Click the blue “Linux” in the upper left corner and select “Set as Favorite“
Get the latest technical articles immediately
☞【Technical】Learning Path for Embedded Driver Engineers
☞【Technical】Linux Embedded Knowledge Points - Mind Map - Free Access
☞【Employment】A Comprehensive IoT Project Based on Linux for Your Resume
☞【Employment】Resume Template
btop is a very cool real-time system monitoring tool that you will definitely love after using it!
btop is an advanced real-time system monitoring tool, a modern alternative to the traditional top command, providing a rich graphical interface and enhanced interactive features.
btop supports multiple operating systems, including Linux, FreeBSD, and macOS. It can display system memory, disk, network utilization, and process information, allowing users to operate easily with a mouse or keyboard.
Project Address:
https://gitcode.com/gh_mirrors/bt/btop
1. Installation
Installing btop (a modern system monitoring tool) on Ubuntu is very simple. Here are the installation steps:
Method 1: Using Snap
Ubuntu 16.04 and later versions support Snap, a simple way to package and distribute Linux applications. You can install btop with the following command:
sudo snap install btop
Tested and effective!
Method 2: Using APT
Although btop is not available in the official Ubuntu repository by default, you can install it by adding a third-party repository. For example, you can add a repository named nerdctl that contains btop:
First, import the repository’s GPG key:
curl -s https://packagecloud.io/install/repositories/linuxserver/btop/script.deb.sh | sudo bash
Then, update your package list and install btop:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install btop
Some versions of Ubuntu may not support this, so it is recommended to use Method 1.
Method 3: Compile from Source
If you want to install btop from source, you can follow these steps:
First, install the necessary build tools and dependencies:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install build-essential cmake pkg-config libncursesw5-dev libncurses-dev gettext liblocale-gettext-perl gettext
Clone the btop repository:
git clone https://github.com/aristocratis/btop.git
cd btop
Compile and install:
mkdir build && cd build
cmake ..
make
sudo make install
Method 4: Using Docker (if you prefer this method)
You can also run btop via Docker, so you don’t need to install it directly on your system. First, install Docker, then run:
docker run -it --rm arslan/btop:latest
Method 5: git clone
For systems that do not support the default repository, you can compile from source:
git clone https://github.com/aristocratis/btop.git
cd btop
cmake .
make
sudo make install
Ensure you have the correct dependencies (like GCC or Clang, coreutils, and sed).
Uninstalling btop (optional)
If you need to uninstall btop, you can use the following command:
sudo apt remove btop
2. Testing
After installation, you can check if btop is installed successfully with the following command:
btop --version

If installed successfully, it will display the version information of btop.
Run btop directly in the terminal:
btop
This will display the interactive system monitoring interface of btop, showing CPU, memory, disk, network usage, etc. 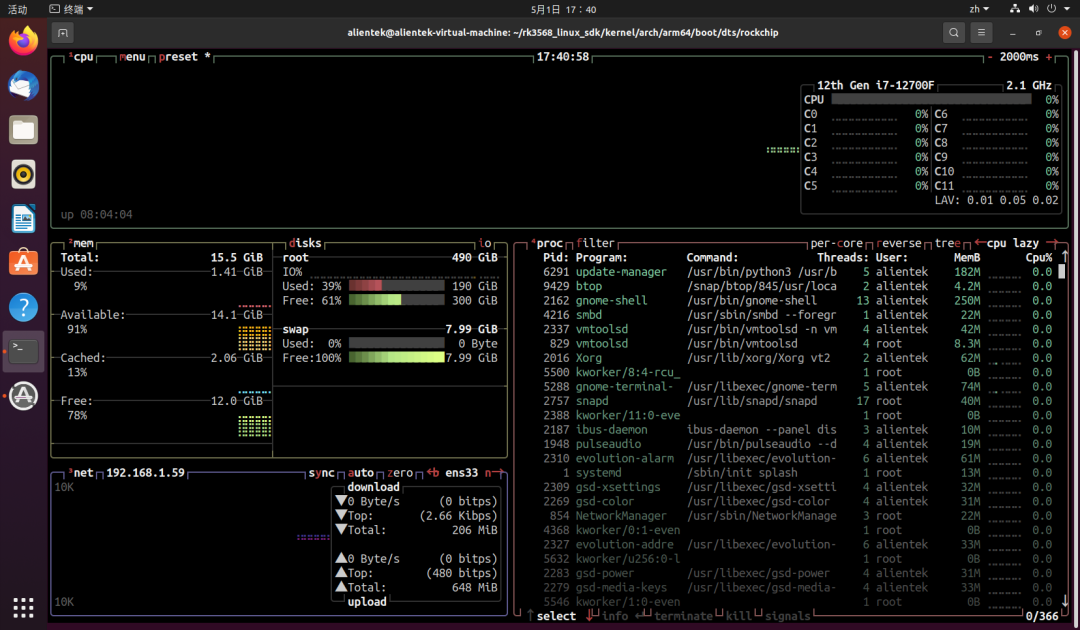 The interface is divided into the following sections:
The interface is divided into the following sections:
- CPU Area: Displays usage, frequency, temperature, etc. for each core
- Memory Area: Displays total memory, cache, swap, current usage rate
- Disk Area: Read/write speed and usage rate for each device or mount point
- Network Area: Displays send/receive rates, IP, data volume, etc. for each network card
- Process Area: Displays active processes, supports sorting, searching, and terminating
3. Shortcuts
The operation of btop is very similar to vim, relying on some shortcut keys. Here are the commonly used shortcuts:
| Shortcut | Function |
|---|---|
| ESC: | Open/close settings menu |
| m: | Toggle memory display units (KB/MB/GB) |
| e: | Expand/collapse process tree (default is tiled) |
| f: | Search process name (real-time filtering) |
| ↑ / ↓: | Move process cursor up/down |
| ← / →: | Move horizontally to different modules (CPU/memory/disk) |
| Enter: | Enter settings menu or confirm |
| k: | Kill selected process (send default SIGTERM) |
| z: | Show detailed process information (similar to top details) |
| q: | Exit btop |
| s: | Modify process sorting method |
4. Other Features
Settings Menu (Enter by pressing ESC)
- Theme
- Enable graphical animations
- Update frequency
- Default sorting method
- Expand process tree on startup
- Enable Swap display, etc.
Process Management Features
- Select process using ↑ / ↓
- Terminate (kill) it by pressing k (send SIGTERM)
- Use z to view detailed status of the process (e.g., CPU time, number of threads, etc.)
- Search for processes (press f, enter keywords to filter)
Configuration File Location
~/.config/btop/btop.conf
Theme Switching
View themes
ls /usr/share/btop/themes/
Switch method:
btop --theme monokai
end
Linux
Follow us and reply with 【1024】 to receive a wealth of Linux materials
Collection of Exciting Articles
Article Recommendations
☞【Collection】ARM☞【Collection】Fan Q&A☞【Collection】All Originals☞【Collection】LinuxIntroduction☞【Collection】Computer Networks☞【Collection】Linux Drivers☞【Technical】Learning Path for Embedded Driver Engineers☞【Technical】All Knowledge Points of Linux Embedded – Mind Map