
In the last issue, we introduced the core of MQTT:
The core of MQTT communication: Topic
This time we will detail QoS, which stands for Quality of Service. (QoS) is a protocol between the message sender and receiver that defines the level of delivery guarantee for specific messages. Below, we will delve deeper into the different levels of Quality of Service (QoS) in MQTT.

Three Levels of QoS
The quality of message transmission is crucial for any protocol. MQTT has defined a clear set of quality of service standards.

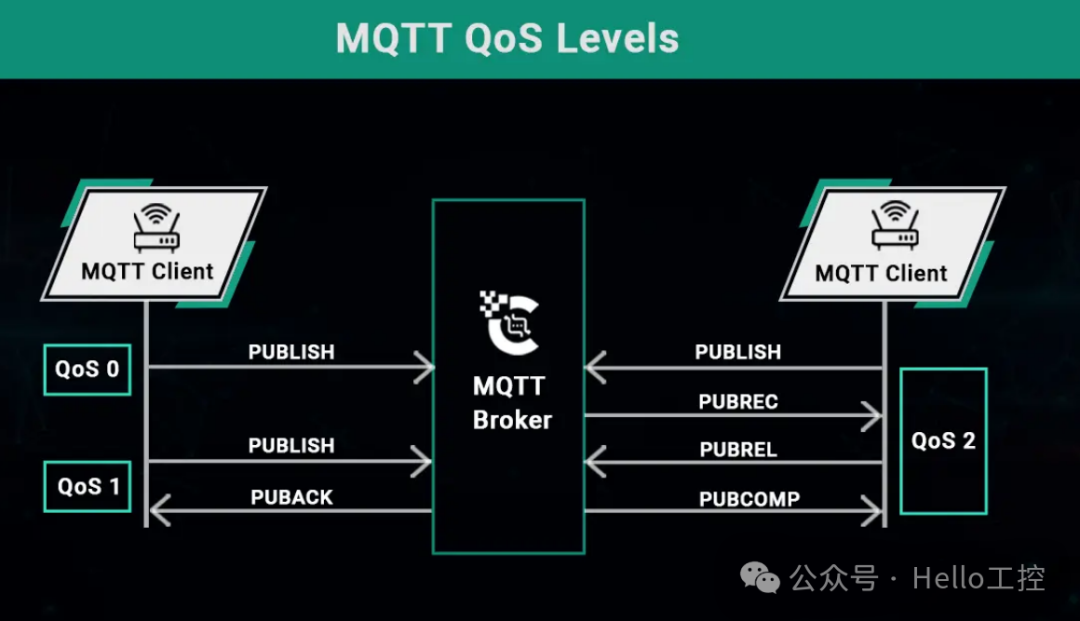
MQTT defines three levels of message delivery quality (QoS) for the Internet of Things. Each MQTT QoS level comes with an increase in data transmission rate. However, the higher the QoS level, the greater the likelihood of ensuring MQTT message delivery. The MQTT standard decouples the QoS level from the publisher and subscriber, allowing clients to use different QoS levels based on bandwidth and message delivery needs. Clients can also use different QoS levels for different MQTT topics when publishing and subscribing.
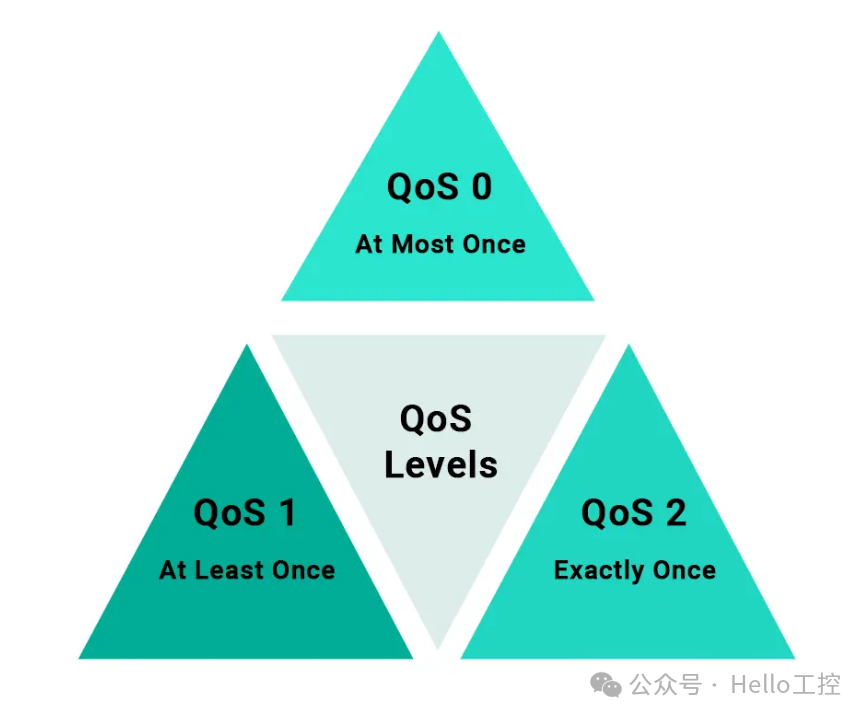
- QoS 0 — At most once, with no message delivery guarantee.
- QoS 1 — At least once. Messages may be received multiple times. However, the publisher or MQTT broker should send a second message as a duplicate message with a flag.
- QoS 2 — Exactly once.
QoS 0 – At Most Once
The entry-level or first level is QoS level 0, also known as “fire and forget”. This level ensures that messages are sent to the receiver either once or not at all. There is no guarantee of message delivery; that is, the receiver may or may not receive the message. The subscribing client or MQTT server does not send any acknowledgment of message receipt.
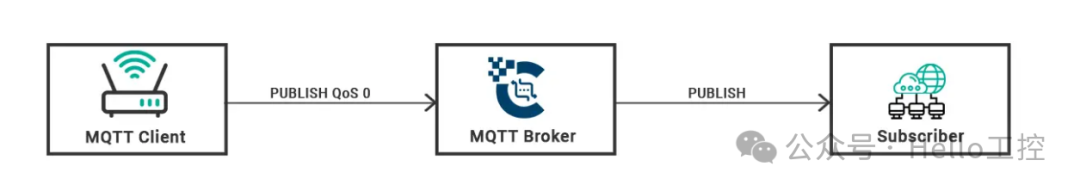
QoS 0 can be used in situations where the message is not critical for decision-making. For example, the location of students does not need to be recorded precisely every 5 minutes, even though we may use this data to monitor whether students attended classes. The specific location of students is not critical information. From a macro perspective, the presence of students on campus is sufficient for the attendance system.
QoS 1 – At Least Once
The next QoS level is 1. This level ensures that messages are received by the receiver at least once. Messages may be received multiple times by the receiver (subscriber or MQTT broker) until the receiver sends a PUBACK packet to the sender (MQTT broker or publisher). A packet identifier is used for the sender to compare the PUBLISH packet with the appropriate PUBACK packet. If the sender does not receive the PUBACK packet within a certain time, it will resend the MQTT packet with the Dup flag, indicating to the receiver to ignore the packet if it has already received the original message and resend the PUBACK packet.
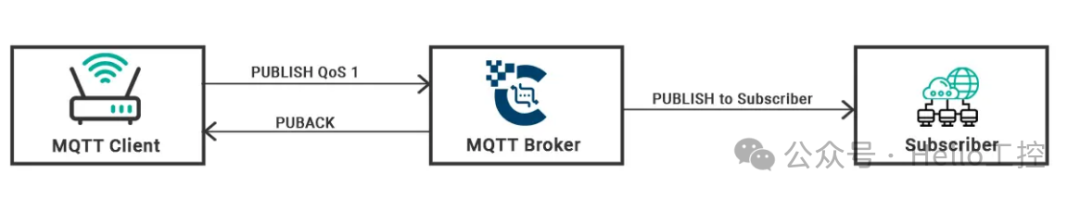
QoS 1 is used when every message is important during transmission, and the entire network has sufficient capacity to handle the additional load and ensure message delivery, even through retransmission during network congestion. When monitoring driver behavior based on parameters such as speed and acceleration, the collected data is very important. Therefore, data transmission needs to be set to at least once (QoS 1) to ensure that every piece of data is available for data analysis.
QoS 2 – Exactly Once
The third level, which is also the highest level of MQTT QoS, is 2, known as the maximum level of quality of service. This level ensures that the receiver will receive each message exactly once. This is the safest quality of service level because there are at least two response flows between the sender and receiver to provide message guarantees.
To achieve this, QoS 2 involves a four-step handshake between the sender and receiver. The delivery of messages will be organized by the sender and receiver using the packet identifier of the native PUBLISH message.
The sender sends the QoS 2 PUBLISH packet to the receiver. The receiver then appropriately processes the published message and acknowledges the PUBLISH packet by sending a PUBREC packet back to the publisher. If the publisher does not receive the PUBREC, it will resend the packet with the DUP flag until acknowledgment is received.

The publisher, upon receiving the PUBREC packet, will store that packet and reply with a PUBREL packet. At this point, the original published message no longer needs to be stored in the sender’s database and can be safely discarded. The packet identifier is used to pair the PUBLISH packet with the appropriate PUBREC and PUBREL packets.
The receiver, upon receiving the PUBREL, will reply to the sender with a PUBCOMP packet using the same packet identifier. The receiver can complete data processing at the same time as sending PUBCOMP. Once the entire QoS 2 process is completed, the sender will receive delivery confirmation.If the packet is lost during transmission, the sender needs to resend the message within a reasonable time. This applies equally whether the sender is an MQTT client or an MQTT broker. The receiver is responsible for responding to each command message.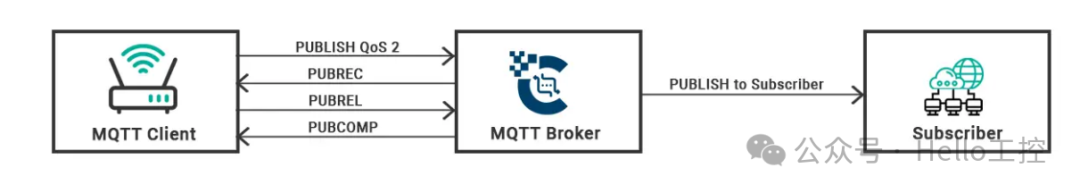
For mission-critical functions, if delivery time is very important, QoS 2 should be used. For patient monitoring systems, the relationship between data and time is crucial for all critical metrics (such as heart rate, respiration, blood oxygen saturation, etc.), and it is recommended to use the highest MQTT QoS level to ensure timely data delivery.

How are the differences in MQTT QoS levels handled?
The quality of service for messages is allocated between two clients connected to the server or broker, rather than end-to-end. Therefore, the quality of service level of the message received by the client (subscriber) depends on the quality of service level of the published message and the quality of service level of the subscribed topic. In short, the final quality of service of the received message depends on the quality of service of both the publishing and subscribing clients.After connecting to the broker, the subscribing client will inform the broker of the QoS attributes it requires for the messages using messages with QoS attributes.The following table provides a detailed scheme of the QoS level at which data will be received at the subscribing MQTT client end: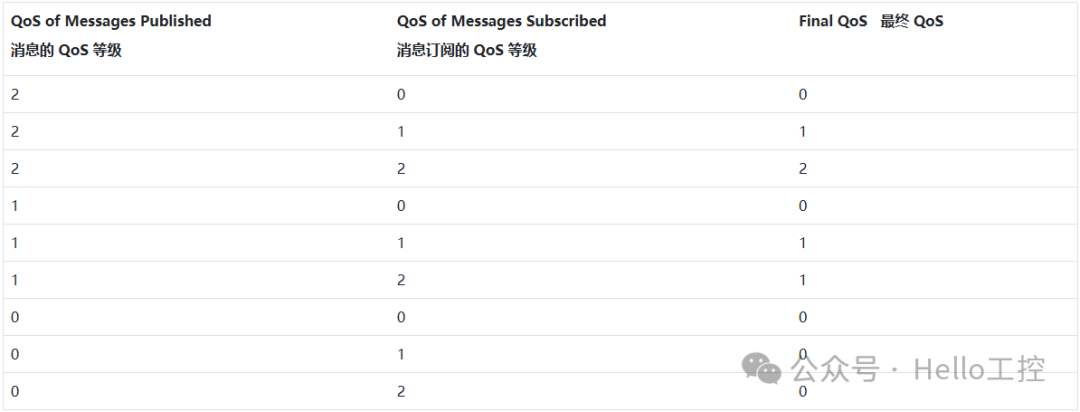 Therefore, the QoS levels defined by the sender and receiver can be different, and the final QoS of the received message depends on the joint result of the QoS of the published and subscribed messages.
Therefore, the QoS levels defined by the sender and receiver can be different, and the final QoS of the received message depends on the joint result of the QoS of the published and subscribed messages.

How to choose different QoS in MQTT?
Determining whether data is signal or noise helps decide which QoS level to use. In critical industries such as healthcare, nuclear energy, and defense, every piece of data is important, so every message must use QoS 2. If the client can handle duplicate messages, QoS 1 can be used instead of QoS 2.
Below is a detailed explanation of how to choose the appropriate QoS:
Situations suitable for using QoS 0:
-
There is a completely or mostly stable connection with the receiver. A classic use case for QoS 0 is connecting a test client or frontend application to the MQTT broker via a wired connection.
-
It is acceptable to occasionally lose a few messages. If the data is not very important, or if the data is sent at short intervals, allowing some message loss is acceptable.
-
No message queue is required. Messages are only queued if the QoS of the disconnected client is 1 or 2 and has a persistent session.
Situations suitable for using QoS 1:
-
Every message needs to be received, and your application scenario can handle duplicate messages. QoS level 1 is the most commonly used level because it guarantees that messages are delivered at least once but allows for multiple deliveries. Of course, your application must be able to tolerate duplicate messages and handle them accordingly.
- Cannot afford the overhead of QoS 2. QoS 1 delivers messages faster than QoS 2.
Situations suitable for using QoS 2:
-
It is crucial for your application to receive all messages exactly once. This usually occurs in situations where duplicate delivery could harm application users or subscribing clients. Be aware of the overhead and know that QoS 2 interactions take more time to complete.

Common Questions about QoS in MQTT
Q: How to assign different QoS levels for specific messages or topics in MQTT?
A: You can assign the QoS level of the message in the PUBLISH packet.
Q: Why do QoS 0 messages get lost?A: QoS messages can be lost because there is no acknowledgment mechanism at this level. If a message is lost during transmission due to network issues, or if the subscriber is offline when the message is sent, that message will be lost. The publisher has no way of knowing whether the message was successfully received and will not attempt to resend.Q: What happens if multiple clients subscribe to the same topic with different QoS levels?A: If multiple clients subscribe to the same topic but with different quality of service (QoS) levels, the broker will send messages to each client based on the QoS level subscribed by that client, rather than the QoS level at which the message was published. Q:What happens if the QoS level of a retained message is different from that of the subscriber?A: The broker will deliver the retained message at the lower of the QoS level set when the message was published and the QoS level of the subscription. Q:What happens if a QoS 0 message sent is not received by the subscriber?A: If a message sent with QoS level 0 is not received by the subscriber, the message will be lost.Q: What additional mechanisms does QoS 2 use in MQTT to ensure message delivery?A: To provide this guarantee, QoS 2 introduces a four-step handshake process between the publisher and receiver (which may be a broker or client, depending on the direction of the message). This process involves using PUBLISH, PUBREC, PUBREL, and PUBCOMP messages.Q: Why do QoS 1 messages get duplicated? How are message duplicates and reordering handled?A: If the broker receives the original message and sends a PUBACK, but the PUBACK does not reach the publisher (again, possibly due to network issues), then the broker will receive duplicate messages. Include a unique identifier or sequence number in the payload when publishing messages.Q: What trade-offs are there in message overhead and delivery latency when using QoS 2?A: Message overhead – Compared to QoS 0 or 1, the additional communication results in more network traffic and uses more bandwidth. Transmission latency – Due to the additional round trips required for the four-step handshake, QoS 2 has higher end-to-end latency than QoS 0 or 1. Q: Does using a higher QoS level affect bandwidth or network utilization?A: Yes, using a higher Quality of Service (QoS) level in MQTT does affect bandwidth and network utilization.Q: How does MQTT handle interactions between publishers and subscribers at different QoS levels?A: When a publisher sends a message to the broker, it specifies the QoS level of the message. The broker will acknowledge and process the message based on the QoS level specified by the publisher. When the broker sends messages to subscribers, the QoS level of the message is the lower of the QoS level published by the publisher and the QoS level of the subscribed topic.Q: What happens to QoS 1 or QoS 2 messages when the network connection is interrupted?A: In MQTT, when the network connection is interrupted, the handling of QoS 1 and QoS 2 messages depends on the stage of the message delivery process at the time of the connection interruption and whether a persistent session is used (also known as clean sessions).Q: How does MQTT handle backpressure when using different QoS levels?A: MQTT itself does not have a built-in mechanism for handling backpressure, but the concept is relevant when it comes to quality of service (QoS) levels and can be managed.Q: Can I configure the number of retransmission attempts for messages with higher QoS levels?A: While the MQTT protocol does not explicitly define limits on retransmissions, the client library or broker you are using may allow you to configure this. Specific details depend on the particular implementation you are using.
Reference Links:
-
https://www.bevywise.com/blog/mqtt-qos-level-use/
-
https://www.hivemq.com/blog/mqtt-essentials-part-6-mqtt-quality-of-service-levels/

- [Video Course] Introduction to Codesys V3.5 Series(139 people have learned)
- [Video Course] Basics of Codesys SoftMotion(42 people have learned)
- [Video Course] Codesys SoftMotion Electronic Gear Course(14 people have learned)
- [Video Course] Codesys SoftMotion Electronic Cam Course(9 people have learned)
- [Video Course] Creating Custom Libraries in Codesys(23 people have learned)
-
Comprehensive Free Resources for Codesys V3.5 Series
-
Top 10 Common Filtering Algorithms (ST Language)
-
What Does a PLC Integrated with Chat GPT Look Like?
-
Sharing the Top 10 PLC Programming Books of 2023
-
Customize Your Own CODESYS Motion Controller
-
MC_Power.status = FALSE, Can the Axis Still Move?
-
Summary of ST Language Learning Materials

——–END——–
 If you like this article, please share and “like” it below and “see it”
If you like this article, please share and “like” it below and “see it”