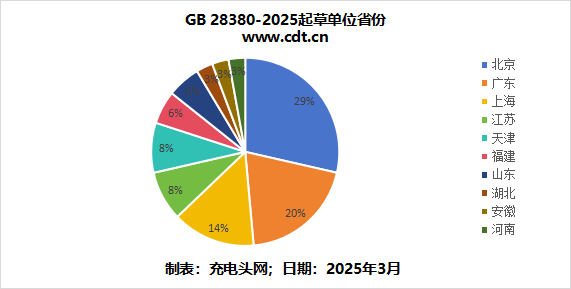 Charging Head Network has created pie charts and bar graphs showing the provinces and cities of the drafting units for GB 28380-2025. It can be seen that Beijing accounts for 29%, with 10 companies. Following that, Guangdong accounts for 20%, with 7 companies. Shanghai comes next at 14%, with 5 companies, while the remaining provinces are more dispersed.
Charging Head Network has created pie charts and bar graphs showing the provinces and cities of the drafting units for GB 28380-2025. It can be seen that Beijing accounts for 29%, with 10 companies. Following that, Guangdong accounts for 20%, with 7 companies. Shanghai comes next at 14%, with 5 companies, while the remaining provinces are more dispersed.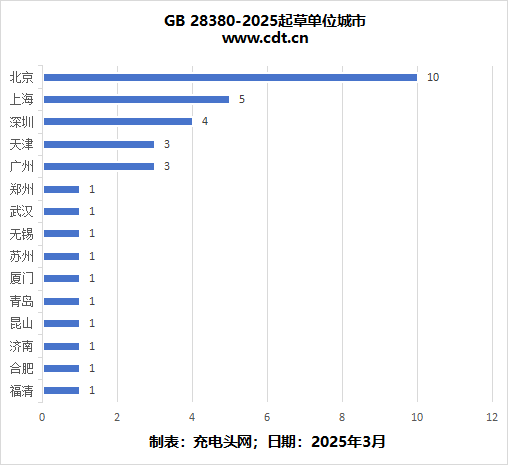 Looking at the cities where the drafting units are located, the distribution is roughly the same as the aforementioned provinces, with Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen appearing most frequently.
Looking at the cities where the drafting units are located, the distribution is roughly the same as the aforementioned provinces, with Beijing, Shanghai, and Shenzhen appearing most frequently. Overall, as the capital, Beijing gathers national-level standardization institutions, research institutes, and industry associations, significantly leading the policy resources and industry discourse power in standard formulation. Therefore, it occupies a dominant position among the drafting units. Guangdong and Shanghai are core hubs for the electronic information, smart terminal, and charging industries, with strong technological innovation capabilities and a complete industrial chain, leading to a pressing demand for industry standards and strong motivation to participate in drafting, thus forming the leading position of Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong.
Overall, as the capital, Beijing gathers national-level standardization institutions, research institutes, and industry associations, significantly leading the policy resources and industry discourse power in standard formulation. Therefore, it occupies a dominant position among the drafting units. Guangdong and Shanghai are core hubs for the electronic information, smart terminal, and charging industries, with strong technological innovation capabilities and a complete industrial chain, leading to a pressing demand for industry standards and strong motivation to participate in drafting, thus forming the leading position of Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong.
Main Changes in the New GB 28380-2025 Regulations
Compared to GB 28380-2012, the revisions in the new GB 28380-2025 standard are as follows:1. The definition of “microcomputer energy-saving evaluation value” has been deleted.2. Definitions for “tablet computer”, “long idle”, “short idle”, and “alternative low-power state” have been added.3. The “energy-saving evaluation value” has been deleted.4. Changes have been made to the classification of microcomputers and energy efficiency grade indicators.5. Changes have been made to the calculation methods for typical energy consumption of microcomputers, the percentage of time spent in each state, and the power factor for additional functions.6. Changes have been made to the testing methods.7. The inspection rules have been deleted.Charging Head Network notes that the new GB 28380-2025 adjusts the power limit for the applicable range of microcomputers, reducing the power limit from ≤750W in the 2012 version to ≤500W, narrowing the power range covered by this standard, which means that microcomputers with a rated power above 500W will no longer be subject to the supervision of the new GB 28380-2025 standard.
Summary from Charging Head Network
Charging Head Network understands that the release of the new GB 28380-2025 standard marks a new stage in the energy efficiency management of microcomputers in China. As an upgrade to the 2012 version, the new regulations further promote the green and low-carbon transformation of the industry through stringent revisions of energy efficiency indicators, optimization of testing methods, and adjustments to the applicable range.The drafting units are mainly concentrated in core industrial areas such as Beijing, Shanghai, and Guangdong, gathering authoritative institutions and leading enterprises in the industry, highlighting the deep integration of policy guidance and industrial collaboration. As the implementation date approaches, enterprises need to accelerate technological iteration and product optimization to meet stricter energy efficiency requirements. The implementation of the new national standard will accelerate industry reshuffling and promote the popularization of high-efficiency computers, injecting new momentum into China’s achievement of its “dual carbon” goals.Related Reading:1. The latest version of China’s power supply energy efficiency standard has been released!Click on the blue text to learn about the following hot topics, or reply with the following keywords in the Charging Head Network WeChat backend to access the topic.
“Annual Teardown”
2024,2023,2022,2021,2020,2019,2018,2017,2016,2015
“Teardown Categories”
Outdoor power supplies, inverters, charging guns, charging piles, server power supplies, PC power supplies, chargers, power banks, wireless charging, car chargers, charging cables, power strips, air pumps, hair dryers, car inverters, electric toothbrushes, docking stations,air pumps, cooling back clips, V-port batteries, mobile Wi-Fi, small fans, electric mosquito swatters, flashlights, monitors, electric tools
“Application Cases”
Nanxin,Yingjixin,Zhirong,BiYiWei,Meixinsheng,Jiahua,Maoruixin,Huayuan,Silicon Power,TianDeYu,Dongke,Xinhai,Yichong,Qinheng,Yutai,Chengxinwei,Hengchengwei,Xinjing Electronics,Terui Xiang,World,Innosilicon,Nitride,Weizhao,Yuhongjin、ChuanTuWei、AOS Global、Songtian