1. Introduction to PID Control
The PID (Proportional-Integral-Derivative) controller is the most classic feedback control algorithm in industrial control. It generates the control quantity through a linear combination of the proportional (Proportional), integral (Integral), and derivative (Derivative) parts of the error signal, achieving precise control of the system.
Mathematical Model of PID Controller:

2. Case Analysis: DC Motor Speed Control
Problem Description
Control the speed of a DC motor to quickly track the target speed (1000 RPM) and suppress load disturbances.
System Model
The simplified transfer function of the motor is:
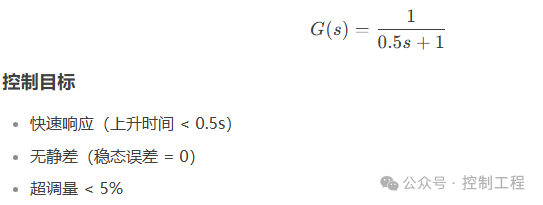
3. MATLAB Simulation Implementation
Step 1: Establish System Model
s = tf(‘s’);
sys = 1 / (0.5*s + 1); % Motor transfer function
Step 2: Design PID Controller
Preliminary parameter determination by trial and error:
Kp = 1.2;
Ki = 0.5;
Kd = 0.1;
C = pid(Kp, Ki, Kd);
Step 3: Closed-loop Simulation Analysis
T = feedback(C * sys, 1); % Unit feedback closed-loop system
t = 0:0.01:5;
step(T, t); % Step response
grid on;
title(‘PID Control of DC Motor’);
xlabel(‘Time (s)’);
ylabel(‘Speed (RPM)’);
Step 4: Add Disturbance Test
Simulate a sudden load increase at t=3s:
% Generate disturbance signal
disturbance = zeros(size(t));
disturbance(t>=3) = -0.3; % Speed drop disturbance
% Simulate response with disturbance
lsim(T, 1000*(t>=0) + disturbance, t); % Target value 1000RPM + disturbance
Step 5: Parameter Optimization (Using PID Tuner)
pidTuner(sys, ‘pid’) % Open PID parameter tuning tool
Automatically obtain optimized parameters by adjusting the response time and robustness sliders.
4. Simulation Result Analysis
Before Optimization (Manual Parameters):
-
Rise Time: 0.8s (too slow)
-
Overshoot: 15% (too large)
-
Disturbance Recovery Time: >2s
After Optimization (PID Tuner Recommended Parameters: Kp=1.8, Ki=1.5, Kd=0.05):
-
Rise Time: 0.4s ✅
-
Overshoot: 4.2% ✅
-
Disturbance Suppression Time: 0.7s ✅
Conclusion: The optimized PID significantly improves the dynamic performance and robustness of the system.
5. Complete MATLAB Code
%% DC Motor Speed Control with PID
clc; clear; close all;
% 1. Define System Model
s = tf(‘s’);
sys = 1 / (0.5*s + 1);
% 2. Tuned PID Parameters (from PID Tuner)
Kp = 1.8;
Ki = 1.5;
Kd = 0.05;
C = pid(Kp, Ki, Kd);
% 3. Closed-loop System
T = feedback(C * sys, 1);
% 4. Step Response
figure(1);
step(T);
title(‘Step Response with Optimized PID’);
grid on;
% 5. Disturbance Rejection Test
t = 0:0.01:5;
ref = 1000 * (t>=0); % Reference = 1000 RPM
disturbance = -0.3 * (t>=3); % Load disturbance at t=3s
figure(2);
lsim(T, ref + disturbance, t);
title(‘Response with Step + Disturbance’);
grid on;
6. Key Points for Engineering Applications
-
Tuning Methods:
-
Ziegler-Nichols Method (Critical Ratio Method)
-
Model Reference Adaptive Control (MRAC)
-
Self-tuning PID (e.g., MATLAB PID Tuner)
Improvement Strategies:
-
Integral Anti-windup
-
Derivative Filtering (to suppress noise)
-
Setpoint Weighting
Applicable Scenarios:
-
Temperature Control
-
Liquid Level Regulation
-
Robot Joint Position Control
-
Aerospace Attitude Stabilization
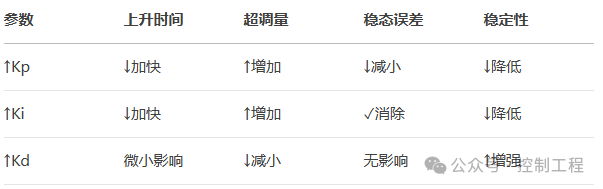
Appendix: Quick Reference Table for PID Parameter Effects